Table of Contents
Problem Statement
In the Degree of an array problem we have given a non-empty array of non-negative integers nums, the degree of this array is defined as the maximum frequency of any one of its elements.
Your task is to find the smallest possible length of a (contiguous) subarray of nums, that has the same degree as nums.
Input: [1, 2, 2, 3, 1] Output: 2
Approach 1: Using binary search
arr: Given array
n: size of array
Let’s say the given array has degree k, now the minimum size of subarray which has the same degree can not be less than k and not be greater than n.
So if we run a binary search on the size of the subarray and check if it is possible to have a subarray of that size with degree k, then we can get the optimal answer.
Also, the search space of this binary search should be from k to n.
Algorithm
- Find the degree of the given array( let it be k).
- Take three variable left=k, right=n and ans=n.
- Run loop till left<=right:
- Find the degree of (left+right)/2 size subarrays( let it be x).
- If x==k, then ans=min(ans,x) and right = (left+right)/2 -1.
- If x<k, then left = (left+right)/2 +1.
- Return ans.
Implementation
C++ Program for Degree of an array
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findDegree(vector<int>& v, int k){
unordered_map<int,int> m;
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
m[v[i]]++;
ans=max(ans,m[v[i]]);
}
for(int i=k;i<v.size();i++){
m[v[i-k]]--;
m[v[i]]++;
ans=max(ans,m[v[i]]);
}
return ans;
}
int findShortestSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int k=findDegree(nums,nums.size());
int l=k,r=nums.size(),m,ans=nums.size();
while(l<=r){
m=l+(r-l)/2;
int x=findDegree(nums,m);
if(x==k){
ans=m;
r=m-1;
}
else{
l=m+1;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> arr(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>arr[i];
}
cout<<"The smallest possible length of a subarray of the given array, that has same degree is: "<<findShortestSubArray(arr);
}
7 1 2 2 3 1 4 2
The smallest possible length of a subarray of the given array, that has same degree is: 6
Complexity
Time complexity: O(nlogn), we do logn search on size and in each search, we are traversing the array once.
Space complexity: O(1), no extra space required.
Approach 2: Using hashing
Let’s say we have the degree of the given array as k and the element which has maximum frequency is a, now we can conclude that the minimum size of subarray which has the same degree should start and end with a only.
Algorithm
- Take three hashmaps left, right and count.
- Run a loop on i from 0 to n:
- If arr[i] is not in left, then insert {arr[i], i} in left.
- Update {arr[i], i} in right.
- Update {arr[i], count[arr[i]]+1} in count.
- Take a variable ans=n.
- For every arr[i] whose count[arr[i]]==k:
- ans=min(right[arr[i]]-left[arr[i]]+1, ans)
- Return ans.
Example of Degree of an array
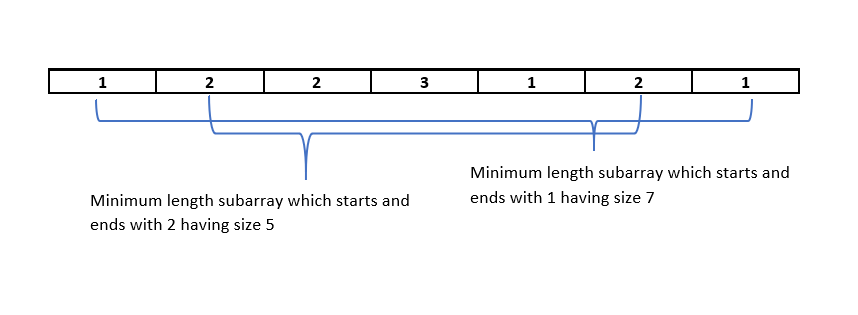
Here we have two elements that has a maximum frequency of 3, these are 1 and 2.
Now we have two choices either we can take the subarray which starts and ends with 1 or 2.
We will choose the one which has a minimum length i.e., the answer will be 5.
Implementation
C++ program for the Degree of an array
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findShortestSubArray(vector<int>& nums){
unordered_map<int,int> left, right, count;
int degree = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
int x = nums[i];
if (left.find(x)==left.end())
left.insert({x,i});
right[x]=i;
count[x]++;
degree=max(degree,count[x]);
}
int ans = nums.size();
for (auto &it:count) {
if (it.second == degree) {
ans = min(ans, right[it.first] - left[it.first] + 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
vector<int> arr={1, 2, 2, 3, 1, 4, 2};
cout<<"The smallest possible length of a subarray of the given array, that has same degree is: "<<findShortestSubArray(arr);
}
The smallest possible length of a subarray of the given array, that has same degree is: 6
JAVA program for the Degree of an array
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static int findShortestSubArray(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> left = new HashMap(),
right = new HashMap(), count = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int x = nums[i];
if (left.get(x) == null) left.put(x, i);
right.put(x, i);
count.put(x, count.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);
}
int ans = nums.length;
int degree = Collections.max(count.values());
for (int x: count.keySet()) {
if (count.get(x) == degree) {
ans = Math.min(ans, right.get(x) - left.get(x) + 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3,4,4,3,2,2,4};
System.out.println("The smallest possible length of a subarray of the given array, that has same degree is: "+findShortestSubArray(arr));
}
}
The smallest possible length of a subarray of the given array, that has same degree is: 6
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n) as we are traversing the array and map at once.
Space complexity: O(n) as we used three hashmaps.