Table of Contents
Problem
In Reverse Nodes in K-Group problem we have given a linked list, Reverse the linked list in a group of k and return the modified list.
If the nodes are not multiple of k then reverse the remaining nodes. The value of k is always smaller or equal to the length of the linked list and it is always greater than 0.
Example
Input
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] K=3
Output
[ 3, 2, 1, 5, 4]
Explanation
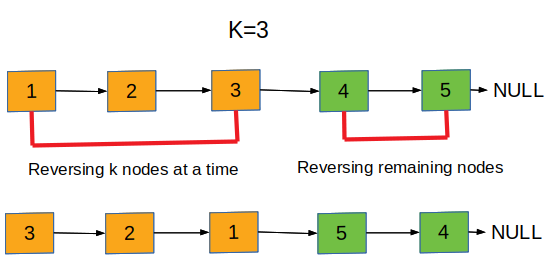
We will reverse nodes in a group of k. As a value of k =3. So we will reverse first k nodes. The nodes are not a multiple of k so we are left with 2 nodes. We will reverse the remaining two nodes this is our answer.
Approach for Reverse Nodes in K-Group
We will use a recursive approach to reverse the given linked list in a group of k.
- Reverse the first k nodes of the linked list. While reversing the first k nodes of the list maintain previous and next pointer. The previous pointer will point to the first node of the k-group nodes that we are reversing. The next pointer will point to the next node after the k-group node that we are reversing.
- After reversing the k-group nodes the recursive function will return the head of the k-group reversed node. So we will assign head->next=reverse(next, k).
- next is now pointing to the k+1th node. We will recursively call for the list starting from the current and will make the rest of the list as next to the first node.
- After all the recursive operation we will get a linked list which is formed after performing the reverse operation in a group of k nodes.
Implementation for Reverse Nodes in K-Group
C++ code for Reverse Nodes in K-Group
// CPP program to reverse a linked list
// in groups of given size
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
/* Reverses the linked list in groups
of size k and returns the pointer
to the new head node. */
Node *reverse (Node *head, int k)
{
Node* current = head;
Node* next = NULL;
Node* prev = NULL;
int count = 0;
/*reverse first k nodes of the linked list */
while (current != NULL && count < k)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
/* next is now a pointer to (k+1)th node
Recursively call for the list starting from current.
And make rest of the list as next of first node */
if (next != NULL)
head->next = reverse(next, k);
/* prev is new head of the input list */
return prev;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to push a node */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout<<node->data<<" ";
node = node->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
/* Created Linked list is 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9 */
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout<<"Given linked list \n";
printList(head);
head = reverse(head, 3);
cout<<"\nReversed Linked list \n";
printList(head);
return(0);
}Given Linked List 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Reversed list 3 2 1 6 5 4 9 8 7
Java code for Reverse Nodes in K-Group
// Java program to reverse a linked list in groups of
// given size
class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {data = d; next = null; }
}
Node reverse(Node head, int k)
{
Node current = head;
Node next = null;
Node prev = null;
int count = 0;
/* Reverse first k nodes of linked list */
while (count < k && current != null)
{
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
/* next is now a pointer to (k+1)th node
Recursively call for the list starting from current.
And make rest of the list as next of first node */
if (next != null)
head.next = reverse(next, k);
// prev is now head of input list
return prev;
}
/* Utility functions */
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
System.out.print(temp.data+" ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
/* Constructed Linked List is 1->2->3->4->5->6->
7->8->8->9->null */
llist.push(9);
llist.push(8);
llist.push(7);
llist.push(6);
llist.push(5);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
System.out.println("Given Linked List");
llist.printList();
llist.head = llist.reverse(llist.head, 3);
System.out.println("Reversed list");
llist.printList();
}
}Given Linked List 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Reversed list 3 2 1 6 5 4 9 8 7
Time complexity
O(n) as each node is traversed only once.
Space complexity
O(1) as we are using only variables to store the address of prev and next nodes.