Given a Binary Search Tree, write an algorithm to find the node with the minimum value in a given binary search tree.
Table of Contents
Example
Input
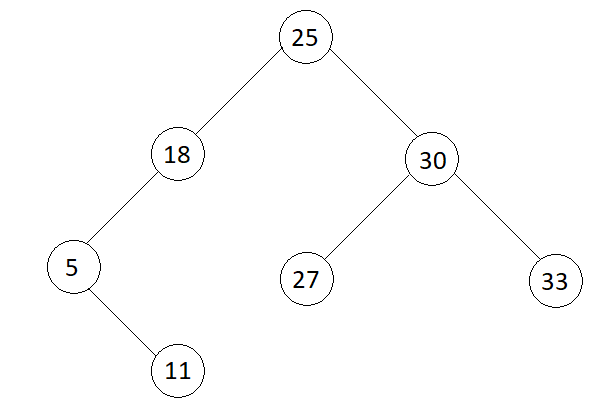
Output
5
Naive Approach
A simple approach is to do a tree traversal and find the node with the minimum value among all the nodes. This method is not only valid for a binary search tree, but also for any general tree.
Suppose we do a level-order traversal to find the minimum value.
- If the root is null, there is no minimum value, return infinity.
- Initialize the minimum value is infinite.
- Create a queue and push the root to it. Repeat step 4 while the queue is not empty.
- Remove a node from the queue, update the minimum value as a minimum of minimum value, and the current node’s value. Push the children of the current node to the queue.
- Return minimum value.
Time Complexity = O(n)
Space Complexity = O(n)
where n is the total number of nodes in the given BST.
JAVA Code for Find the node with a minimum value
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class FindTheNodeWithMinimumValueInABinarySearchTree {
// class representing node of a binary tree
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private static int minValue(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// initialize min as infinite
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// do a level order traversal of the tree
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = queue.poll();
// update minimum
min = Math.min(min, curr.data);
// add children of curr to queue
if (curr.left != null)
queue.add(curr.left);
if (curr.right != null)
queue.add(curr.right);
}
return min;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example Tree
Node root = new Node(25);
root.left = new Node(18);
root.right = new Node(30);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(27);
root.right.right = new Node(33);
root.left.left.right = new Node(11);
System.out.println(minValue(root));
}
}5
C++ Code for Find the node with a minimum value
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// class representing node of a binary tree
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
int minValue(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return INT_MAX;
}
// initialize min as infinite
int min = INT_MAX;
// do a level order traversal of the tree
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node *curr = q.front();
q.pop();
// update minimum
min = std::min(min, curr->data);
// add children of curr to queue
if (curr->left != NULL)
q.push(curr->left);
if (curr->right != NULL)
q.push(curr->right);
}
return min;
}
int main() {
// Example Tree
Node *root = new Node(25);
root->left = new Node(18);
root->right = new Node(30);
root->left->left = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(27);
root->right->right = new Node(33);
root->left->left->right = new Node(11);
cout<<minValue(root)<<endl;
return 0;
}5
Optimal Approach
The given binary tree is a Binary Search Tree. Binary Search Tree has a special property that all the nodes less than a node are present in its left sub-tree and all the nodes greater than this node are present in the right sub-tree.
Using this property, we can say that the node with minimum value is present as the leftmost node in the tree.
- If the root is null, there is no minimum, return infinite.
- Else initialize temp as root. Repeat step 3 while temp’s left node is not null.
- Make temp equals temp’s left.
- At this point, temp is pointing to the leftmost node, that is, the node with minimum value. Return temp’s data.
Time Complexity = O(h)
Space Complexity = O(1)
where h is the height of given binary search tree, in worst case h equals to n(number of nodes).
JAVA Code for Find the node with a minimum value
public class FindTheNodeWithMinimumValueInABinarySearchTree {
// class representing node of a binary tree
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private static int minValue(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// initialize temp as root
Node temp = root;
// go to the left most node
while (temp.left != null) {
temp = temp.left;
}
// return value of left most node
return temp.data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example Tree
Node root = new Node(25);
root.left = new Node(18);
root.right = new Node(30);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(27);
root.right.right = new Node(33);
root.left.left.right = new Node(11);
System.out.println(minValue(root));
}
}5
C++ Code for Find the node with a minimum value
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// class representing node of a binary tree
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
int minValue(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return INT_MAX;
}
// initialize temp as root
Node *temp = root;
// go to the left most node
while (temp->left != NULL) {
temp = temp->left;
}
// return value of left most node
return temp->data;
}
int main() {
// Example Tree
Node *root = new Node(25);
root->left = new Node(18);
root->right = new Node(30);
root->left->left = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(27);
root->right->right = new Node(33);
root->left->left->right = new Node(11);
cout<<minValue(root)<<endl;
return 0;
}5