Fibonacci numbers are the numbers that form the series called Fibonacci series and are represented as Fn. The first two Fibonacci numbers are 0 and 1 respectively i.e. F0=0 and F1=1. Starting from the third Fibonacci number each Fibonacci number is the sum of its previous two numbers in the series.
Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2
Table of Contents
The fibonacci series – 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13……
Given an integer n. Find the nth Fibonacci number.
Example
Input: n=5
Output: 5
Input: n=9
Output: 34
Recursive Method
Algorithm
- Initialise a variable n.
- Base case – if n is less than equal to 1 return n.
- Recursive case – return fn (n-1) + fn (n-2).
Time Complexity : O(1.6180)n (1.6180 is also known as the golden ratio)
Space Complexity : O(1)
C++ Program for Fibonacci numbers
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fn(int n){
if(n<=1)
return n;
return fn(n-1) + fn(n-2);
}
int main (){
int n=6;
cout<<fn(n);
return 0;
}Output : 8
Java Program for Fibonacci numbers
class fibNumbers{
static int fn(int n){
if(n<=1)
return n;
return fn(n-1) + fn(n-2);
}
public static void main (String args[]){
int n = 6;
System.out.println(fn(n));
}
}Output : 8
Recursive tree for the above code
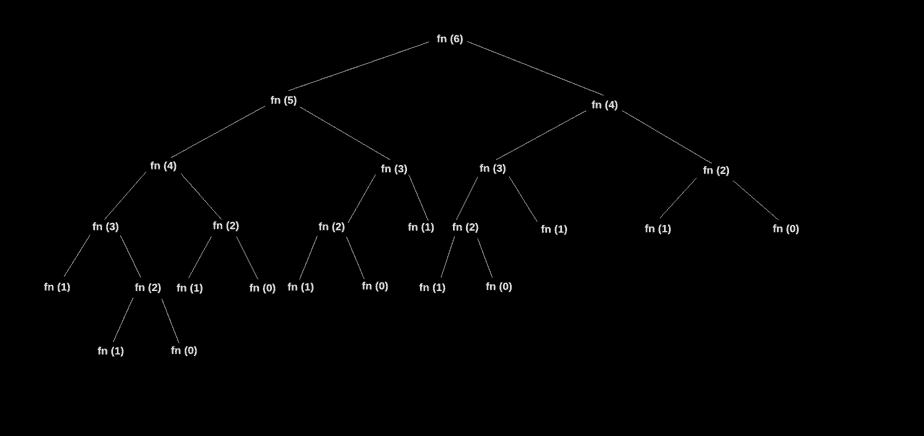
We can see from the above tree that some functions are being called more than once.
Dynamic Programming Method
Re-calculations of same functions like above can be avoided using DP.
Algorithm
- Initialize a variable n and an array f to store Fibonacci numbers.
- Initialize the first two elements of array as 0 and 1 respectively..
- Traverse all the values till n starting from 2 one by one and update the array values as the sum of the previous two elements in array.
- Return f[n].
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
C++ Program for Fibonacci numbers
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fn(int n){
int f[n+2];
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++){
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
int main (){
int n = 6;
cout<<fn(n);
return 0;
}Output : 8
Java Program for Fibonacci numbers
class fibNumbers{
static int fn(int n){
int[] f = new int[n+2];
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++){
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
public static void main (String args[]){
int n = 6;
System.out.println(fn(n));
}
}Output : 8
More space-optimized Method
Algorithm
- Initialise three variable x=0, y=1, z.
- Traverse all the values till n starting from 2 one by one and update z as the sum of x and y, x=y, and y=z.
- Return y.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
C++ Program for Fibonacci numbers
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fn(int n){
int x=0, y=1, z;
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++){
z = x + y;
x = y;
y = z;
}
return y;
}
int main (){
int n = 6;
cout<<fn(n);
return 0;
}Output : 8
Java Program for Fibonacci numbers
class fibNumbers{
static int fn(int n){
int x=0, y=1, z;
if(n == 0)
return x;
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++){
z = x + y;
x = y;
y = z;
}
return y;
}
public static void main (String args[]){
int n = 6;
System.out.println(fn(n));
}
}Output : 8
Using Direct Formula
Here we’ll directly use the formula to find the nth Fibonacci number i.e.
Fn = ( ( ( (√5 + 1) / 2) ^ n) / √5)
Time Complexity : O(1)
Space Complexity : O(1)
C++ Program
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fn(int n){
double gr = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return round(pow(gr, n) / sqrt(5));
}
int main (){
int n = 6;
cout<<fn(n);
return 0;
}Output : 8
Java Program
import java.util.*;
class fibNumbers{
static int fn(int n){
double gr = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int) Math.round(Math.pow(gr, n) / Math.sqrt(5));
}
public static void main (String args[]){
int n = 6;
System.out.println(fn(n));
}
}Output : 8