Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Notice: that the solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example
#1
[-1,0,1,2,-1,4]
[[-1,0,1],[-1,-1,2]]
Explanation: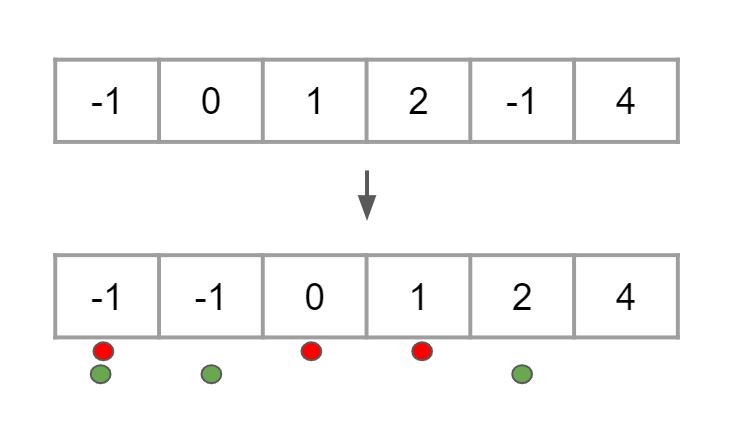
#2
[0]
[]
Approach 1 (Brute Force + Binary Search)
we need to find unique triplets with a+b+c =0, let’s say we know the value of a and b, using the equation( a+b+c =0 ) we can find the value of c, which is -(a+b).
if we take all the possible (a,b) pairs, we can get all pairs of a,b using 2 nested for loops. after that, we can use binary search to know if c=-(a+b) exists in the given array or not.
if it exists then the triplet (a,b,-(a+b)) will be a possible triplet. in this way, we will get all the possible triplets with a+b+c=0, but we need to find the unique triplets,
for that we can insert all these possible triplets in some data structure( i.e. set) to get unique triplets.
Implementation for 3Sum Leetcode Solution
C++ Program
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
set<vector<int>> s;//to get unique triplets
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
int n=nums.size();
vector<int> temp;
temp.resize(3);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(binary_search(nums.begin()+j+1,nums.end(),-nums[i]-nums[j])){
temp[0]=nums[i],temp[1]=nums[j],temp[2]=-nums[i]-nums[j];
sort(temp.begin(),temp.end());
//to get triplet in an order, will be easy to check if
//duplicate exists or not
s.insert(temp);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for(auto triplet: s)
ans.push_back(triplet);
return ans;
}
void display_ans(vector<vector<int>> temp)
{
for(auto triplet : temp)
cout<<triplet[0]<<" "<<triplet[1]<<" "<<triplet[2]<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v{-1,0,1,2,-1,-4};
display_ans(threeSum(v));
return 0;
}-1 -1 2 -1 0 1
Java Program
import java.util.*;
class Rextester{
static boolean binary_search(int l,int r,int[]nums, int x)
{
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)/2;
if(nums[mid]==x) return true;
else if(nums[mid]>x) r=mid-1;
else l=mid+1;
}
return false;
}
public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
int n=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(binary_search(j+1,n-1,nums,-(nums[i]+nums[j])))
{
List<Integer> t=new ArrayList<Integer>();
t.add(nums[i]);
t.add(nums[j]);
t.add(-(nums[i]+nums[j]));
ans.add(t);
}
while(j+1<n && nums[j+1]==nums[j]) j++;
}
while(i+1<n && nums[i+1]==nums[i]) i++;
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[] nums={-1,0,1,2,-1,-4};
for(List<Integer> list: threeSum(nums))
{
for(int x: list)
System.out.print(x+ " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}-1 -1 2 -1 0 1
Complexity Analysis for 3Sum Leetcode Solution
Time Complexity
Space Complexity
Approach 2 (Two Pointer)
Implementation for 3Sum Leetcode Solution
C++ Program
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
int n=nums.size();
for(int i=0;i<n; i++)
{
int j=i+1,k=n-1;//two pointers
while(j<n && j<k)
{
if(nums[j]+nums[k] == -nums[i])
{
ans.push_back({nums[i],nums[j],nums[k]});
while(k!=0 && nums[k]==nums[k-1]) k--;//to avoid duplicates
while(j!=n-1 && nums[j]==nums[j+1]) j++;
j++,k--;
}
else if(nums[j]+nums[k] > -nums[i])
{
while(k!=0 && nums[k]==nums[k-1]) k--;
k--;
}
else
{
while(j!=n-1 && nums[j]==nums[j+1]) j++;
j++;
}
}
while(i!=n-1 && nums[i]==nums[i+1]) i++;
}
for(auto triplet : ans)
sort(triplet.begin(),triplet.end());
return ans;
}
void display_ans(vector<vector<int>> temp)
{
for(auto triplet : temp)
cout<<triplet[0]<<" "<<triplet[1]<<" "<<triplet[2]<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v{-1,0,1,2,-1,-4};
display_ans(threeSum(v));
return 0;
}
-1 -1 2 -1 0 1
Java Program
import java.util.*;
class Rextester{
public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
int n=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int p=i+1,q=n-1;
while(p<q)
{
if(nums[p]+nums[q]==-nums[i])
{ //System.out.println(p+" "+q);
List<Integer> t=new ArrayList<Integer>();
t.add(nums[i]);
t.add(nums[p]);
t.add(nums[q]);
ans.add(t);
while(p+1<q && nums[p+1]==nums[p]) p++;
while(q-1>p && nums[q-1]==nums[q]) q--;
p++; q--;
}
else if(nums[p]+nums[q] < -nums[i]) p++;
else q--;
}
while(i+1<n && nums[i+1]==nums[i]) i++;
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[] nums={-1,0,1,2,-1,-4};
for(List<Integer> list: threeSum(nums))
{
for(int x: list)
System.out.print(x+ " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}-1 -1 2 -1 0 1
Complexity Analysis for 3Sum Leetcode Solution
Time Complexity
O(N^2): we are using one for loops to get values of a, and for every value of a, we find the pair b,c (such that a+b+c=0) using two pointer approach that takes O(N) time. so total time complexity is of the order of O(N^2).
Space Complexity
O(N): we are using a vector to store the answer.