Given a Binary Search Tree, write an algorithm to Convert a BST to a Binary Tree such that the sum of all greater keys is added to every key.
Table of Contents
Example
Input
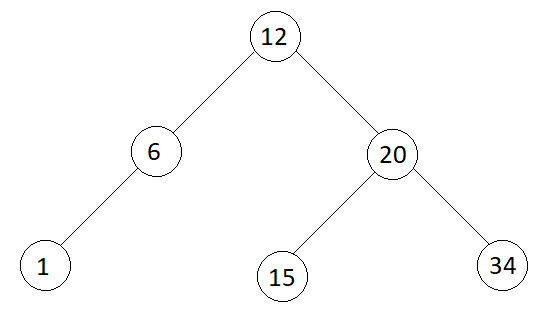
Output
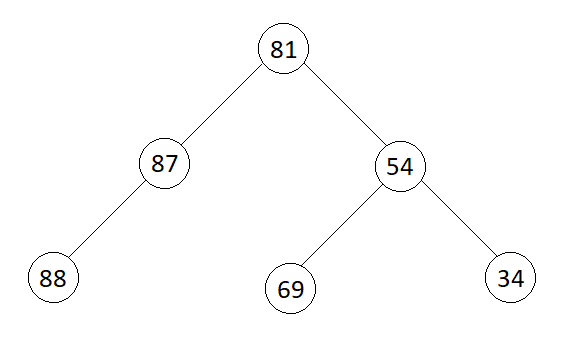
Pre-order : 81 87 88 54 69 34
Naive Approach
The idea is very simple, traverse all the nodes one by one, and for each node again traverse the whole tree and find the sum of nodes greater than it. Store the sum in an array and after computing, the sum for all the nodes, increment the nodes with their corresponding sums. This approach is applicable for any general binary tree and not particularly for BST.
- Traverse the given BST in in-order form.
- For each node, again traverse the tree in in-order form and find the sum of all the nodes that are greater than the current node.
- Store the sum in an array or a list.
- After traversing all the nodes, again traverse the tree in in-order form and increment every node with its corresponding sum in the array or list.
Time Complexity = O(n2)
Space Complexity = O(h)
where n is the number of nodes in the tree.
JAVA Code for Convert a BST to a Binary Tree
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class ConvertABSTToABinaryTreeSuchThatSumOfAllGreaterKeysIsAddedToEveryKey {
// class representing the node of a binary tree
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// function to print the pre-order traversal of a binary tree
private static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
private static int findSum(Node root, int value) {
// if root is null, sum is 0
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// initialize sum as 0
int sum = 0;
// traverse the tree and find the sum of all the values greater than value
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = queue.poll();
if (curr.data > value) {
sum += curr.data;
}
if (curr.left != null)
queue.add(curr.left);
if (curr.right != null)
queue.add(curr.right);
}
// return sum
return sum;
}
private static void formSumList(Node root, Node curr, ArrayList<Integer> sumList) {
// traverse the tree in in-order form and for each node
// calculate the sum of elements greater than it
if (curr != null) {
formSumList(root, curr.left, sumList);
// Check for all the nodes to find the sum
int sum = findSum(root, curr.data);
sumList.add(sum);
formSumList(root, curr.right, sumList);
}
}
private static void convertToGreaterSumTree(Node root, ArrayList<Integer> sumList) {
// traverse the tree in in-order form and for each node
// increment its value by sum
if (root != null) {
convertToGreaterSumTree(root.left, sumList);
// increment this value
root.data += sumList.get(0);
sumList.remove(0);
convertToGreaterSumTree(root.right, sumList);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example Tree
Node root = new Node(12);
root.left = new Node(6);
root.right = new Node(20);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(15);
root.right.right = new Node(34);
ArrayList<Integer> sumList = new ArrayList<>();
formSumList(root, root, sumList);
convertToGreaterSumTree(root, sumList);
preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
}
}81 87 88 54 69 34
C++ Code for Convert a BST to a Binary Tree
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// class representing node of a binary tree
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// function to print the preorder traversal of a binary tree
void preOrder(Node *root) {
if (root != NULL) {
cout<<root->data<<" ";
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
int findSum(Node *root, int value) {
// if root is null, sum is 0
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
// initialize sum as 0
int sum = 0;
// traverse the tree and find the sum of all the values greater than value
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node *curr = q.front();
q.pop();
if (curr->data > value) {
sum += curr->data;
}
if (curr->left != NULL) {
q.push(curr->left);
}
if (curr->right != NULL) {
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
// return sum
return sum;
}
void formSumList(Node *root, Node *curr, vector<int> &sumList) {
// traverse the tree in in-order form and for each node
// calculate the sum of elements greater than it
if (curr != NULL) {
formSumList(root, curr->left, sumList);
// Check for all the nodes to find the sum
int sum = findSum(root, curr->data);
sumList.push_back(sum);
formSumList(root, curr->right, sumList);
}
}
void convertToGreaterSumTree(Node *root, vector<int> &sumList) {
// traverse the tree in in-order form and for each node
// replace its value with the corresponding sum
if (root != NULL) {
convertToGreaterSumTree(root->left, sumList);
// change this value
root->data += sumList[0];
sumList.erase(sumList.begin());
convertToGreaterSumTree(root->right, sumList);
}
}
int main() {
// Example Tree
Node *root = new Node(12);
root->left = new Node(6);
root->right = new Node(20);
root->left->left = new Node(1);
root->right->left = new Node(15);
root->right->right = new Node(34);
vector<int> sumList;
formSumList(root, root, sumList);
convertToGreaterSumTree(root, sumList);
preOrder(root);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}81 87 88 54 69 34
Optimal Approach
The above approach can be optimized for a BST, as a BST store the data in a very specified way.
Traverse the BST in reverse in-order, that is, right->root->left form. In this way we will traverse the nodes in decreasing order and before visiting any node we will visit the nodes greater than it, hence we can find the sum of all nodes greater than a node in just one traversal and hence during this traversal increment every node by the sum of nodes greater than it.
- Initialize a variable sum as 0, it is passed by reference or defined globally.
- Traverse the BST in reverse in-order form, in this way we will get the data in decreasing order.
- For each node we traverse, increment its value by sum, and increment sum by the original value of the node(before updating).
Time Complexity = O(n)
Space Complexity = O(h)
where n is the total number of nodes in the given BST.
JAVA Code for Convert a BST to a Binary Tree
public class ConvertABSTToABinaryTreeSuchThatSumOfAllGreaterKeysIsAddedToEveryKey {
// class representing node of a binary tree
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// function to print the pre-order traversal of a binary tree
private static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
// sum defined globally and initialized as 0
private static int sum = 0;
private static void convertToGreaterSumTree(Node root) {
// traverse the tree in reverse in-order form
if (root != null) {
convertToGreaterSumTree(root.right);
// update the sum and increment the node's value
int prevValue = root.data;
root.data += sum;
sum += prevValue;
convertToGreaterSumTree(root.left);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example Tree
Node root = new Node(12);
root.left = new Node(6);
root.right = new Node(20);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(15);
root.right.right = new Node(34);
convertToGreaterSumTree(root);
preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
}
}81 87 88 54 69 34
C++ Code for Convert a BST to a Binary Tree
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// sum defined globally and initialized as 0
int sum = 0;
// class representing node of a binary tree
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// function to print the preorder traversal of a binary tree
void preOrder(Node *root) {
if (root != NULL) {
cout<<root->data<<" ";
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
void convertToGreaterSumTree(Node *root) {
// traverse the tree in reverse in-order form
if (root != NULL) {
convertToGreaterSumTree(root->right);
// update the sum and the node's value
int prevValue = root->data;
root->data += sum;
sum += prevValue;
convertToGreaterSumTree(root->left);
}
}
int main() {
// Example Tree
Node *root = new Node(12);
root->left = new Node(6);
root->right = new Node(20);
root->left->left = new Node(1);
root->right->left = new Node(15);
root->right->right = new Node(34);
convertToGreaterSumTree(root);
preOrder(root);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}81 87 88 54 69 34