Table of Contents
Duplicate Subtrees
Subtrees are said to be duplicate if they have the same node values and structure. Given a binary tree with n nodes. Find all the duplicate subtrees and return their root node.
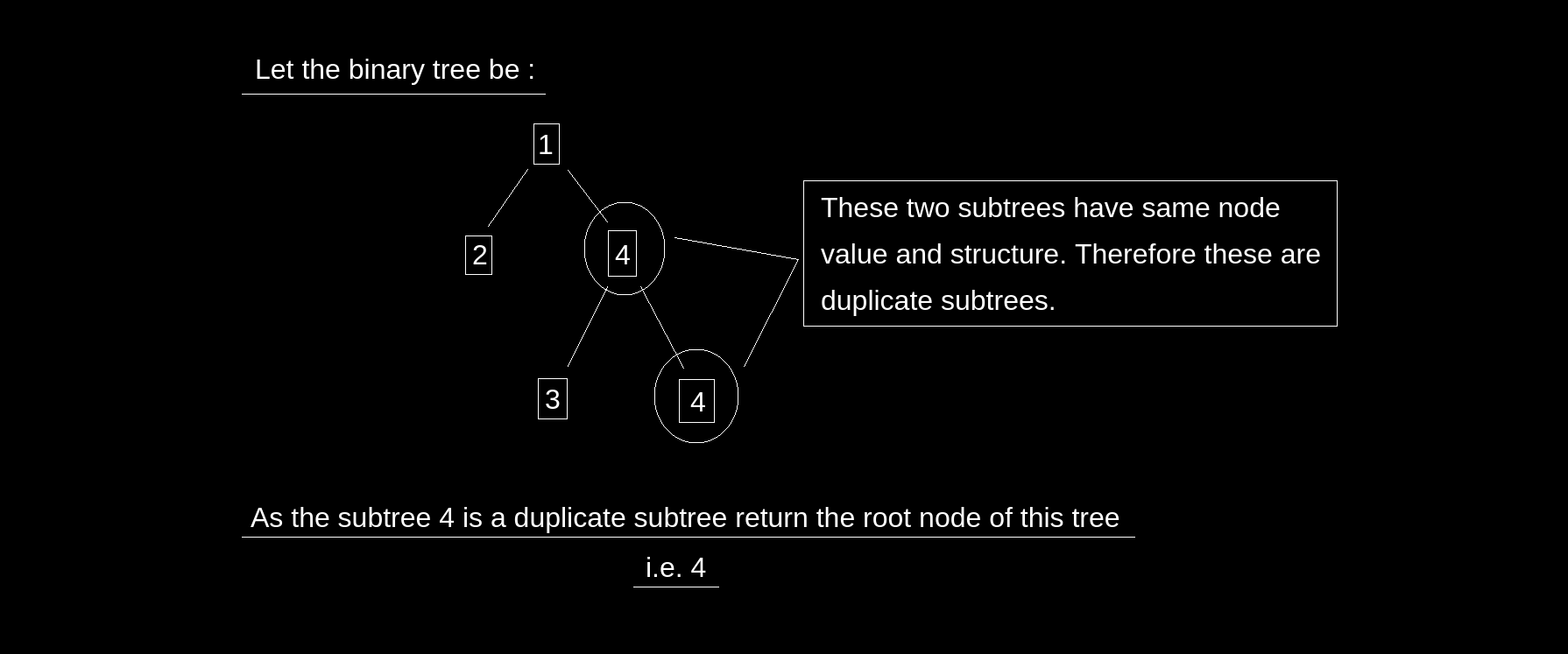
Example
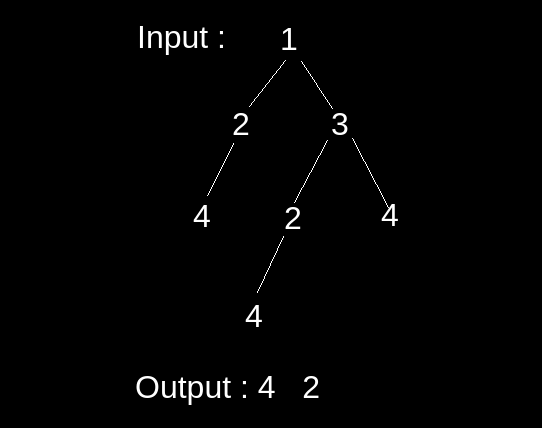
Here, the subtrees 4 and 2->4 appear more than once therefore we will return root nodes of both the subtrees i.e. 4 and 2.
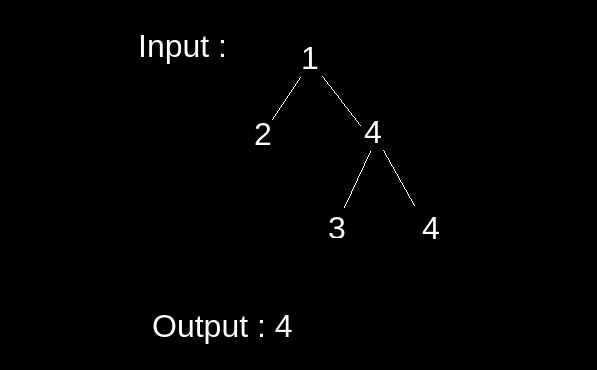
Here, the subtree 4 appears more than once therefore we will return the root node of the sub-tree i.e. 4.
Using the Hashmap Method
Algorithm for Find Duplicate Subtrees
- Initialize a binary tree.
- Create an unordered map to store string and int types.
- If the node is null return empty string.
- Store the values of nodes in a string by converting them to string type.
- Check if a string value is already present in the map i.e. map[string] is equal to one print the value of the node.
- Else increment value in the map by 1.
- Return string.
Time Complexity: O(n^2) where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree. We visit each node once but the creation may take O(n)O(n) work therefore the time complexity is O(n^2).
Space Complexity: O(n^2) is the space used for hashmap and creation of tree.
C++ Program
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int value;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
string inorder(Node* node, unordered_map<string, int>& m){
if(!node)
return "";
string str = "(";
str += inorder(node->left, m);
str += to_string(node->value);
str += inorder(node->right, m);
str += ")";
if(m[str] == 1)
cout << node->value << " ";
m[str]++;
return str;
}
void Duplicates(Node* root){
unordered_map<string, int> m;
inorder(root, m);
}
Node* newNode(int data){
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->value = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
int main(){
Node* root = NULL;
root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->right->left = newNode(2);
root->right->left->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(4);
Duplicates(root);
return 0;
}4 2
Java Program
import java.util.HashMap;
class Duplicate_subtress{
static HashMap<String, Integer> m;
static class Node{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
static String inorder(Node node){
if(node == null)
return "";
String str = "(";
str += inorder(node.left);
str += Integer.toString(node.data);
str += inorder(node.right);
str += ")";
if(m.get(str) != null && m.get(str)==1 )
System.out.print( node.data + " ");
if(m.containsKey(str))
m.put(str, m.get(str) + 1);
else
m.put(str, 1);
return str;
}
static void Duplicates(Node root){
m = new HashMap<>();
inorder(root);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Node root = null;
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
root.right.left.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(4);
Duplicates(root);
}
}4 2