Table of Contents
Deque interface in Java
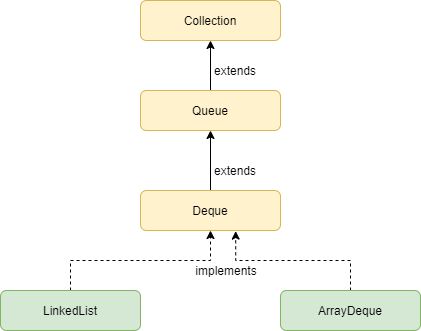
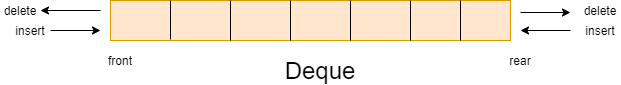
Deque in Java is an interface that extends the queue interface. It stands for the double-ended queue which means we can insert and delete elements from both sides. It supports both queue implementation which is First-In-First-Out(FIFO) and stack implementation which is Last-In-First-Out(LIFO). Deque interface is part of the java.util package and belongs to the Collection framework.
Deque Hierarchy
Features of Deque in Java
- Deque in Java implements both FIFO and LIFO
- It is a dynamically resizable array
- We cannot store null values in a Deque
- It is not thread-safe by default.
Classes that implement Deque interface in Java
Below are the classes that implement the Deque interface:
- LinkedList:
Deque<Type> d = new LinkedList<Type>();
- ArrayDeque:
Deque<Type> d = new ArrayDeque<Type>();
Methods of Deque in Java
| Method | Description | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Boolean add(Element e) | Adds the specified element to the end of the deque. | e - the element to be added. Return value - True |
| Boolean addAll(Collection c) | Adds a collection of specified elements to the deque. | c - collection of elements to be added Return value - true |
| void addFirst(Element e) | Inserts an element at the beginning of the deque | e - the element to be inserted |
| void addLast(Element e) | Inserts an element at the end of the deque | e - the element to be inserted |
| void clear() | Clears all the elements in the deque. | |
| Boolean contains(Object o) | Checks if the deque contains the specified element | Return value - true if the deque contains the element |
| Boolean containsAll(Collection c) | Checks if the deque contains all the elements in the collection | Return value - true if the deque contains all the elements |
| Iterator descendingIterator() | Returns an iterator over elements in the deque in the reverse order | |
| Object element() | Returns the first element(head) in the deque | |
| Boolean equals(Object o) | Compares if the deque contains all the specified elements in the exact order | Return value - true if object elements match with the deque |
| Object getFirst() | Returns the first element(head) in the deque | |
| Object getLast() | Returns the last element(tail) in the deque | |
| Boolean isEmpty() | Checks if the deque is empty or not | Return value - true if deque contains no values |
| Iterator iterator() | Retrieves the iterator of deque in sequence | Return value - Iterator |
| Boolean offer(Object e) | Inserts the element as the tail | e - element to be added |
| Boolean offerFirst(Object e) | Inserts the element at the front of the deque | e - element to be added |
| Boolean offerLast(Object e) | Inserts the element at the end of the deque | e - element to be added |
| Object peek() | Retrieves the first element of the deque(head) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object peekFirst() | Retrieves the first element of the deque(head) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object peekLast() | Retrieves the last element of the deque(tail) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object poll() | Retrieves and removes the first element of the deque(head) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object pollFirst() | Retrieves and removes the first element of the deque(head) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object pollLast() | Retrieves and removes the last element of the deque(tail) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object pop() | Retrieves or removes the first element from the stack of the deque | |
| void push(Object e) | Inserts the element to the front of the deque | e - the element to be added |
| Object remove() | Removes the first element from the deque | |
| Boolean remove(Object o) | Removes the first occurrence of the specified object from the deque if present | o - The element that needs to be removed Return value - true if deque contains the element |
| Boolean removeAll(Collection c) | Removes the first occurrence of all the elements in the collection from the deque if present | c - collection of elements Return value - true if the deque contains the collection |
| Object removeFirst() | Removes the first element of the deque | |
| Boolean removeFirstOccurence(Object e) | Removes the first occurrence of the element specified in the deque | e - the element to be removed |
| Object removeLast() | Removes the last element from the deque | |
| Boolean removeLastOccurence(Object e) | Removes the last occurrence of the specified element from the deque | e - the element to be removed |
| Boolean retainAll(Collection c) | Retains all the elements specified in collection in deque. Other elements will be removed | c - collection of elements that has to be retained Return value - true if the deque changed due to the method called |
| int size() | Fetches the size of the deque | Return value - size of the deque |
| Object[] toArray() | Returns an array of elements in proper sequence | Return value - Array of all elements in the deque in proper sequence |
| String toString() | Returns a String representation of the elements collection | Return value - String of array elements separated by comma and space and enclosed within [] |
Example: Insert elements in a Deque
In Java, there are several methods to insert elements in a deque. The below example illustrates how to insert elements using all the methods. The add() and offer() methods insert elements in the normal order. The addFirst(), offerFirst() and push() methods, inserts value to the first of the deque. Using the addLast() and offerLast() methods, we can insert elements to the end of the deque. To add a collection of elements, we can use the addAll() method.
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class InsertDequeElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<String> d = new LinkedList<String>();
d.add("C");
d.addFirst("C++");
d.addLast("Java");
System.out.println("Elements in the Deque after add, addFirst and addLast: " + d);
Deque<String> dq = new LinkedList<String>();
dq.add("JavaScript");
dq.add("Python");
d.addAll(dq);
System.out.println("Elements in the Deque after addAll: " + d);
d.offer(".Net");
d.offerFirst("C#");
d.offerLast("VBScript");
System.out.println("Elements in the Deque after offer, offerFirst and offerLast: " + d);
d.push("HTML");
System.out.println("Elements in the Deque after push: " + d);
}
}
Example: Delete elements from a Deque
Similar to different add operations, deque in Java supports several delete operations as well which is detailed in the below example. The remove() and poll() methods delete the element from the beginning of the deque. The removeFirst(), pollFirst() and pop() methods removes the first element. To remove the last element, we can use the removeLast() and pollLast() methods. We can also remove a collection of elements using the removeAll() method. The retainAll() method retains only the collection of elements and deletes the others from the deque.
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
public class DeleteDequeElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> d = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
d.add(30);
d.add(20);
d.add(10);
d.add(50);
d.add(40);
d.add(200);
d.add(300);
Deque<Integer> dq = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
dq.add(70);
dq.add(60);
dq.add(80);
dq.add(90);
dq.add(100);
d.addAll(dq);
System.out.println("Elements in the Deque: " + d);
d.remove();
d.remove(50);
System.out.println("Elements after remove: " + d);
d.removeFirst();
d.removeLast();
System.out.println("Elements after removeFirst and removeLast: " + d);
d.poll();
d.pollFirst();
d.pollLast();
System.out.println("Elements after poll, pollFirst and pollLast: " + d);
d.pop();
System.out.println("Elements after pop: " + d);
d.retainAll(dq);
System.out.println("Elements after retainAll: " + d);
d.removeAll(dq);
System.out.println("Elements after removeAll: " + d);
}
}
Elements in the Deque: [30, 20, 10, 50, 40, 200, 300, 70, 60, 80, 90, 100] Elements after remove: [20, 10, 40, 200, 300, 70, 60, 80, 90, 100] Elements after removeFirst and removeLast: [10, 40, 200, 300, 70, 60, 80, 90] Elements after poll, pollFirst and pollLast: [200, 300, 70, 60, 80] Elements after pop: [300, 70, 60, 80] Elements after retainAll: [70, 60, 80] Elements after removeAll: []
Example: Retrieve elements from Deque
The below example shows how to check if an element exists and retrieve head and tail elements of Deque in Java. To check for value existence, we can use the contains() and containsAll() method. We can retrieve the head element using the element(), peek(), peekFirst(), and getFirst() methods whereas to retrieve the tail element, we can use the getLast() and peekLast() methods.
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
public class RetrieveDequeElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> d = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
d.add(30);
d.add(20);
d.add(10);
d.add(50);
d.add(40);
d.add(60);
d.add(70);
Deque<Integer> dq = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
dq.add(80);
dq.add(90);
d.addAll(dq);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(d.contains(10));
System.out.println(d.contains(200));
System.out.println(d.containsAll(dq));
System.out.println("Output of element: " + d.element());
System.out.println("Get first element using getFirst: " + d.getFirst());
System.out.println("Get last element using getLast: " + d.getLast());
System.out.println("Output of peek: " + d.peek());
System.out.println("Get first element using peekFirst: " + d.peekFirst());
System.out.println("Get last element using peekLast: " + d.peekLast());
}
}
[30, 20, 10, 50, 40, 60, 70, 80, 90] true false true Output of element: 30 Get first element using getFirst: 30 Get last element using getLast: 90 Output of peek: 30 Get first element using peekFirst: 30 Get last element using peekLast: 90
Example: Clear Deque and check if empty
The below example illustrates how to clear the deque by removing all the elements using the clear() method. We can also check if the deque is empty using the isEmpty() method.
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
public class ClearDeque {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> d = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
d.add(30);
d.add(20);
d.add(10);
d.add(50);
System.out.println("Is Empty: " + d.isEmpty());
d.clear();
System.out.println("Is Empty after clear: " + d.isEmpty());
}
}
Is Empty: false Is Empty after clear: true
Example: Iterate elements in a Deque
By default, we can iterate through the elements in the deque using the iterator() method that returns the elements in the same sequence. To retrieve the values in the descending order in which it is inserted, we can use the descendingIterator() method.
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class IterateDeque {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> d = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
d.add(30);
d.add(20);
d.add(10);
d.add(50);
d.add(40);
System.out.println("Iterate using iterator:");
Iterator<Integer> i = d.iterator();
while(i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
System.out.println("Iterate using descendingIterator:");
Iterator<Integer> di = d.descendingIterator();
while(di.hasNext())
System.out.println(di.next());
}
}
Iterate using iterator: 30 20 10 50 40 Iterate using descendingIterator: 40 50 10 20 30
Example: Convert Deque to Array
In the below example, we are converting the deque into an array representation using the toArray() method. In this way, we can access the values based on the array index.
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Deque;
public class ConvertDequeToArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<String> d = new ArrayDeque<String>();
d.add("James");
d.add("John");
d.add("Xavior");
d.add("Thomas");
String[] arr = d.toArray(new String[d.size()]);
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(arr));
System.out.println("Value at index 2: "+ arr[2]);
}
}
[James, John, Xavior, Thomas] Value at index 2: Xavior