Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Write an algorithm to perform searching and insertion in Binary Search Tree. So what we are going to do is insert some of the elements from input into a binary search tree. Whenever asked to search a particular element, we’ll be searching it among the elements in BST(short for Binary Search Tree).
Example
Insert 10 Insert 15 Search 5 Insert 5 Insert 18 Search 5 Insert 12 Search 10
false true true
What is Binary Search Tree?
A Binary Search Tree is a special kind of Binary Tree that follows the following properties,
- All the nodes smaller than the current node are present in its left sub-tree.
- All the nodes greater than the current node are present in its right sub-tree.
- Left and right sub-tree of a node is also Binary Search Tree and there are no repeated elements.
Searching
Algorithm
Binary Search Tree stores the data in a sorted way(as its in-order traversal leads to sorted data). So, searching in BST is quite simple and easy.
We check if the root equals to the target node, if yes, return true, else if the target is smaller than the root’s value we search it in the left sub-tree else we search it in the right sub-tree.
1. Check if root equals to the target node, if yes, return true, else go to step 2. 2. If the target is smaller than the root's value, search the target in the left sub-tree. 3. Else search the target in the right sub-tree.
Time Complexity = O(n)
Since we are going to traverse the whole tree in the worst case. A worst-case can be we have a skewed tree and have our target value as the leaf of the tree. By the way, both searching and insertion in Binary Search Tree have same time complexity.
Space Complexity = O(1)
Since we are not using an array, or storing values for nodes during the algorithm. Thus, searching occurs in O(1) space complexity. The same goes for space complexity, both searching and insertion in Binary Search Tree are O(1) space complexity algorithms.
Insertion
Inserting a new node into BST is similar to searching. We search for the first empty position in the BST, by fulfilling the properties of BST and insert the new Node at that place.
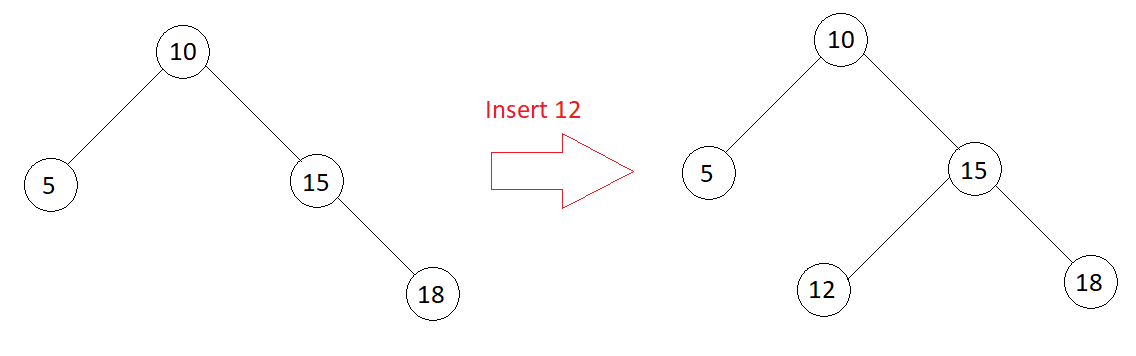
Algorithm
1. Allocate space for new Node, let it be node. 2. If root is null, make root as node and return. 3. If the value of new node is smaller than the root's value, insert the new node in the left sub-tree. 4. Else insert the new node in the right sub-tree.
Time Complexity = O(n)
Here again, we have a case we are provided elements either in increasing or decreasing order, or such that we may end up having a skewed tree. Then in that case, if the element to be inserted is such that it is going to become a leaf. We’ll have to traverse the whole of the tree. Thus contributing to O(n) time complexity.
Space Complexity = O(1)
Here since we did not store any value corresponding to each node. We have constant space complexity.
Code
JAVA Code for searching and insertion in Binary Search Tree
class BSTSearchAndInsert {
// class to represent node of a binary tree
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private static Node insertToBST(Node root, Node node) {
// if root is null, then make root as node and return
if (root == null) {
root = node;
return root;
}
// if node's value is less than root, insert it to left subtree
if (node.data < root.data) {
root.left = insertToBST(root.left, node);
}
// else insert it to right subtree
else {
root.right = insertToBST(root.right, node);
}
// return the updated root
return root;
}
private static Node insert(Node root, int value) {
// allocate memory for new node
Node node = new Node(value);
// insert the new node to tree
return insertToBST(root, node);
}
private static boolean search(Node root, int val) {
// if root is null, return false
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
// if root is equals to target, return true
if (root.data == val) {
return true;
}
// else if val is less than root, search in left subtree
else if (val < root.data) {
return search(root.left, val);
}
// else search in right subtree
else {
return search(root.right, val);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 15);
System.out.println(search(root, 5));
root = insert(root, 5);
root = insert(root, 18);
System.out.println(search(root, 5));
root = insert(root, 12);
System.out.println(search(root, 10));
}
}false true true
C++ Code for searching and insertion in Binary Search Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// class representing node of a binary tree
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
Node* insertToBST(Node *root, Node *node) {
// if root is null, then make root as node and return
if (root == NULL) {
root = node;
return root;
}
// if node's value is less than root, insert it to left subtree
if (node->data < root->data) {
root->left = insertToBST(root->left, node);
}
// else insert it to right subtree
else {
root->right = insertToBST(root->right, node);
}
// return the updated root
return root;
}
Node* insert(Node *root, int value) {
// allocate memory for new node
Node *node = new Node(value);
// insert the new node to tree
return insertToBST(root, node);
}
bool search(Node *root, int value) {
// if root is null, return false
if (root == NULL) {
return false;
}
// if root is equals to target, return true
if (root->data == value) {
return true;
}
// else if val is less than root, search in left subtree
else if (value < root->data) {
return search(root->left, value);
}
// else search in right subtree
else {
return search(root->right, value);
}
}
int main() {
// Example
Node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 15);
if (search(root, 5)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
root = insert(root, 5);
root = insert(root, 18);
if (search(root, 5)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
root = insert(root, 12);
if (search(root, 10)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}false true true