In the maximum product subarray problem, we have given an array of integers, find the contiguous sub-array with atleast one element which has the largest product.
Table of Contents
Example
Arr=[ 0, -1, 0 ,1 ,2, -3]
Maximum product = 2
Arr=[-1, -1, -1]
Maximum product = -1
Arr=[0, -1, 0, -2, 0]
Maximum product = 0
For Array Contains Only Positive Values
Let’s solve this problem first when the array contains only non-negative integers.
In that case we can have a positive product if a sub-array does not contain a zero. Hence the answer will the maximum of products of subarrays without a zero.
Lets take an example:
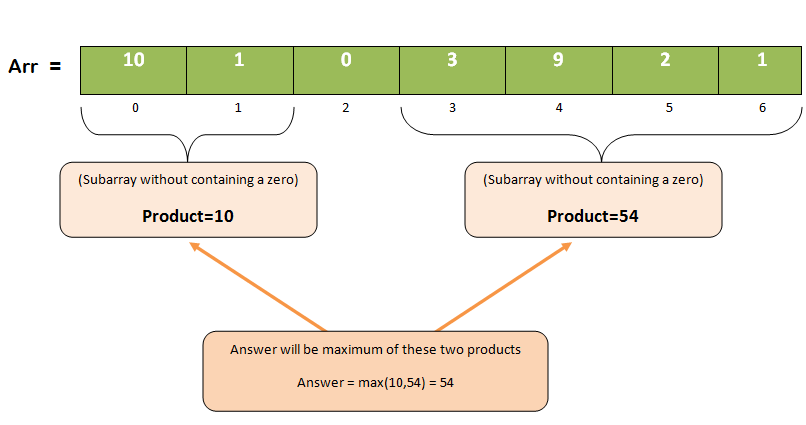
C++ Program for Maximum Product Subarray
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n=7;
int arr[]={10, 1, 0, 3, 9, 2, 1};
int ans=0,curr_product=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(arr[i]==0){
ans=max(ans,curr_product);
curr_product=0;
}
else{
curr_product=max(arr[i]*curr_product,arr[i]);
}
}
ans=max(ans,curr_product);
cout<<ans;
}
54
For Array Also Contains Negative Values
Now, what if the array also contains negative values?
In that case, we can’t ensure that the maximum product ending with (i-1)th index will multiply with arr[i] to give an optimal answer.
For example:
arr = [1 -2 -3]
Maximum product till:
- if i = 0 is 1
- i = 1 is 1
- i = 2 is 6 (-2*-3)
To overcome this issue, we can simply create two arrays:
- One to store maximum product ending at ith index.
- Other to store minimum product ending at ith index.
Now you have three options at every position in the array:
- Multiply the current element with maximum product calculated so far.
- Multiply the current element with minimum product calculated so far.
- Take current element as the starting position for maximum product sub
array.
C++ Program for Maximum Product Subarray
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxProduct(int n,int a[]) {
int mini[n]; // minimum product ending with ith index
int maxi[n]; // maximum product ending with ith index
mini[0]=a[0];
maxi[0]=a[0];
int ans = a[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[i]>0)
{
maxi[i] = max(maxi[i-1]*a[i], a[i]);
mini[i] = min(mini[i-1]*a[i], a[i]);
}
else
{
maxi[i] = max(mini[i-1]*a[i], a[i]);
mini[i] = min(maxi[i-1]*a[i], a[i]);
}
ans = max(ans, maxi[i]);
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int a[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
int ans =maxProduct(n,a);
cout<<"Maximum product of a subarray in the given array is "<<ans;
}
5 -2 7 5 -2 1
Maximum product of a subarray in the given array is 140
JAVA Program
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
static int maxProduct(int a[], int n)
{
int mini[] = new int[n]; // minimum product ending with ith index
int maxi[] = new int[n]; // maximum product ending with ith index
mini[0]=a[0];
maxi[0]=a[0];
int ans = a[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[i]>0)
{
maxi[i] = Math.max(maxi[i-1]*a[i], a[i]);
mini[i] = Math.min(mini[i-1]*a[i], a[i]);
}
else
{
maxi[i] = Math.max(mini[i-1]*a[i], a[i]);
mini[i] = Math.min(maxi[i-1]*a[i], a[i]);
}
ans = Math.max(ans, maxi[i]);
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n;
n = sc.nextInt();
int a[] = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Maximum product of a subarray in the given array is "+maxProduct(a, n));
}
}
6 4 6 -2 -9 -3 1
Maximum product of a subarray in the given array is 432
Complexity Analysis for Maximum Product Subarray
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the length of an array, as only one traversal of the array is required.
Space Complexity: O(n) because we use two arrays for storing the minimum and maximum products for each position.