In Sliding Window Maximum problem we have given an array nums, for each contiguous window of size k, find the maximum element in the window.
Table of Contents
Example
Input
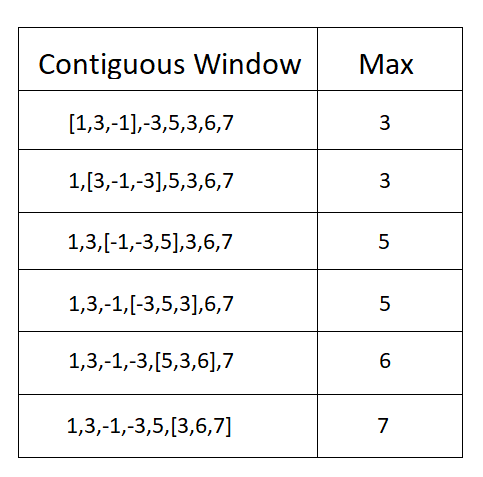
nums[] = {1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7} k = 3
Output
{3,3,5,5,6,7}
Explanation

Naive Approach for Sliding Window Maximum
For every contiguous window of size k, traverse in the window and find the maximum element.
- Run a loop from index 0 to (size of array – k – 1)
- Run another nested loop from index i to (i + k)
- Nested loop represents a window, find the maximum value inside the nested loop
- The maximum value found above is the current window’s maximum value.
- Repeat above steps to find all the maximums
Time Complexity = O(n * k)
Space Complexity = O(1)
JAVA Code
public class Naive {
private static int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int ans[] = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
// Traverse all the windows one by one
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - k + 1; i++) {
// Initialise max as -infinite
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Traverse the current window and find the maximum
for (int j = i; j < i + k; j++) {
max = Math.max(max, nums[j]);
}
// assign the current ans as maximum
ans[i] = max;
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example
int nums[] = new int[]{1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int k = 3;
int max[] = maxSlidingWindow(nums, k);
// Print the maximums
for (int i = 0; i < max.length; i++) {
System.out.print(max[i] + " ");
}
}
}3 3 5 5 6 7
C++ Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(int *nums, int k, int n) {
vector<int> ans;
// Traverse all the windows one by one
for (int i = 0; i < n - k + 1; i++) {
// Initialise max as -infinite
int max = INT_MIN;
// Traverse the current window and find the maximum
for (int j = i; j < i + k; j++) {
max = std::max(max, nums[j]);
}
// assign the current ans as maximum
ans.push_back(max);
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
// Example
int nums[] = {1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int k = 3;
vector<int> ans = maxSlidingWindow(nums, k, sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0]));
// Print the maximums
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}3 3 5 5 6 7
Optimal Approach for Sliding Window Maximum
Store the first k elements in a self balancing BST, the largest element in the BST gives the maximum element for the first window.
For the remaining subarrays, remove the first element of the previous window from self balancing BST and add the current element, the largest element again returns the maximum element in the current window.
To handle the case of repeated elements store element vs frequency in the BST.
Time Complexity = O(n log(k))
Space Complexity = O(k)
JAVA Code
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Optimal {
private static int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int ans[] = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
// Store the first k elements and their frequencies in a self balancing BST
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
map.put(nums[i], map.get(nums[i]) + 1);
} else {
map.put(nums[i], 1);
}
}
// Largest value of BST gives the first maximum
ans[0] = map.lastKey();
int index = 1;
// Traverse the remaining elements
for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
// Remove first element of previous window from BST
int freq = map.get(nums[i - k]);
if (freq == 1) {
map.remove(nums[i - k]);
} else {
map.put(nums[i - k], freq - 1);
}
// Add current element to BST
if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
map.put(nums[i], map.get(nums[i]) + 1);
} else {
map.put(nums[i], 1);
}
// Current asnwer is maximum value in BST
ans[index++] = map.lastKey();
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example
int nums[] = new int[]{1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int k = 3;
int max[] = maxSlidingWindow(nums, k);
// Print the maximums
for (int i = 0; i < max.length; i++) {
System.out.print(max[i] + " ");
}
}
}3 3 5 5 6 7
C++ Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(int *nums, int k, int n) {
vector<int> ans;
map<int, int> eleFreq;
// Store the first k elements and their frequencies in a self balancing BST
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
std::map<int, int>::iterator itr;
itr = eleFreq.find(nums[i]);
if (itr == eleFreq.end()) {
eleFreq.insert(make_pair(nums[i], 1));
} else {
itr->second++;
}
}
ans.push_back(eleFreq.rbegin()->first);
for (int i = k; i < n; i++) {
// Remove first element of previous window from BST
std::map<int, int>::iterator itr = eleFreq.find(nums[i - k]);
if (itr->second > 1) {
itr->second--;
} else {
eleFreq.erase(itr->first);
}
// Add current element to BST
itr = eleFreq.find(nums[i]);
if (itr == eleFreq.end()) {
eleFreq.insert(make_pair(nums[i], 1));
} else {
itr->second++;
}
// Current answer is maximum value in BST
ans.push_back(eleFreq.rbegin()->first);
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
// Example
int nums[] = {1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int k = 3;
vector<int> ans = maxSlidingWindow(nums, k, sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0]));
// Print the maximums
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}3 3 5 5 6 7