Table of Contents
Problem Statement
The Palindrome Partitioning LeetCode Solution – “Palindrome Partitioning” states that you’re given a string, partition the input string such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. Return all possible palindrome partitioning of the input string.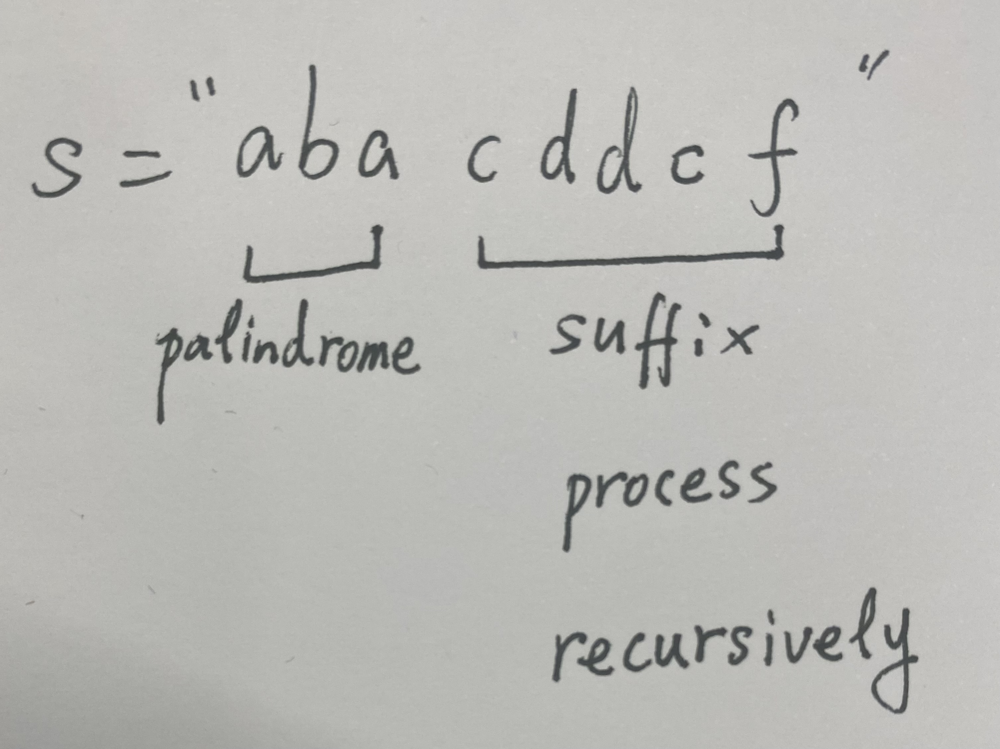
Example:
Input: s = "aab"
Output: [["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
Explanation:
- There exist exactly 2 valid partitions of the input string.
- [[“a”,”a”,”b”],[“aa”,”b”]]
Input: s = "a"
Output: [["a"]]
Explanation:
- All possible valid partition includes: [a]
Approach
Idea:
- The main idea to solve this problem is to use Backtracking.
- Perform the Backtracking starting from index = 0.
- Maintain a string variable used to store the current substring and the path used to store the current valid partition.
- At each index, there are at most 2 choices:
- Extend the current substring.
- If the current substring is a palindrome, go for the next substring from the next index.
- As we reach the index strictly greater than the last position of the string, we need to store the path, which is a palindrome partition.
Code for Palindrome Partitioning Leetcode Solution
C++ Solution:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> ans;
bool isPal(string s){
int l = 0,r = s.length() - 1;
while(l<r){
if(s[l++]!=s[r--]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void recurse(int i,string s,string curr,vector<string>& now){
if(i==s.length()){
if(curr.empty()){
ans.push_back(now);
}
return;
}
curr.push_back(s[i]);
if(isPal(curr)){
now.push_back(curr);
recurse(i+1,s,"",now);
now.pop_back();
}
recurse(i+1,s,curr,now);
}
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
vector<string> curr;
recurse(0,s,"",curr);
return ans;
}
};Java Solution:
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> now = new ArrayList<>();
helper(0, s, now, ans);
return ans;
}
public void helper(int index, String s, List<String> curr, List<List<String>> ans){
if(index == s.length()){
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(curr));
return;
}
for(int i = index; i < s.length(); i++){
if(isPalindrome(s, index, i)){
curr.add(s.substring(index, i + 1));
helper(i + 1, s, curr, ans);
curr.remove(curr.size() - 1);
}
}
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String s, int l, int r){
while(l <= r){
if(s.charAt(l++) != s.charAt(r--)) return false;
}
return true;
}
}Complexity Analysis for Palindrome Partitioning Leetcode Solution
Time Complexity
The time complexity of the above code is O(N*2^N) since every index has 2 choices and for all possible combinations, we’re checking the condition of being palindrome which takes linear time. Hence, the overall complexity is O(N*2^N).
Space Complexity
The space complexity of the above code is O(N) [considering recursive calls also]. The Space will be used to store the recursion stack.