Given the level order traversal of a Binary Search Tree, write an algorithm to construct the Binary Search Tree or BST from ITS given level order traversal.
Table of Contents
Example
Input
levelOrder[] = {18, 12, 20, 8, 15, 25, 5, 9, 22, 31}
Output
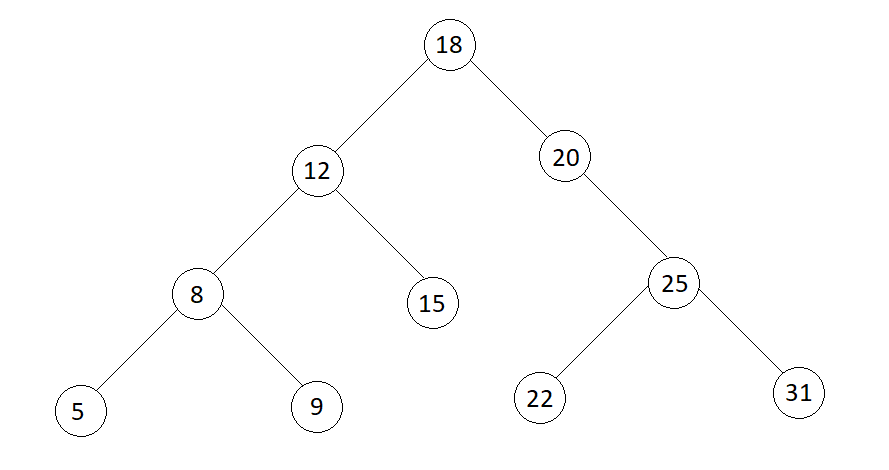
In-order : 5 8 9 12 15 18 20 22 25 31
Input
levelOrder[] = {4, 2, 5, 1, 3, 6}
Output
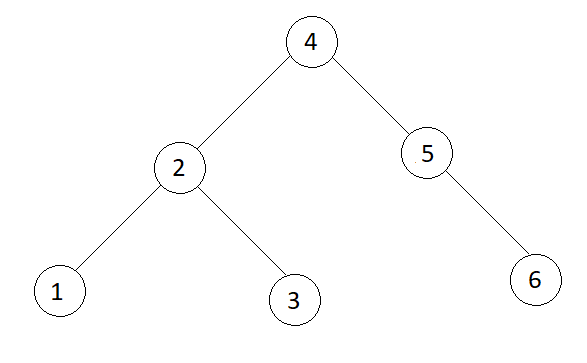
In-order : 1 2 3 4 5 6
Algorithm for constructing BST from level order traversal
The first element in the level order traversal always forms the root of the Binary Search Tree. The next value may form the left node or the right node depending on its value.
If the next node is smaller than root than it will be inserted to the left of the root, else it will be inserted to the right.
The idea is as follows, if the root of BST is null, form the current element is smaller than the root, then insert it at the appropriate position in the left sub-tree of the root, else insert it inappropriate position in the right subtree of root.
- Initialize the root of BST as null. If there are no elements in the level order traversal, return root.
- For every element in the levelOrder array, repeat steps 3, 4, and 5.
- If the root is null, make the current element as the root.
- Else if the current element is less than root, go to step 3, the root becomes root.left and the element remains the same.
- Else if the current element is greater than root, go to step 3, the root becomes root.right and the element remains the same.
- Return root.
JAVA Code for constructing BST from level order traversal
public class ConstructBSTFromItsGivenLevelOrderTraversal {
// class representing node of a binary tree
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// function to print in order traversal of a binary tree
private static void inorder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
private static Node attachNode(Node root, int value) {
// if root is null, make the current element as root
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(value);
return root;
}
// if element is less than root
if (value < root.data) {
// attach it to left subtree
root.left = attachNode(root.left, value);
} else {
// attach it to right subtree
root.right = attachNode(root.right, value);
}
// return root
return root;
}
private static Node formBST(int[] levelOrder) {
// initialize root as null
Node root = null;
// for each element attach the node to required position in the BST
for (int i = 0; i < levelOrder.length; i++) {
// Step 3 to 5
root = attachNode(root, levelOrder[i]);
}
// return root
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
int levelOrder1[] = new int[] {18, 12, 20, 8, 15, 25, 5, 9, 22, 31};
Node root1 = formBST(levelOrder1);
inorder(root1);
System.out.println();
// Example 2
int levelOrder2[] = new int[] {4, 2, 5, 1, 3, 6};
Node root2 = formBST(levelOrder2);
inorder(root2);
System.out.println();
}
}5 8 9 12 15 18 20 22 25 31 1 2 3 4 5 6
C++ Code for constructing BST from level order traversal
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// class representing node of a binary tree
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// function to print the in-order traversal of a binary tree
void inOrder(Node *root) {
if (root != NULL) {
inOrder(root->left);
cout<<root->data<<" ";
inOrder(root->right);
}
}
Node* attachNode(Node *root, int value) {
// if root is null, make the current element as root
if (root == NULL) {
root = new Node(value);
return root;
}
// if element is less than root
if (value < root->data) {
// attach it to left subtree
root->left = attachNode(root->left, value);
} else {
// attach it to right subtree
root->right = attachNode(root->right, value);
}
// return root
return root;
}
Node* formBST(int *levelOrder, int n) {
// initialize root as null
Node *root = NULL;
// for each element attach the node to required position in the BST
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Step 3 to 5
root = attachNode(root, levelOrder[i]);
}
// return root
return root;
}
int main() {
// Example 1
int levelOrder1[] = {18, 12, 20, 8, 15, 25, 5, 9, 22, 31};
Node *root1 = formBST(levelOrder1, sizeof(levelOrder1) / sizeof(levelOrder1[0]));
inOrder(root1);
cout<<endl;
// Example 2
int levelOrder2[] = {4, 2, 5, 1, 3, 6};
Node *root2 = formBST(levelOrder2, sizeof(levelOrder2) / sizeof(levelOrder2[0]));
inOrder(root2);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}5 8 9 12 15 18 20 22 25 31 1 2 3 4 5 6
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity = O(n2)
Space Complexity = O(n), due to recursion
where n is the total number of elements in the level order array.