In averages of levels in binary tree problem we have given a binary tree, print the averages of all the nodes of every level in the tree.
Table of Contents
Example
Input:
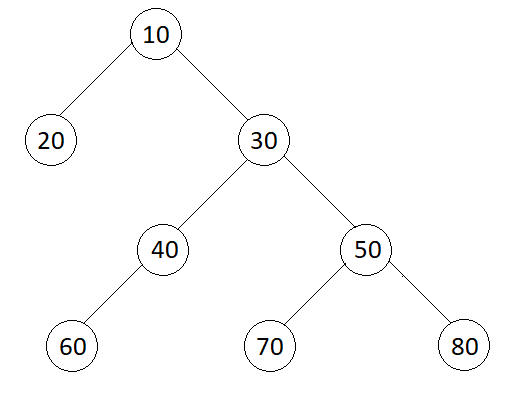
Output:
{10.0, 25.0, 45.0, 70.0}
Explanation:
First Level : Average = (10) / 1 = 10.0
Second Level : Average = (20 + 30) / 2 = 25.0
Third Level : Average = (40 + 50) / 2 = 45.0
Fourth Level : Average = (60 + 70 + 80) = 70.0
Algorithm for Averages of Levels in Binary Tree
Do a level order traversal and find the average of all the nodes in a level for each level of the tree.
- Create a queue named queue to traverse level order in the tree, push the root element to the queue.
- While the queue is not empty, repeat steps 3 to 6.
- Initialize two variables sum and total as 0, where sum represents the sum of all the nodes in a level and total represents the total number of nodes in that level. Create another queue named temp.
- While the queue is not empty, one by one removes all the elements from the queue, adds the value of the current element to the sum and increment total, and adds the children of the removed node to the queue temp.
- The average current level is (sum/total). Print it.
- Transfer all the elements from queue temp to queue ‘queue’.
Explanation for Averages of Levels in Binary Tree
Consider the tree,
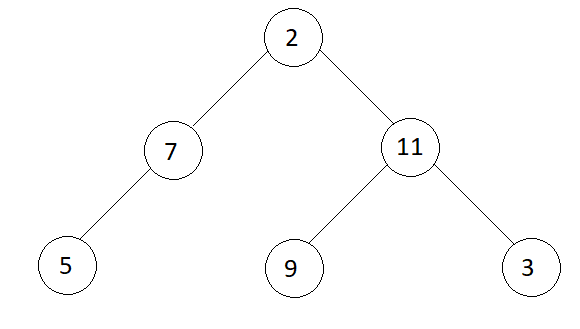
Step 1
Create a queue and push the root to it.
queue = 2
Step 2
Repeat Step 3 to 6, while the queue is not empty.
Step 3 to 6
Iteration 1
Initialize sum and total as 0, that is, sum = 0 and total = 0
Remove the elements from queue ‘queue’, increment total and add the value of current element to total. Also push the children of removed elements to queue temp.
sum = 2, total = 1, temp = 7 -> 11
Average of this level = (2 / 1) = 2.0
Transfer all the elements of queue temp to queue ‘queue’.
queue = 7-> 11
Iteration 2
Initialize sum and total as 0, that is, sum = 0 and total = 0
Remove the elements from queue ‘queue’, increment total and add the value of current element to total. Also push the children of removed elements to queue temp.
sum = (7+ 11) = 18, total = 2, temp = 5 -> 9 -> 3
Average of this level = (18 / 2) = 9.0
Transfer all the elements of queue temp to queue ‘queue’.
queue = 5 -> 9 -> 3
Iteration 3
Initialize sum and total as 0, that is, sum = 0 and total = 0
Remove the elements from queue ‘queue’, increment total and add the value of current element to total. Also push the children of removed elements to queue temp.
sum = (5 + 9 + 3) = 17, total = 3, temp = null
Average of this level = (17 / 3) = 6.7
Transfer all the elements of queue temp to queue ‘queue’.
queue = null
As the queue becomes null, so we stop here.
JAVA Code for Averages of Levels in Binary Tree
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class AveragesOfAllLevelsInBinaryTree {
// class representing node of a tree
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private static void averages(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// create a queue for level order traversal
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// add root to queue
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// initialize sum and total as 0
int sum = 0;
int total = 0;
// create another queue temp
Queue<Node> temp = new LinkedList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = queue.poll();
// add the data of current node to sum
sum += curr.data;
// increment total
total++;
// add children of curr node to queue temp
if (curr.left != null) {
temp.add(curr.left);
}
if (curr.right != null) {
temp.add(curr.right);
}
}
// average of current level is (sum / total)
double average = (double) sum / (double) total;
System.out.format("%.1f ", average);
// move all the elements of queue temp to queue 'queue'
queue = temp;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example tree
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(20);
root.right = new Node(30);
root.right.left = new Node(40);
root.right.right = new Node(50);
root.right.left.left = new Node(60);
root.right.right.left = new Node(70);
root.right.right.right = new Node(80);
averages(root);
}
}10.0 25.0 45.0 70.0
C++ Code for Averages of Levels in Binary Tree
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// class representing a tree node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
// function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int x) {
Node *node = new Node(x);
return node;
}
void averages(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
// create a queue for level order traversal
queue<Node *> q;
// add root to queue
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
// initialize sum and total as 0
int sum = 0;
int total = 0;
// create another queue temp
queue<Node *> temp;
while (!q.empty()) {
Node *curr = q.front();
q.pop();
// add the data of current node to sum
sum += curr->data;
// increment total
total++;
// add children of curr node to queue temp
if (curr->left != NULL) {
temp.push(curr->left);
}
if (curr->right != NULL) {
temp.push(curr->right);
}
}
// average of current level is (sum / total)
double average = (double) sum / (double) total;
printf("%.1f ", average);
// move all the elements of queue temp to queue q
q = temp;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
// Example tree
Node *root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(20);
root->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(40);
root->right->right = newNode(50);
root->right->left->left = newNode(60);
root->right->right->left = newNode(70);
root->right->right->right = newNode(80);
averages(root);
return 0;
}10.0 25.0 45.0 70.0
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity = O(n)
Space Complexity = O(n)
where n is the total number of nodes in the tree