Reservoir Sampling is a technique of selecting k reservoir items randomly from a given list of n items, where n is very large.
For example, search lists in Google, YouTube etc.
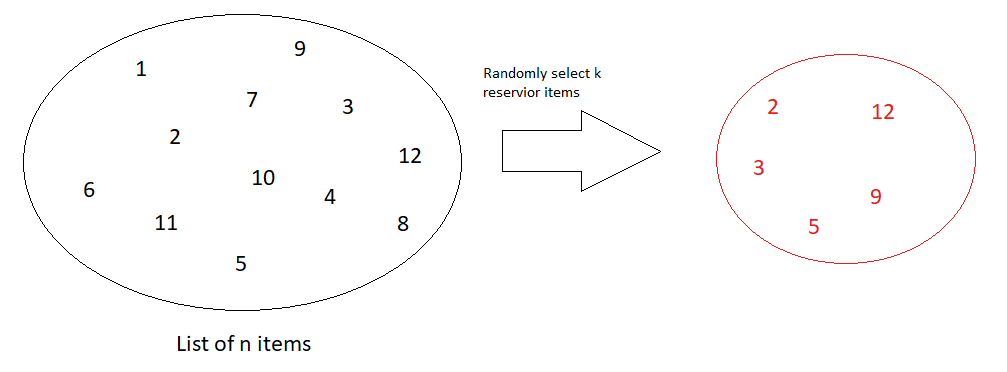
Table of Contents
Naive Approach for Reservoir Sampling
Build a reservoir array of size k, randomly select items from the given list. If the chosen item does not exist in the reservoir, add it, else continue for the next item.
- Create a reservoir array of size k.
- Initialize curr as 0, curr represent the curr position of reservoir array to be filled. Repeat step 3 and 4 while curr is less than k.
- Generate a random number between 0 to n(not included). Let the generated random number be rand.
- If the element at stream[rand] is already present in the reservoir array, repeat step 3. Else set reservoir[curr] as stream[rand] and increment curr.
- Print the elements of the reservoir array.
JAVA Code for Reservoir Sampling
public class ReservoirSampling {
private static void selectReservoir(int[] stream, int k) {
int n = stream.length;
int reservoir[] = new int[k];
// Index where the current item has to be placed
int curr = 0;
while (curr < k) {
// Randomly generate an index between 0 to n
int i = (int) (Math.random() * n) % n;
boolean found = false;
// Check if it is already present
for (int j = 0; j < curr; j++) {
if (reservoir[j] == stream[i]) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
// If not present add it to the reservoir list
if (!found) {
reservoir[curr] = stream[i];
curr++;
}
}
// Print the randomly selected items
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
System.out.print(reservoir[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example
int stream[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
int k = 5;
selectReservoir(stream, k);
}
}C++ Code for Reservoir Sampling
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void selectReservoir(int stream[], int k, int n) {
int reservoir[k];
// Index where the current item has to be placed
int curr = 0;
srand(time(0));
while (curr < k) {
// Randomly generate an index between 0 to n
int i = rand() % n;
bool found = false;
// Check if it is already present
for (int j = 0; j < curr; j++) {
if (reservoir[j] == stream[i]) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
// If not present add it to the reservoir list
if (!found) {
reservoir[curr] = stream[i];
curr++;
}
}
// Print the randomly selected items
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
cout<<reservoir[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
// Example
int stream[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
int k = 5;
int n = sizeof(stream) / sizeof(stream[0]);
selectReservoir(stream, k, n);
return 0;
}2 12 9 3 5
Output may differ, as the code chooses reservoirs randomly.
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity = O(k2)
Space Complexity = O(1)
where k is the number of elements present in the reservoir array.
Optimal Approach for Reservoir Sampling
The above problem can be solved efficiently for a given stream as,
- Create a reservoir array of size k and copy the first k items of stream into the array.
- Traverse the stream from index (k + 1) to n.
- For ith element in the stream generate a random number, say j, if the number lies in between 0 and (k – 1), replace reservoir[j] with stream[i].
- Reservoir array contains k random numbers selected from the stream, print them.
JAVA Code for Reservoir Sampling
public class ReservoirSampling {
private static void selectReservoir(int[] stream, int k) {
int n = stream.length;
int reservoir[] = new int[k];
// Copy first k items to the reservoir array
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
reservoir[i] = stream[i];
}
// Traverse the remaining stream
for (int i = k; i < n; i++) {
// Generate a random number between 0 to n
int randomNumber = (int) (Math.random() * n) % n;
// If this number lies between 0 to k, replace reservoir[randomNumber] with stream of i
if (randomNumber >= 0 && randomNumber < k) {
reservoir[randomNumber] = stream[i];
}
}
// Print the reservoir array
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
System.out.print(reservoir[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int stream[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
int k = 5;
selectReservoir(stream, k);
}
}C++ Code for Reservoir Sampling
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void selectReservoir(int stream[], int k, int n) {
int reservoir[k];
// Copy first k items to the reservoir array
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
reservoir[i] = stream[i];
}
srand(time(0));
// Traverse the remaining stream
for (int i = k; i < n; i++) {
// Generate a random number between 0 to n
int randomNumber = rand() % n;
// If this number lies between 0 to k, replace reservoir[randomNumber] with stream of i
if (randomNumber >= 0 && randomNumber < k) {
reservoir[randomNumber] = stream[i];
}
}
// Print the randomly selected items
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
cout<<reservoir[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
// Example
int stream[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
int k = 5;
int n = sizeof(stream) / sizeof(stream[0]);
selectReservoir(stream, k, n);
return 0;
}11 2 8 4 6
Output may differ, as the code chooses reservoirs randomly.
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity = O(n)
Space Complexity = O(1)
where n is the total number of elements in the stream and k is the number of elements present in the reservoir array.