In merging intervals problem we have given a set of intervals of the form [l, r], merge the overlapping intervals.
Table of Contents
Examples
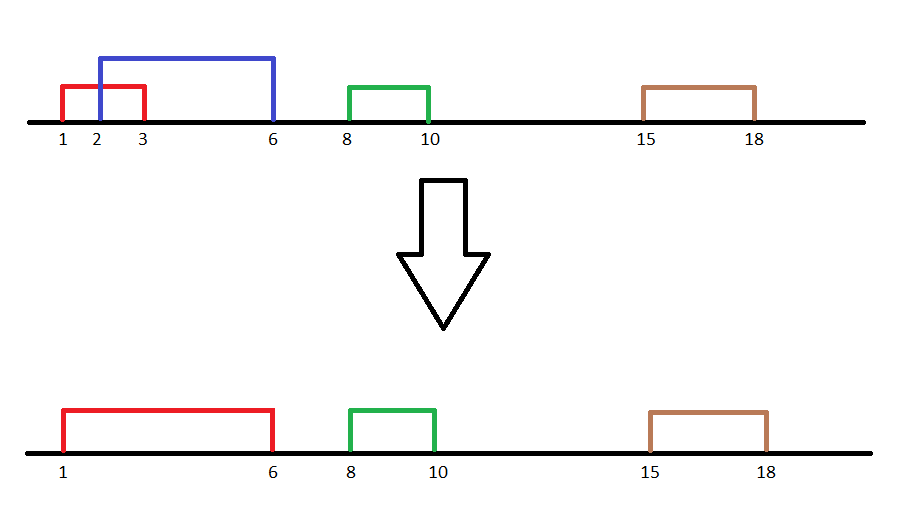
Input
{[1, 3], [2, 6], [8, 10], [15, 18]}
Output
{[1, 6], [8, 10], [15, 18]}
Input
{[1, 4], [1, 5]}
Output
{[1, 5]}
Naive Approach for merging intervals
The naive approach for merging intervals is to simply compare every interval with all the other remaining intervals. If there is some intersection point, remove the second part, and merge it into the first.
Pseudo Code
Let l[] represents the lower limit(starting point) of all intervals and r[] represents the upper limit(ending point) of all intervals.
int n = total number of intervals
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Removed interval
if (l[i] == -infinity && r[i] == -infinity) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// Do not compare with itself
if (i == j)
continue;
// Do not compare with removed intervals
if (l[i] == infinity && r[i] == -infinity) {
continue;
}
// Check if there is some intersection point
if ((l[j] >= l[i] && l[j] <= r[i]) || (r[j] >= l[i] && r[j] <= r[i])) {
// Merge the intervals
l[i] = min(l[i], l[j])
r[i] = min(r[i], r[j])
// Remove the other interval
l[j] = -infinity
r[j] = -infinity
} else {
// Do not merge
}
}
}
// Print the merged intervals
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!(l[i] == -infinity && r[i] == -infinity)) {
print(l[i] + " " + r[i]);
}
}Time Complexity = O(n^2) where n is the number of intervals given. Here we check for each pair of the interval which takes N*N time.
JAVA Code
public class MergingIntervals {
// Function to merge the intervals and print merged intervals
private static void mergeIntervals(Interval intervals[]) {
int n = intervals.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Removed intervals
if (intervals[i].l == Integer.MIN_VALUE
&& intervals[i].r == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// Do not compare with itself
if (i == j)
continue;
// Do not compare with removed intervals
if (intervals[i].l == Integer.MIN_VALUE
&& intervals[i].r == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
continue;
}
// Check if there is some intersection point
if ((intervals[j].l >= intervals[i].l && intervals[j].l <= intervals[i].r) ||
intervals[j].r >= intervals[i].l && intervals[j].r <= intervals[i].r) {
// Merge the intervals
intervals[i].l = Math.min(intervals[j].l, intervals[i].l);
intervals[i].r = Math.max(intervals[j].r, intervals[i].r);
// Remove the other interval
intervals[j].l = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
intervals[j].r = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else {
// Do not merge
}
}
}
// Print the merged intervals
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!(intervals[i].l == Integer.MIN_VALUE && intervals[i].r == Integer.MIN_VALUE)) {
System.out.println(intervals[i].l + " " + intervals[i].r);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
Interval intervals[] = new Interval[4];
intervals[0] = new Interval(1, 3);
intervals[1] = new Interval(2, 6);
intervals[2] = new Interval(8, 10);
intervals[3] = new Interval(15, 18);
mergeIntervals(intervals);
// Example 2
Interval intervals2[] = new Interval[2];
intervals2[0] = new Interval(1, 4);
intervals2[1] = new Interval(1, 5);
mergeIntervals(intervals2);
}
// Class representing an interval
static class Interval {
int l; // Staring point
int r; // Ending point
public Interval(int l, int r) {
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
// Comparator to sort the intervals
public static final Comparator<Interval> comp = new Comparator<Interval>() {
@Override
public int compare(Interval o1, Interval o2) {
int l1 = o1.l;
int l2 = o2.l;
int r1 = o1.r;
int r2 = o2.r;
if (l1 == l2) {
return Integer.compare(r1, r2);
}
return Integer.compare(l1, l2);
}
};
}
}C++ Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure representing an interval
struct Interval {
int l, r;
};
// Function to merge the intervals and print merged intervals
void mergeIntervals(Interval intervals[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Removed intervals
if (intervals[i].l == INT_MIN && intervals[i].r == INT_MIN) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// Do not compare with itself
if (j == i) {
continue;
}
// Do not compare with removed intervals
if (intervals[i].l == INT_MIN && intervals[i].r == INT_MIN) {
continue;
}
// Check if there is some intersection point
if ((intervals[j].l >= intervals[i].l && intervals[j].l <= intervals[i].r) || (intervals[j].r >= intervals[i].l && intervals[j].r <= intervals[i].r)) {
// Merge the intervals
intervals[i].l = std::min(intervals[i].l, intervals[j].l);
intervals[i].r = std::max(intervals[i].r, intervals[j].r);
// Remove the other interval
intervals[j].l = INT_MIN;
intervals[j].r = INT_MIN;
} else {
// Do not merge
}
}
}
// Print the merged intervals
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!(intervals[i].l == INT_MIN && intervals[i].r == INT_MIN)) {
cout<<intervals[i].l<<" "<<intervals[i].r<<endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
// Example 1
Interval intervals[] = {{1, 3}, {2, 6}, {8, 10}, {15, 18}};
int n1 = sizeof(intervals) / sizeof(intervals[0]);
mergeIntervals(intervals, n1);
// Example 2
Interval intervals2[] = {{1, 4}, {1, 5}};
int n2 = sizeof(intervals2) / sizeof(intervals2[0]);
mergeIntervals(intervals2, n2);
return 0;
}{[1, 4], [1, 5]}{[1, 5]}Optimal Approach for merging intervals
The optimal approach to merge intervals is to sort the intervals according to their starting point(lower limit) in ascending order, if two intervals have the same starting point, sort them according to their ending point in ascending order. This will ensure that the intervals that may have some common points occur one after another. After sorting, compare the adjacent intervals and merge them, as done in the naive approach.
Example
Original intervals : {[5, 8], [3, 6], [15, 25], [10, 14], [9, 13]}
After Sorting : {[[3, 6], [5, 8], [9, 13], [10, 14], [15, 25]}
In this example, it is clear that the intersecting intervals came next to one another after sorting, so we just need to compare the adjacent intervals.
[3, 6] and [5, 8] merges to [3, 8]
[9, 14] and [10, 14] merges to [9, 14]
Output : {[3, 8], [9, 14], [15, 25]}
Pseudo Code
l[] –> Lower limit(Starting point) of all the intervals
r[] –> Upper limit(Ending point) of all the intervals
n –> Total number of intervals
Sort l and r as described.
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// Compare i and (i + 1)th intervals
if ((l[i] >= l[i + 1] && l[i] <= r[i + 1]) || (r[i] >= l[i + 1] && r[i] <= r[i + 1])) {
// Merge intervals
l[i + 1] = min(l[i], l[i + 1])
r[i + 1] = max(r[i], r[i + 1])
// Remove the previous interval
l[i] = -infinity
r[i] = -infinity
}
}
// Print the merged intervals
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!(l[i] == -infinity && r[i] == -infinity)) {
// Print only non removed intervals
print(l[i] + " " + r[i])
}
}Time Complexity = O(n * log(n)) where n is the number of intervals given. We use sort function for sorting which take long time.
JAVA Code
public class MergingIntervals {
// Function to merge the intervals and print merged intervals
private static void mergeIntervals(Interval intervals[]) {
// Sort the intervals array
Arrays.sort(intervals, Interval.comp);
// Traverse the sorted array
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length - 1; i++) {
// Compare i and (i + 1)th intervals
if ((intervals[i].l >= intervals[i + 1].l && intervals[i].l <= intervals[i + 1].r)
|| (intervals[i].r >= intervals[i + 1].l && intervals[i].r <= intervals[i + 1].r)) {
// Merge intervals
intervals[i + 1].l = Math.min(intervals[i].l, intervals[i + 1].l);
intervals[i + 1].r = Math.max(intervals[i].r, intervals[i + 1].r);
// Remove previous interval
intervals[i].l = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
intervals[i].r = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else {
// Do not merge
}
}
// Print the merged intervals
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
if (!(intervals[i].l == Integer.MIN_VALUE && intervals[i].r == Integer.MIN_VALUE)) {
System.out.println(intervals[i].l + " " + intervals[i].r);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
Interval intervals[] = new Interval[4];
intervals[0] = new Interval(1, 3);
intervals[1] = new Interval(2, 6);
intervals[2] = new Interval(8, 10);
intervals[3] = new Interval(15, 18);
mergeIntervals(intervals);
// Example 2
Interval intervals2[] = new Interval[2];
intervals2[0] = new Interval(1, 4);
intervals2[1] = new Interval(1, 5);
mergeIntervals(intervals2);
}
// Class representing an interval
static class Interval {
int l; // Staring point
int r; // Ending point
public Interval(int l, int r) {
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
// Comparator to sort the intervals
public static final Comparator<Interval> comp = new Comparator<Interval>() {
@Override
public int compare(Interval o1, Interval o2) {
int l1 = o1.l;
int l2 = o2.l;
int r1 = o1.r;
int r2 = o2.r;
if (l1 == l2) {
return Integer.compare(r1, r2);
}
return Integer.compare(l1, l2);
}
};
}
}C++ Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure representing an interval
struct Interval {
int l, r;
};
// Comparator for sorting intervals
bool compareInterval(Interval i1, Interval i2) {
if (i1.l == i2.l) {
return (i1.r < i2.r);
}
return (i1.l < i2.l);
}
// Function to merge the intervals and print merged intervals
void mergeIntervals(Interval intervals[], int n) {
// Sort the intervals array
sort(intervals, intervals + n, compareInterval);
// Traverse the sorted array
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// Compare i and (i + 1)th intervals
if ((intervals[i].l >= intervals[i + 1].l && intervals[i].l <= intervals[i + 1].r) || (intervals[i].r >= intervals[i + 1].l && intervals[i].r <= intervals[i + 1].r)) {
// Merge intervals
intervals[i + 1].l = std::min(intervals[i].l, intervals[i + 1].l);
intervals[i + 1].r = std::max(intervals[i].r, intervals[i + 1].r);
// Remove previous interval
intervals[i].l = INT_MIN;
intervals[i].r = INT_MIN;
} else {
// Do not merge
}
}
// Print the merged intervals
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!(intervals[i].l == INT_MIN && intervals[i].r == INT_MIN)) {
cout<<intervals[i].l<<" "<<intervals[i].r<<endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
// Example 1
Interval intervals[] = {{1, 3}, {2, 6}, {8, 10}, {15, 18}};
int n1 = sizeof(intervals) / sizeof(intervals[0]);
mergeIntervals(intervals, n1);
// Example 2
Interval intervals2[] = {{1, 4}, {1, 5}};
int n2 = sizeof(intervals2) / sizeof(intervals2[0]);
mergeIntervals(intervals2, n2);
return 0;
}{[5, 8], [3, 6], [15, 25], [10, 14], [9, 13]}{[3, 8], [9, 14], [15, 25]}