We have to design and create a stack that performs the operations in constant time. Here we have one problem which is how to create mergable stack? Here we perform the below operation for merge two stacks.
- push(element): Insert the element in the stack.
- pop(): Remove the top element in the stack.
- merge (stack 1, stack 2): Merge or join 2 stacks.
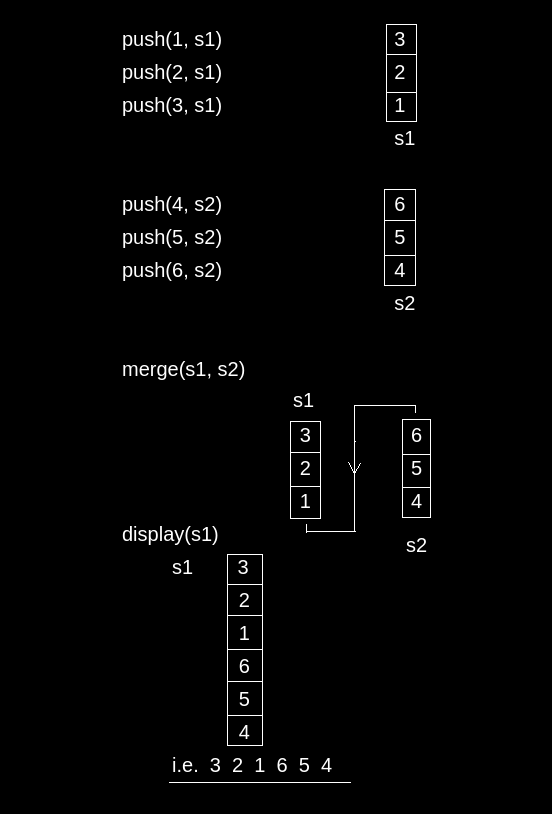
Table of Contents
Example
Here is some example of creating a mergable stack please have a look.
Input
push(1, s1);
push(2, s1);
push(3, s1);
push(4, s2);
push(5, s2);
push(6, s2);
merge(s1, s2);
display(s1);
Output
Merged Stack : 3 2 1 6 5 4
Input
push(1, s1);
push(5, s2);
push(6, s2);
merge(s1, s2);
display(s1);
Output
Merged Stack : 1 6 5
Algorithm
Here we first create two stacks and then try making mergable stack.
- Create two stacks s1 and s2.
- Create a function push that accepts integer value and stack as parameter. Initialize a node in it. update data of the new node as given integer and link it to the head of the stack.
- If the head of the stack is null update tail of stack as a new node. Else update the head of the stack as a new node.
- Create a function pop that accepts stack as parameter. Check if the head of the stack is null print “stack underflow” else store the head of the stack in a new node, update head as next of head. Return the data of the new node and delete the node.
- Create a function merge which accepts two stacks as a parameter. Check if the head of stack 1 is null update it’s head as a head of stack 2 and tail as the tail of stack 2 and returns.
- Else update next of the tail of stack 1 as head of stack 2 and tail of stack 1 as the tail of stack 2.
C++ Program to create mergable stack
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class node{
public:
int data;
node* next;
};
class newStack{
public:
node* head;
node* tail;
newStack(){
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
}
};
newStack* create(){
newStack* ns = new newStack();
return ns;
}
void push(int data, newStack* ns){
node* temp = new node();
temp->data = data;
temp->next = ns->head;
if(ns->head == NULL)
ns->tail = temp;
ns->head = temp;
}
int pop(newStack* ns){
if (ns->head == NULL) {
cout << "stack underflow" << endl;
return 0;
}
else{
node* temp = ns->head;
ns->head = ns->head->next;
int popped = temp->data;
delete temp;
return popped;
}
}
void merge(newStack* ns1, newStack* ns2){
if (ns1->head == NULL){
ns1->head = ns2->head;
ns1->tail = ns2->tail;
return;
}
ns1->tail->next = ns2->head;
ns1->tail = ns2->tail;
}
void display(newStack* ns){
node* temp = ns->head;
cout<<"Merged Stack : ";
while(temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
}
int main(){
newStack* s1 = create();
newStack* s2 = create();
push(1, s1);
push(2, s1);
push(3, s1);
push(4, s2);
push(5, s2);
push(6, s2);
merge(s1, s2);
display(s1);
return 0;
}Merged Stack : 3 2 1 6 5 4
Complexity Analysis to create mergable stack
Time Complexity: O(1) as all the operations are using constant time i.e. O(1).
Auxiliary Space: O(1) because we are using no extra space.