Table of Contents
What is a HashSet in Java
HashSet in Java is a class that implements the Set interface and stores data in a hashtable. It is part of the java.util package. It uses the hashing technique to store and retrieve the elements from the HashSet. During the hashing process, it uses the generated hashcode value to store the elements at the required index.
Features of Java HashSet
- It stores only unique value which means it does not allow duplicate values.
- It does not maintain any insertion order since it stores the data based on the hashcode value.
- HashSet allows storing null values.
- It is non-synchronized.
- Java HashSet class can be used as the best option for search operations since its performance is faster.
Hierarchy of HashSet
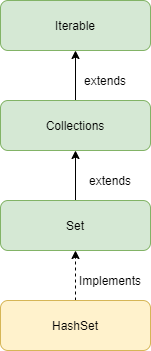
Constructors in HashSet
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| HashSet() | Creates a default HashSet |
| HashSet(int capacity) | Creates a HashSet with specified capacity |
| HashSet(int capacity, float loadFactor) | Creates a HashSet with the specified capacity and load factor. |
| HashSet(Collection c) | Creates a HashSet with the specified collection |
Methods in HashSet
Below are the methods supported by the Java HashSet class.
| Method | Description | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| boolean add(Object e) | Adds the specified element to the set | e - The element to be added Returns true if the element is not present already Returns false if element is already present |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | Adds all the elements in the specified collection | c - collection that contains elements to add |
| void clear() | Removes all the elements in the set and makes the set empty | |
| Object clone() | Returns a shallow copy of the TreeSet instance | |
| boolean contains(Object o) | Returns true if the set contains the specified element | o - the element to search |
| boolean containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if the set contains all elements specified in the collection | c - collection elements to search |
| boolean equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object in the set | Returns true if present Returns false if not present |
| boolean isEmpty() | Returns true if the set is empty and does not contain any elements | |
| Iterator iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in the ascending order | |
| boolean remove(Object o) | Removes the specified element from the set | o - the element to be removed |
| boolean removeAll(Collection c) | Removes all the elements in the specified collection | c - the collection of elements to be removed |
| boolean retainAll(Collection c) | Retains all the elements in the specified collection in the set and removes the other elements in the Set | c - the collection of elements to be retained |
| int size() | Returns the size of the set that is the number of elements in the set | |
| Spliterator spliterator() | Returns the spliterator over the elements in the set | |
| Object[] toArray() | Returns an array representation of the elements in the set | |
| String toString() | Returns a string representation of the elements in the set |
Example: Add elements
Below is an example to add elements to the Java HashSet using the add() method. We can also add a collection of elements to the Set using the addAll() method.
import java.util.HashSet;
public class AddHashSetElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<Integer>();
hs.add(30);
hs.add(10);
hs.add(20);
hs.add(40);
System.out.println("Elements in the HashSet after add operation: " + hs);
HashSet<Integer> h = new HashSet<Integer>();
h.add(60);
h.add(50);
hs.addAll(h);
System.out.println("ELements in the HashSet after addAll operation: " + hs);
}
}
Elements in the HashSet after add operation: [20, 40, 10, 30] ELements in the HashSet after addAll operation: [50, 20, 40, 10, 60, 30]
Example: Remove elements
The below example shows how to remove the elements from the HashSet in Java using the remove() method. To remove the collection of elements, we can use the removeAll() method, and to retain only the collection elements we can use the retainAll() method.
import java.util.HashSet;
public class RemoveHashSetElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<Integer>();
hs.add(30);
hs.add(10);
hs.add(20);
hs.add(40);
HashSet<Integer> h = new HashSet<Integer>();
h.add(60);
h.add(50);
hs.addAll(h);
System.out.println("Elements in the HashSet: " + hs);
hs.remove(30);
System.out.println("Elements in the HashSet after remove method: " + hs);
hs.retainAll(h);
System.out.println("Elements in the HashSet after retainAll method: " + hs);
hs.removeAll(h);
System.out.println("Elements in the HashSet after removeAll method: " + hs);
}
}
Elements in the HashSet: [50, 20, 40, 10, 60, 30] Elements in the HashSet after remove method: [50, 20, 40, 10, 60] ELements in the HashSet after retainAll method: [50, 60] Elements in the HashSet after removeAll method: []
Example: Clear the HashSet and check if empty
We can clear the HashSet by using the clear() method which removes all the elements from the set. The isEmpty() method checks if the HashSet is empty or not.
import java.util.HashSet;
public class RemoveHashSetElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<Integer>();
hs.add(30);
hs.add(10);
hs.add(20);
hs.add(40);
System.out.println("Elements in the HashSet: " + hs);
System.out.println("Size of the HashSet: " + hs.size());
hs.clear();
System.out.println("Is HashSet empty: " + hs.isEmpty());
}
}
Elements in the HashSet: [20, 40, 10, 30] Size of the HashSet: 4 Is HashSet empty: true
Example: Check if elements exist
The below example uses the contains() method to check if the HashSet contains the specified element. We can use the containsAll() method to check if the set contains a collection of elements.
import java.util.HashSet;
public class CheckElement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> city = new HashSet<String>();
city.add("Bangalore");
city.add("Chennai");
city.add("Delhi");
city.add("Mumbai");
System.out.println("Elements in the HashSet: " + city);
System.out.println("Check if Chennai exist: " + city.contains("Chennai"));
System.out.println("Check if Hyderabad exist: " + city.contains("Hyderabad"));
HashSet<String> c = new HashSet<String>();
c.add("Hyderabad");
c.add("Jaipur");
city.addAll(c);
System.out.println("Elements after addAll method: " + city);
System.out.println("Check if collection exist: " + city.containsAll(c));
}
}
Elements in the HashSet: [Delhi, Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore] Check if Chennai exist: true Check if Hyderabad exist: false Elements after addAll method: [Delhi, Chennai, Jaipur, Mumbai, Hyderabad, Bangalore] Check if collection exist: true
Example: Iterate over HashSet elements
We can traverse through the elements in the HashSet in Java using the iterator() method. Below is an example to illustrate the same.
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class IterateHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> names = new HashSet<String>();
names.add("Ravi");
names.add("Rakesh");
names.add("Suresh");
names.add("Dinesh");
Iterator<String> it = names.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
Suresh Ravi Dinesh Rakesh