Table of Contents
EnumMap in Java
EnumMap in Java is a specialized class that implements the Map interface for enum data types. It belongs to the java.util package. It maintains natural sorting order on the basis of the keys in the map.
Features of EnumMap
- It is an ordered collection of elements of enum data type
- Not synchronized
- Performance is higher than HashMap
- All keys are an instance of elements in the Enum data type
- We cannot store null keys in an EnumMap class.
- EnumMap stores data internally in the form of arrays hence it is more efficient.
Java EnumMap hierarchy
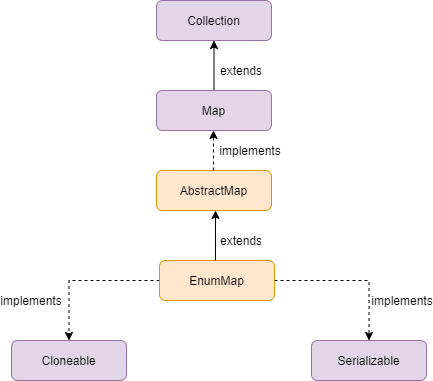
EnumMap Constructors
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| EnumMap(Class keyType) | Creates an EnumMap with the specified keytype |
| EnumMap(EnumMap m) | Creates an EnumMap with the specified keys in the enummap |
| EnumMap(Map m) | Create an EnumMap with the specified map |
Methods
| Method | Description | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| void clear() | Removes all the mappings in this map which means map will be empty | |
| Boolean containsKey(Object key) | Returns true if there is a mapping value for the specified key | key - the key for which we need to retrieve the value |
| Boolean containsValue(Object value) | Returns true if there is mapping of key for the specified value | value - the value for which specified key is mapped |
| Set<Entry> entrySet() | Returns a set view of the mapping of the map | |
| Boolean equals(Object o) | Returns true if the object has the same mapping of the map | o - the object to be compared |
| Integer get(Object key) | Returns the value of the specified key in the map. It returns null if there is no mapping | key - the key for which value mapping has to be retrieved |
| Integer getOrDefault(Object key, Integer defaultvalue) | Returns the value of the specified key if mapped, else returns the defaultvalue if there is no mapping | key - the key for which we value has to be returned defaultvalue - the default value to be returned when there is no mapping |
| int hashCode() | Returns the hashcode value of the map | |
| Boolean isEmpty() | Returns true is the map does not have any key-value pairs | |
| Set keySet() | Returns the set view of the keys present in the map | |
| Integer put(String key, int value) | Associates the key with value. If the key is already present, it replaces the old value with new value | key - key for mapping value - value for the specified key |
| void putAll(Map m) | Associates all key - value mappings of m to the current map | m - the copies of the mapping to be added to the current map |
| Integer putIfAbsent(String key,Integer value) | Associates the value if already not mapped to the key else returns the current value | key - key for mapping value - value to be associated |
| Integer remove(Object key) | Removes the mapping for the specified key in the map | key - the key in the map for which mapping has to be removed |
| Boolean remove(Object key, Object value) | Removes the entry of the specified key only if it is mapped with the specified value | key - key in map value - value mapped to the key |
| Integer replace(String key, Integer value) | Replaces the value of the specified key with the value only if it currently mapped with some value | key - key in map value - value to be replaced |
| Boolean replace(String key, integer oldvalue, Integer newvalue) | Replaces the entry of the specified key with new value only if it already mapped with the specified oldvalue | key - key in the map oldvalue - oldvalue mapped to key newvalue - newvalue to be mapped to the key |
| int size() | Returns the size of the map | |
| String toString() | Returns a string representation of the map | |
| Collection values() | Returns a collection view of values present in the map |
Example: Add elements to EnumMap
Below is an example of adding enum elements to the Java EnumMap using the put() and putAll() methods.
import java.util.EnumMap;
enum Weight {
UNDERWEIGHT, NORMAL, OVERWEIGHT
}
public class EnumMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Weight, Integer> e = new EnumMap<Weight, Integer>(Weight.class);
e.put(Weight.UNDERWEIGHT, 10);
e.put(Weight.NORMAL, 50);
System.out.println("Size of EnumMap: " + e.size());
System.out.println("Values in EnumMap" + e);
EnumMap<Weight, Integer> e2 = new EnumMap<Weight, Integer>(Weight.class);
e2.put(Weight.OVERWEIGHT, 100);
e.putAll(e2);
System.out.println("Values in EnumMap after putAll: " + e);
}
}
Size of EnumMap: 2
Values in EnumMap{UNDERWEIGHT=10, NORMAL=50}
Values in EnumMap after putAll: {UNDERWEIGHT=10, NORMAL=50, OVERWEIGHT=100}
Example: Replace elements
The below example illustrates how to replace values in an EnumMap using the replace() method.
import java.util.EnumMap;
enum Weight {
UNDERWEIGHT, NORMAL, OVERWEIGHT
}
public class EnumMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Weight, Integer> e = new EnumMap<Weight, Integer>(Weight.class);
e.put(Weight.UNDERWEIGHT, 10);
e.put(Weight.NORMAL, 50);
e.put(Weight.OVERWEIGHT, 80);
System.out.println("Values in EnumMap" + e);
e.replace(Weight.UNDERWEIGHT, 30);
e.replace(Weight.NORMAL, 50, 55);
System.out.println("Values after replace method: " + e);
}
}
Values in EnumMap{UNDERWEIGHT=10, NORMAL=50, OVERWEIGHT=80}
Values after replace method: {UNDERWEIGHT=30, NORMAL=55, OVERWEIGHT=80}
Example: Delete elements
We can delete the elements in a Java EnumMap using the remove() method. The below example shows how to delete a specific element.
import java.util.EnumMap;
enum Weight {
UNDERWEIGHT, NORMAL, OVERWEIGHT
}
public class EnumMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Weight, Integer> e = new EnumMap<Weight, Integer>(Weight.class);
e.put(Weight.UNDERWEIGHT, 10);
e.put(Weight.NORMAL, 50);
e.put(Weight.OVERWEIGHT, 80);
System.out.println("Values in EnumMap" + e);
e.remove(Weight.NORMAL);
e.remove(Weight.UNDERWEIGHT, 10);
System.out.println("Values in EnumMap" + e);
}
}
Values in EnumMap{UNDERWEIGHT=10, NORMAL=50, OVERWEIGHT=80}
Values in EnumMap{OVERWEIGHT=80}
Example: Access elements of Java EnumMap
Below is an example to access the data in the EnumMap using the get method. We can also check if the map contains a specific key or value using the containsKey or containsValue method.
import java.util.EnumMap;
enum Weight {
UNDERWEIGHT, NORMAL, OVERWEIGHT
}
public class EnumMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Weight, Integer> e = new EnumMap<Weight, Integer>(Weight.class);
e.put(Weight.UNDERWEIGHT, 10);
e.put(Weight.NORMAL, 50);
e.put(Weight.OVERWEIGHT, 80);
System.out.println("Values in EnumMap" + e);
System.out.println(e.get(Weight.UNDERWEIGHT));
System.out.println(e.containsKey(Weight.OVERWEIGHT));
System.out.println(e.containsValue(50));
}
}
Values in EnumMap{UNDERWEIGHT=10, NORMAL=50, OVERWEIGHT=80}
10
true
true
Example: Iterate through EnumMap elements
Similar to Map, we can iterate through an EnumMap using the entrySet method. To retrieve only keys, we can use the keySet method, and to retrieve only the values, we can use the Values method of the Collection.
The below example illustrates how to iterate using all three methods.
import java.util.EnumMap;
enum Weight {
UNDERWEIGHT, NORMAL, OVERWEIGHT
}
public class EnumMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Weight, Integer> e = new EnumMap<Weight, Integer>(Weight.class);
e.put(Weight.UNDERWEIGHT, 10);
e.put(Weight.NORMAL, 50);
e.put(Weight.OVERWEIGHT, 80);
System.out.println("Values in EnumMap" + e);
//Using entrySet
System.out.println("Iterate using entrySet: " + e.entrySet());
//Using keySet
System.out.println("Iterate using keySet:");
for(Weight str : e.keySet())
System.out.println(str);
//Using Values
System.out.println("Iterate using Values:");
for(Integer val: e.values())
System.out.println(val);
}
}
Values in EnumMap{UNDERWEIGHT=10, NORMAL=50, OVERWEIGHT=80}
Iterate using entrySet: [UNDERWEIGHT=10, NORMAL=50, OVERWEIGHT=80]
Iterate using keySet:
UNDERWEIGHT
NORMAL
OVERWEIGHT
Iterate using Values:
10
50
80