Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree LeetCode Solution – Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Example
Test Case 1:
Input:
root = [1, 2, 3, null, null, 4, 5]
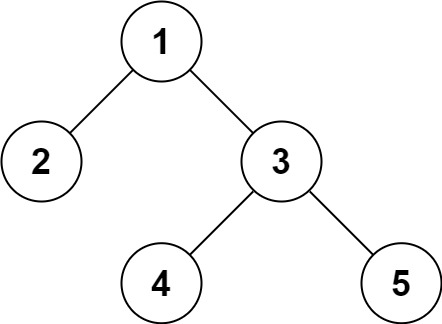
Output:
[1, 2, 3, null, null, 4, 5]
Approach:
we can solve it step by step:
For the encoding a tree to a single string part:
- we can just use preorder of traversing the tree
- And then combine the node to a string with “,” so that we can separate each node.
- after that we can get the result // 1,2,x,x,3,4,x,x,5
For decoding the encoded data to the tree part :
- use a queue to store the string so that we can make it a tree.
- Since the encoded data is included comma to separate each node of the tree, we can just use the continue method to skip it.
- After putting all the nodes into the queue, we just make a deserialize helper do the recursion
For the helper function :
- We need to create a string to store the front of the queue so that we can pop it out each time
- Since I used “x” to be representative NULL of the child, we need to return it to NULL at this time
- After that, we need to transfer the string to an integer so that the value of s can be put in the tree and create a new node to store the value.
- Finally, just do a recursion of the left and right child to fill in the tree.
Serialize:
- We will use preorder traversal to store the data in a string.
- If a valid node is found, we convert its value to a string and add a space e.g. “5 ” and append it to our answer string.
- For valid node, we call DFS(node->left) and DFS(node->right)
- if NULL is encountered, we append “# ” to our answer string.
Note: In place of “# ” any other string which does not conflict with integer values can be used e.g. “null ” or “$ “
Deserialize:
- Since we serialized we preorder traversal, we also need to form the Tree nodes in the same manner.
- We use stringstream (or istringstream) and initialize it with input data. It will simply tokenize the string using extra space that we added after every node. e.g. “1 22 43 54 #” will be broken in 5 different strings {“1”, “22”, “43”, “54”, “#” }
- We call DFS with stringstream and take out one string every time using ss >> value.
- if the value is a valid value, we create a new node with this value and call DFS for the new node’s left and right values.
- if value is “#”, we return NULL.
Code for Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
C++ Program
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
private:
void _serialize(TreeNode* root, string& s) {
if(!root) {
s += "# ";
return;
}
s += (to_string(root->val) + " ");
_serialize(root->left, s);
_serialize(root->right, s);
}
TreeNode* _deserialize(istringstream& ss) {
string value;
ss >> value;
if(value == "#") return NULL;
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(stoi(value));
node->left = _deserialize(ss);
node->right = _deserialize(ss);
return node;
}
public:
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
string data = "";
_serialize(root, data);
return data;
}
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
istringstream ss(data);
return _deserialize(ss);
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec ser, deser;
// TreeNode* ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));Java Program
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Codec {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
preorderTraversal(root);
return sb.toString();
}
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
sb.append("n ");
return;
}
sb.append(root.val+" ");
preorderTraversal(root.left);
preorderTraversal(root.right);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
int index = 0;
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] ss = data.split(" ");
return prebuild(ss);
}
TreeNode prebuild(String[] ss){
if(index>=ss.length)return null;
if(ss[index].equals("n"))return null;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(ss[index]));
index++;
node.left=prebuild(ss);
index++;
node.right=prebuild(ss);
return node;
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec ser = new Codec();
// Codec deser = new Codec();
// TreeNode ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));Complexity Analysis for Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree LeetCode Solution
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)