In the next greater frequency element problem, we have given an array a[ ] of size n containing numbers. For each number in the array print, the number to it’s right in an array with a frequency greater than that of the current number.
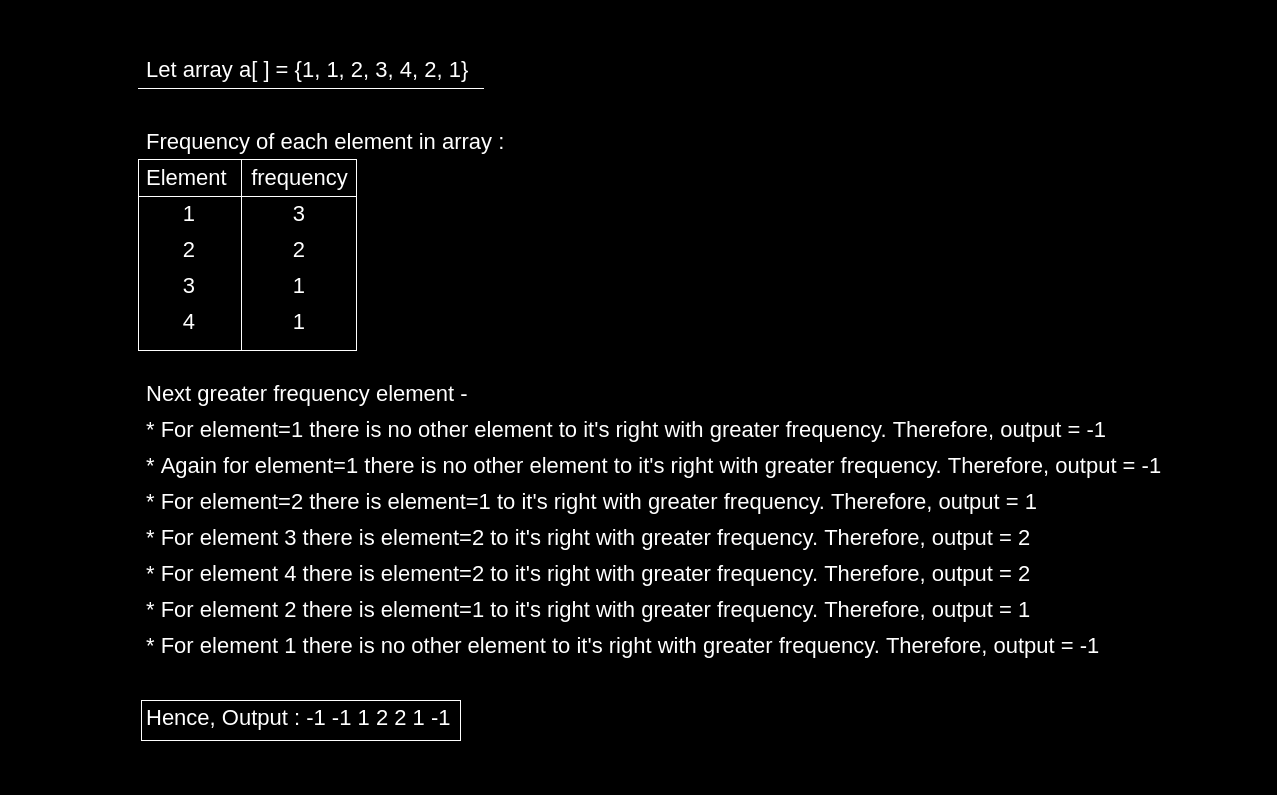
Table of Contents
Example
Input
a[] = {1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 1}
Output
-1 -1 1 2 2 1 -1
Input
a[] = {1, 1, 2, 3}
Output
-1 -1 -1 -1
Algorithm
Now, we know the problem statement for the Next Greater Frequency Element problem. So, we move toward its algorithm.
- Initialize an array a[ ] of size n.
- Create another array freq[ ] of size INT16_MAX to store the frequency and initialize it as 0.
- Traverse the array a[ ] and increment the value in array freq[ ] at index a[i].
- Create a stack s and push 0 in it and an array res of size n to store the result.
- Traverse from 1 to n-1 and check if value at freq[a[s.top()]] is greater than value at freq[a[i]], push the current position/i in stack.
- Else while value at freq[a[s.top()]] is less than value at freq[a[i]] and stack is not empty, update res as res[s.top()] = a[i] and pop the top. Push the current position/i in stack.
- While stack is not empty, update res as res[s.top()] = -1 and pop the top.
- Print the array res[ ].
C++ Program for Next Greater Frequency Element
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void NextGreaterFrequency(int a[], int n, int freq[]){
stack<int> s;
s.push(0);
int res[n] = {0};
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
if(freq[a[s.top()]] > freq[a[i]]){
s.push(i);
}
else{
while((freq[a[s.top()]] < freq[a[i]]) && !s.empty()){
res[s.top()] = a[i];
s.pop();
}
s.push(i);
}
}
while(!s.empty()){
res[s.top()] = -1;
s.pop();
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cout<<res[i]<<" ";
}
}
int main(){
int a[] = {1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
int max = INT16_MAX;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (a[i] > max){
max = a[i];
}
}
int freq[max + 1] = {0};
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
freq[a[i]]++;
}
NextGreaterFrequency(a, n, freq);
return 0;
}-1 -1 1 2 2 1 -1
Java Program for Next Greater Frequency Element
import java.util.*;
class ngf{
static void NextGreaterFrequency(int a[], int n, int freq[]){
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
s.push(0);
int res[] = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
res[i] = 0;
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
if(freq[a[s.peek()]] > freq[a[i]]){
s.push(i);
}
else{
while (freq[a[s.peek()]] < freq[a[i]] && s.size()>0){
res[s.peek()] = a[i];
s.pop();
}
s.push(i);
}
}
while(s.size() > 0){
res[s.peek()] = -1;
s.pop();
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
System.out.print( res[i] + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[] = {1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 1};
int n = a.length;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(a[i] > max){
max = a[i];
}
}
int freq[] = new int[max + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < max + 1; i++){
freq[i] = 0;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
freq[a[i]]++;
}
NextGreaterFrequency(a, n, freq);
}
}-1 -1 1 2 2 1 -1
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the number of elements in the array a[ ]. We use one stack and an array for storing the final answer.
Space Complexity: O(max) where max is equal to INT16_MAX. Here the value of max is fixed which is 32767. We create a frequency array to store the count of number present in the input array.