Table of Contents
Java Files and directories
File handling in Java – Files in Java is a class that is part of the java.io package which we use to perform different operations on files. A file is a repository that stores information. For example, the .java file that we create is a file that contains details about the Java program.
A directory is a collection of files that are saved in a particular location.
In order to perform the file operations, the Java Files class uses the stream concept.
Java Stream
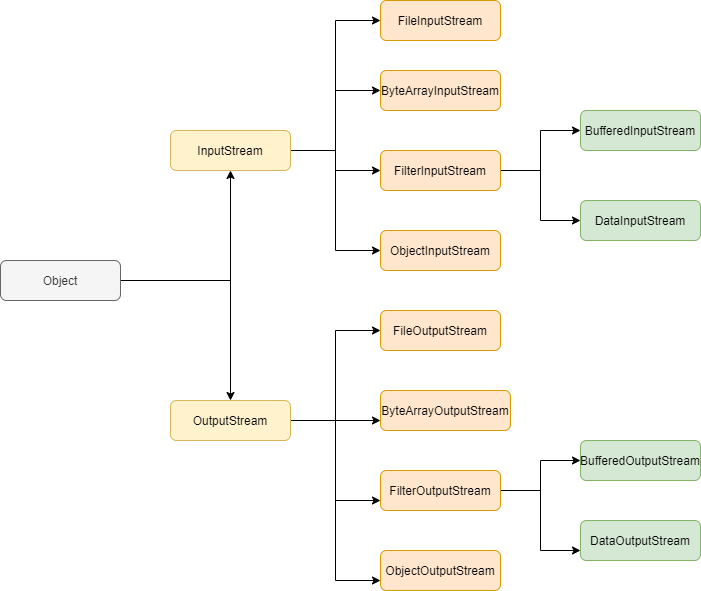
In Java, a stream is a sequence of data. We can classify stream into two types as InputStream and OutputStream. InputStream is used to read input data and we use OutputStream to write data into the output file.
We can also classify streams into ByteStream and CharacterStream.
ByteStream: This performs read and write operations on 8-bit data. The FileInputStream and FileOutputStream are examples of the ByteStream.
CharacterStream: This performs read and write operations on 16-bit data. The FileReader and FileWriter are examples of the CharacterStream.
Java Files Constructors
Below are the constructors that the File class in Java supports.
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| File(String filepath) | Creates a new file by converting the specified file path into absolute pathname |
| File(URI uri) | Creates a new file by converting the specified uri into absolute path |
| File(File parent, String child) | Creates a new file from the instance of the specified parent absolute pathname and child pathname string |
| File(String parent, String child) | Creates a new file with the instance of the specified parent string file name and child string file name |
Java Files Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| boolean canExecute() | Checks whether the application can execute the file with an absolute path |
| boolean canRead() | Checks whether the application can read the file with the absolute path |
| boolean canWrite() | Checks whether the application can write the file with the absolute path |
| int compareTo(File pathname) | Compares the two abstract pathname. Returns 0 if both are equal |
| boolean createNewFile() | Creates a new file with the absolute pathname if it does not exist |
| boolean delete() | Delete the file with the abstract filename |
| boolean exists() | Checks if the file exists |
| File getAbsoluteFile() | Returns the absolute form of the given abstract filename |
| String getAbsolutePath() | Returns the absolute string pathname of the abstract path |
| String getName() | Returns the name of the file |
| String getParent() | Returns the pathname string of the parent's abstract pathname |
| String getPath() | Returns the string pathname |
| boolean isDirectory() | Checks whether the specified file is a directory |
| boolean isFile() | Checks whether the specified file is a file |
| boolean isHidden() | Checks if the specified file is hidden |
| long lastModified() | Returns the time when the specified file was last modified |
| long length() | Returns the length of the file specified by the abstract path name |
| String[] list() | Lists the files and directories in the specified directory path |
| File[] listFiles() | Returns an array of the abstract pathnames of the files in the specified directory |
| boolean mkdir() | Creates a new directory with the specified abstract pathname |
| boolean renameTo(File dest) | Renames the file with the specified abstract pathname |
| boolean setExecutable(boolean executable) | Sets the owners execute permission for the specified file |
| boolean setLastModified(long time) | Sets the last modified time for the specified file |
| boolean setReadable(boolean readable) | Sets the owners read permission for the specified file |
| boolean setReadOnly() | Sets the permission such that the specified file has only read permission |
| boolean setWritable(boolean writable) | Sets the owners write permission for the specified file |
| String toString() | Returns the pathname string of the abstract file pathname |
| long getFreeSpace() | Returns the number of unallocated bytes of the specified file |
| long getTotalSpace() | Returns the total space of the specified file |
Files operations in Java
The common operations that we perform on Files in Java are:
- Create a file in Java
- Get file information in Java
- Write into a file in Java
- Read a file in Java
- Copy file in Java
- Set file permissions in Java
Let’s understand these file operations with simple examples.
Create a File in Java
Before we start working on a file, we need to first create a file if it does not exist. For this, we can use the createNewFile() method that accepts the filename as a parameter. It first checks if the file exists, if it does not exist, then it creates a new file in the given path.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CreateFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String pathname = "NewFile.txt";
File f= new File(pathname);
if(f.createNewFile())
System.out.println("File created with filename: " + f.getName());
else
System.out.println("File already exists");
System.out.println("File path: " + f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
File created with filename: NewFile.txt File path: C:\Users\nandi\eclipse-workspace\FilesDemo\NewFile.txt
Retrieve file Information in Java
There are several methods to retrieve file information. The below example lists a few of them.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CreateFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String pathname = "NewFile.txt";
File f= new File(pathname);
if(f.createNewFile())
System.out.println("File created with filename: " + f.getName());
else
System.out.println("File already exists");
System.out.println("File name: " + f.getName());
System.out.println("File path: " + f.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("Available space in bytes: " + f.getFreeSpace());
System.out.println("Path: " + f.getPath());
System.out.println("Total space in bytes: " + f.getTotalSpace());
System.out.println("Usable space in bytes: " + f.getUsableSpace());
}
}
File already exists File name: NewFile.txt File path: C:\eclipse-workspace\FilesDemo\NewFile.txt Available space in bytes: 918902095872 Path: NewFile.txt Total space in bytes: 999306579968 Usable space in bytes: 918902095872
How to write to a File in Java? Write string to file
Java Write to File – FileWriter Java
There are 3 ways to write data into a file: FileWrite, BufferedWriter, or FileOutputStream. The below example uses FileWriter to write information into a file.
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WriteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filename = "NewFile.txt";
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(filename);
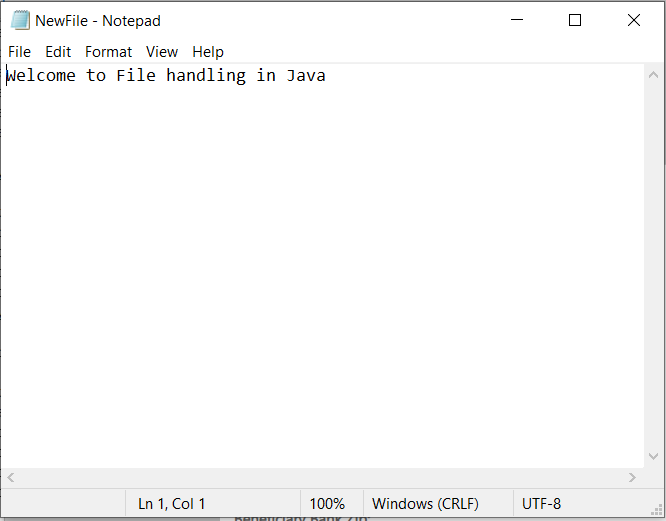
fw.write("Welcome to File handling in Java");
fw.close();
System.out.println("File write operation completed");
}
}
File write operation completed
Read a file in Java
Similar to writing a file, there are different ways to read a file like FileReader, BufferedReader, FileInputStream, or Scanner. In this tutorial, we will see how to read a file using the FileReader class.
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
String filename = "NewFile.txt";
char[] content = new char[100];
FileReader fr = new FileReader(filename);
try {
fr.read(content);
System.out.println("Contents in the file:");
System.out.println(content);
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Contents in the file: Welcome to File handling in Java
Copy file in Java
We can copy the contents of one file to another using the FileInputStream and FileOutputStream classes. Using the FileInputStream class we can read the source file content and using the FileOutputStream class, we can write the same content to the destination file.
In the below example, we are printing the copied contents from the destination file by using the FileReader class.
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class CopyFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
byte[] data = new byte[100];
char[] c = new char[100];
FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("NewFile.txt");
FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("DestFile.txt");
fi.read(data);
fo.write(data);
System.out.println("File contents copied.");
fi.close();
fo.close();
System.out.println("Contents in destination file:");
FileReader fr = new FileReader("DestFile.txt");
try {
fr.read(c);
System.out.println(c);
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
fr.close();
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
File contents copied. Contents in destination file: Welcome to File handling in Java
Delete a file in Java
We can delete a file using the Files class delete() method in Java.
import java.io.File;
public class DeleteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("NewFile.txt");
boolean fdel = f.delete();
if(fdel)
System.out.println("File is deleted");
else
System.out.println("File is not deleted");
}
}
File is deleted
File permissions in Java
We can check file permissions using various methods present in the Files class in Java. The below example checks if the specified file has read, write, and execute permissions.
import java.io.File;
public class FilePermission {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("NewFile.txt");
System.out.println("Executable: " + f.canExecute());
System.out.println("Readable: " + f.canRead());
System.out.println("Writable: " + f.canWrite());
}
}
Executable: true Readable: true Writable: true
List files in the directory in Java
The below example shows how to create a new directory using the mkdir() method and create new files within the directory using the createNewFile(). We can then list the files inside the directory using the list() method.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ListFiles {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("Directory");
if(f.mkdir())
System.out.println("Directory is created");
else
System.out.println("Directory is not created");
String fpath = "C:\\eclipse-workspace\\FilesDemo\\Directory\\File1.txt";
String fpath1 = "C:\\eclipse-workspace\\FilesDemo\\Directory\\File2.txt";
File f1 = new File(fpath);
File f2 = new File(fpath1);
f1.createNewFile();
f2.createNewFile();
System.out.println("List of files in the directory:");
String[] files = f.list();
for(int i=0;i<files.length;i++)
System.out.println(files[i]);
}
}
Directory is created List of files in the directory: File1.txt File2.txt