Given the linked list representation of a complete binary tree. The linked list is in the order of level order traversal of the tree. Write an algorithm to construct the complete binary tree back from its linked list representation.
Table of Contents
Example
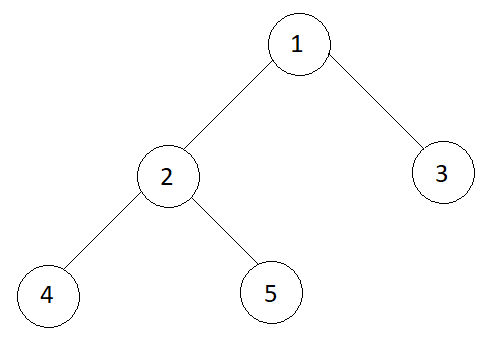
Input
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
Output
In-order traversal
4 2 5 1 3
Algorithm for Construct Complete Binary Tree
A complete binary tree is a binary tree that has all the levels completely filled except for the last level and all the nodes in the last level are as left as possible. Also, when a complete tree is represented through an array a node at index i in the array has its left child at index (2 * i + 1) and right child at index (2 * i + 2). We can visualize the same thing in the linked list representation.
So the children of node at index 0 are present at index 1 and 2, children of node at index 1 are present at index 3 and 4, and so on.
The idea to convert the linked list representation to the tree is that the first node of the linked list is always the root of the tree. So we push the root in a queue, we do a BFS on the tree and simultaneously traverse in the linked list to convert it into the tree. For every node in the tree, we traverse two nodes in the linked list, one for the left child and one for the right child.
- Create a queue, say q.
- Push the head of the linked list to the queue.
- While the end of the linked list is not reached, repeat step 4.
- Remove a node from the queue, let it be the parent. Traverse in the list, the first node is the left child of the parent, and second node is the right child of the parent. Also, enqueue the left and right child to the queue.
JAVA Code for Construct Complete Binary Tree
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class ConstructCompleteBinaryTreeFromItsLinkedListRepresentation {
// class representing node of a linked list
static class ListNode {
int data;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// class representing node of a binary tree
static class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode left, right;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// function to print inorder traversal of a tree
private static void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
private static void constructCompleteBinaryTree(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
// initialize root of the tree as head of linked list
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(head.data);
// create a queue
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
// push the root of the tree to the queue
q.add(root);
while (head != null) {
// remove an element from the queue
TreeNode parent = q.poll();
// traverse in linked list
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
// this node of linked list is the left child of parent
TreeNode leftChild = new TreeNode(head.data);
parent.left = leftChild;
// add left child to the queue
q.add(leftChild);
// traverse in linked list
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
// this node of the linked list is the right child of parent
TreeNode rightChild = new TreeNode(head.data);
parent.right = rightChild;
// add right child to the queue
q.add(rightChild);
}
}
}
// print inorder traversal of the tree
System.out.println("Inorder Traversal");
inorder(root);
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example
ListNode head = new ListNode(1);
head.next = new ListNode(2);
head.next.next = new ListNode(3);
head.next.next.next = new ListNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(5);
constructCompleteBinaryTree(head);
}
}Inorder Traversal 4 2 5 1 3
C++ Code for Construct Complete Binary Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// class representing node of a linked list
class ListNode {
public:
int data;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int d) {
data = d;
next = NULL;
}
};
// class representing node of a binary tree
class TreeNode {
public:
int data;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int d) {
data = d;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// function to print inorder traversal of a tree
void inorder(TreeNode *root) {
if (root != NULL) {
inorder(root->left);
cout<<root->data<<" ";
inorder(root->right);
}
}
void constructCompleteBinaryTree(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL) {
return;
}
// initialize root of the tree as head of linked list
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(head->data);
// create a queue
queue<TreeNode *> q;
// push the root of the tree to the queue
q.push(root);
while (head != NULL) {
// remove an element from the queue
TreeNode *parent = q.front();
q.pop();
// traverse in linked list
head = head->next;
if (head != NULL) {
// this node of linked list is the left child of parent
TreeNode *leftChild = new TreeNode(head->data);
parent->left = leftChild;
// add left child to the queue
q.push(leftChild);
// traverse in linked list
head = head->next;
if (head != NULL) {
// this node of the linked list is the right child of parent
TreeNode *rightChild = new TreeNode(head->data);
parent->right = rightChild;
// add right child to the queue
q.push(rightChild);
}
}
}
// print inorder traversal of the tree
cout<<"Inorder Traversal"<<endl;
inorder(root);
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
ListNode *head = new ListNode(1);
head->next = new ListNode(2);
head->next->next = new ListNode(3);
head->next->next->next = new ListNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = new ListNode(5);
constructCompleteBinaryTree(head);
return 0;
}Inorder Traversal 4 2 5 1 3
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity = O(n)
Space Complexity = O(n)
where n is the number of elements in the linked list.