In the backspace string compare problem we have given two Strings S and T, check if they are equal or not. Note that the strings contain ‘#’ which means backspace character.
Table of Contents
Examples
Input
S = “ab#c”
T = “ad#c”
Output
true (as both S and T converts to “ac”)
Input
S = “ab##”
T = “c#d#”
Output
true (as both S and T are empty)
Input
S = “a#c”
T = “b”
Output
false (as S = “c” and T = “b”)
Naive Approach for backspace string compare
This is the basic approach that takes some extra space for solving the backspace string compare problem. Let’s come to the logic of how to solve it.
Traverse Strings S and T and reform both strings, that is, remove the characters that will be affected by the backspace.
Example
S = “ab#c” is reformed to S = “ac”, because b is removed due to backspace
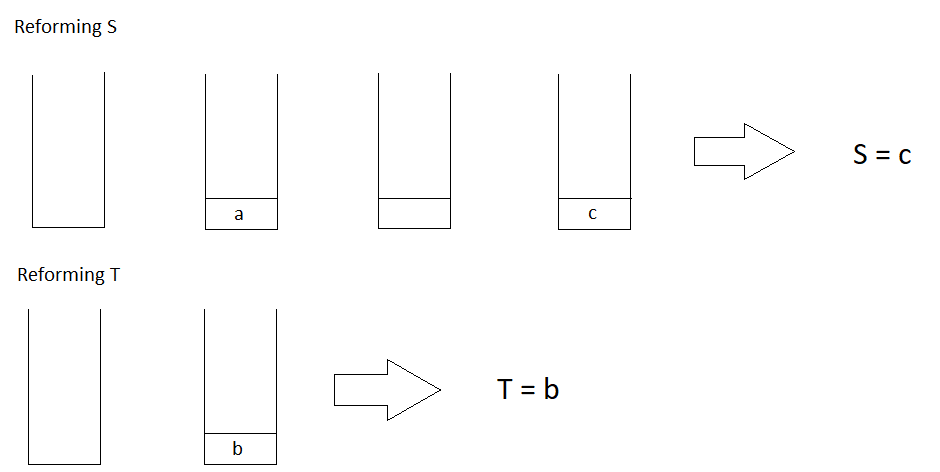
Then, compare the two new Strings, if they are equal return true else return false.
The reformation for a string is done as,
- Create an empty stack of characters.
- Start traversing in the string from index 0.
- If the current character is ‘#’ and the stack is not empty, pop out an item from the stack.
- Else if the current character is not ‘#’ push the current character to the stack.
- After completely traversing the string, stack contains the reformed string in reverse order.
Complexity Analysis for backspace string compare
Time Complexity = O(n + m), where n is the length of string S and m is the length of string T.
Space Complexity = O(n + m)
JAVA Code
import java.util.Stack;
public class BackspaceStringCompare {
private static boolean backSpaceCompare(String S, String T) {
// Reform the strings and check if they are equal
return reform(S).equals(reform(T));
}
// Function to reform a string
private static String reform(String S) {
char sArr[] = S.toCharArray();
// Create an empty stack
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
// Traverse in the string
for (int i = 0; i < sArr.length; i++) {
// If current character is # and stack is empty, pop out an item from stack
if (sArr[i] == '#' && !stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.pop();
}
// If current character is not #, push it into the stack
if (sArr[i] != '#') {
stack.push(sArr[i]);
}
}
// Stack contains the string in reverse order, return the reversed string
// As it does not affect the comparision
return String.valueOf(stack);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
System.out.println(backSpaceCompare("ab#c", "ad#c"));
// Example 2
System.out.println(backSpaceCompare("ab##", "c#d#"));
// Example 3
System.out.println(backSpaceCompare("a#c", "b"));
}
}C++ Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to reform a string
string reform(char *s, int n) {
// Create an empty stack
stack<char> st;
// Traverse in the string
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// If current character is # and stack is empty, pop out an item from stack
if (s[i] == '#' && !st.empty()) {
st.pop();
}
// If current character is not #, push it into the stack
if (s[i] != '#') {
st.push(s[i]);
}
}
// Stack contains the string in reverse order, return the reversed string
// As it does not affect the comparision
char str[st.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < st.size(); i++) {
str[i] = st.top();
st.pop();
}
string ans = str;
return ans;
}
bool backSpaceCompare(char *s, char *t, int n, int m) {
// Reform the strings and check if they are equal
if (reform(s, n).compare(reform(t, m)) == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main() {
// Example 1
if (backSpaceCompare("ab#c", "ad#c", 4, 4)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
// Example 2
if (backSpaceCompare("ab##", "c#d#", 4, 4)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
// Example 3
if (backSpaceCompare("a#c", "b", 3, 1)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}S = "ab#c" T = "ad#c"
true
Optimal Approach for backspace string compare
The time complexity of the naive approach cannot be reduced further, but the space complexity can be optimized to O(1).
Traverse the strings S and T in reverse order, if we see a backspace character(‘#’) in any of the string, the next non-backspace character of that string is skipped, and we compare the non skipped characters only.
- Initialize two integers sSkip and tSkip, that stores the number of backspaces encountered.
- If we see a ‘#’ in S, increment sSkip, and if we see a ‘#’ in T increment tSkip.
- If sSkip and tSkip are 0, then compare the current character of strings S and T, if these are equal continue for remaining string else return false.
- Else if sSkip is not zero, skip the current character in S and decrease sSkip by 1, similarly if tSkip is not zero, skip the current character in T and decrease tSkip by 1.
- Repeat the above steps till we traverse completely one of the strings.
- For the remaining characters of string S, if the current character is ‘#’ increment sSkip by 1, else decrement it by 1. If at any moment sSkip becomes negative return false.
- For the remaining characters of string T, if the current character is ‘#’ increment tSkip by 1, else decrement it by 1. If at any moment tSkip becomes negative return false.
- If the above conditions are safely passed(that is without returning false), return true.
Complexity Analysis for backspace string compare
Time Complexity = O(m + n), where n is the length of string S, and m is the length of string T.
Space Complexity = O(1)
JAVA Code
public class BackspaceStringCompare {
private static boolean backSpaceCompare(String S, String T) {
char sArr[] = S.toCharArray();
char tArr[] = T.toCharArray();
int sP = sArr.length - 1;
int tP = tArr.length - 1;
// Initialize sSkip and tSkip as 0
int sSkip = 0;
int tSkip = 0;
// Traverse the strings in reverse order
while (sP >= 0 && tP >= 0) {
// If current character in S is '#', increment sSkip
if (sArr[sP] == '#') {
sSkip++;
sP--;
}
// If current character in T is '#', increment tSkip
if (tArr[tP] == '#') {
tSkip++;
tP--;
}
// If the traversal for any one string is complete break the loop
if (sP < 0 || tP < 0) {
break;
}
// If both sSkip and tSkip are zero compare the current characters
if (sSkip == 0 && tSkip == 0) {
if (sArr[sP] == tArr[tP]) {
// Continue if these are equal
sP--;
tP--;
} else {
// Else return false immediately
return false;
}
} else {
// If current character in S is '#', increment sSkip
if (sArr[sP] == '#') {
sSkip++;
sP--;
} else {
// If sSkip is not 0, skip the current character
if (sSkip != 0) {
sSkip--;
sP--;
}
}
// If current character in T is '#', increment tSkip
if (tArr[tP] == '#') {
tSkip++;
tP--;
} else {
// If tSkip is not 0, skip the current character
if (tSkip != 0) {
tSkip--;
tP--;
}
}
}
}
// Traverse the remaining S string
while (sP >= 0) {
// If current character is '#', increment sSkip
if (sArr[sP] == '#') {
sSkip++;
} else {
// Else decrement sSkip
sSkip--;
}
// If sSkip becomes negative return false
if (sSkip < 0)
return false;
sP--;
}
// Traverse the remaining T string
while (tP >= 0) {
// If current character is '#', increment tSkip
if (tArr[tP] == '#') {
tSkip++;
} else {
// Else decrement tSkip
tSkip--;
}
// If tSkip becomes negative, return false
if (tSkip < 0) {
return false;
}
tP--;
}
// Return true if encountered above cases safely
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
System.out.println(backSpaceCompare("ab#c", "ad#c"));
// Example 2
System.out.println(backSpaceCompare("ab##", "c#d#"));
// Example 3
System.out.println(backSpaceCompare("a#c", "b"));
}
}C++ Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool backSpaceCompare(char *S, char *T, int n, int m) {
int sP = n - 1;
int tP = m - 1;
// Initialize sSkip and tSkip as 0
int sSkip = 0;
int tSkip = 0;
// Traverse the strings in reverse order
while (sP >= 0 && tP >= 0) {
// If current character in S is '#', increment sSkip
if (S[sP] == '#') {
sSkip++;
sP--;
}
// If current character in T is '#', increment tSkip
if (T[tP] == '#') {
tSkip++;
tP--;
}
// If the traversal for any one string is complete break the loop
if (sP < 0 || tP < 0) {
break;
}
// If both sSkip and tSkip are zero compare the current characters
if (sSkip == 0 && tSkip == 0) {
if (S[sP] == T[tP]) {
// Continue if these are equal
sP--;
tP--;
} else {
// Else return false immediately
return false;
}
} else {
// If current character in S is '#', increment sSkip
if (S[sP] == '#') {
sSkip++;
sP--;
} else {
// If sSkip is not 0, skip the current character
if (sSkip != 0) {
sSkip--;
sP--;
}
}
// If current character in T is '#', increment tSkip
if (T[tP] == '#') {
tSkip++;
tP--;
} else {
// If tSkip is not 0, skip the current character
if (tSkip != 0) {
tSkip--;
tP--;
}
}
}
}
// Traverse the remaining S string
while (sP >= 0) {
// If current character is '#', increment sSkip
if (S[sP] == '#') {
sSkip++;
} else {
// Else decrement sSkip
sSkip--;
}
// If sSkip becomes negative return false
if (sSkip < 0)
return false;
sP--;
}
// Traverse the remaining T string
while (tP >= 0) {
// If current character is '#', increment tSkip
if (T[tP] == '#') {
tSkip++;
} else {
// Else decrement tSkip
tSkip--;
}
// If tSkip becomes negative, return false
if (tSkip < 0)
return false;
tP--;
}
// Return true if encountered above cases safely
return true;
}
int main() {
// Example 1
if (backSpaceCompare("ab#c", "ad#c", 4, 4)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
// Example 2
if (backSpaceCompare("ab##", "c#d#", 4, 4)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
// Example 3
if (backSpaceCompare("a#c", "b", 3, 1)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}S = "ab##" T = "c#d#"
true