In this problem, we have given an array a[ ] of size n. Create the maximum binary tree from the array and return its root node.
It is made from the array using the following steps :
- The root node of the tree should be the maximum value in the given array.
- The left subtree is the maximum tree made using the values which occur before the maximum value in the array.
- The right subtree is the maximum tree made using the values which occur after the maximum value in the array.
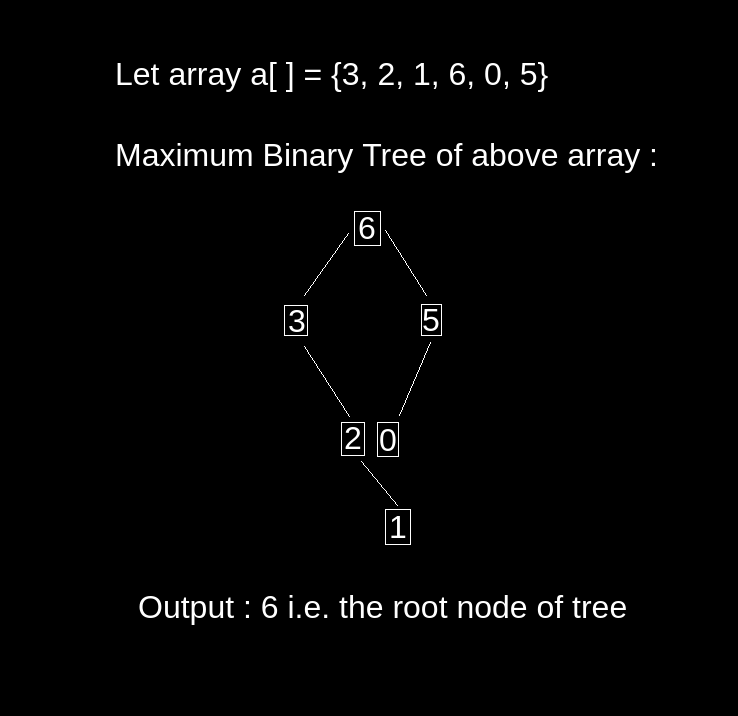
Table of Contents
Example of Maximum Binary Tree
Input : a[ ] = {3, 2, 1, 6, 0, 5}
Output : 6
Input : a[ ] = {3, 1, 7, 4}
Output : 7
Recursive Method for Maximum Binary Tree
Algorithm
This is an algorithm of the maximum binary tree.
- Initialize an array of size n.
- Create the function to create a binary tree that accepts the array, starting index, and last index as parameters.
- If starting and ending index are same return NULL.
- Else find the maximum element in array for root node.
- For left sub-tree recursively call the function for elements which occur before the maximum element in the array.
- Similarly for right sub-tree recursively call the function for elements that occur after the maximum element in the array.
- Return the root node.
C++ Program
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode{
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data){
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
class Max{
public:
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(int nums[], int n){
return construct(nums, 0, n);
}
TreeNode* construct(int nums[], int l, int r){
if (l == r)
return NULL;
int max_i = max(nums, l, r);
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[max_i]);
root->left = construct(nums, l, max_i);
root->right = construct(nums, max_i + 1, r);
return root;
}
int max(int nums[], int l, int r) {
int max_i = l;
for (int i = l; i < r; i++) {
if (nums[max_i] < nums[i])
max_i = i;
}
return max_i;
}
};
int main(){
Max m;
int a[] = {3, 2, 1, 6, 0, 5};
int n = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
TreeNode* root = m.constructMaximumBinaryTree(a, n);
cout<<root->val;
return 0;
}6
Java Program
class TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x){
val = x;
}
}
class Max{
static TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums){
return construct(nums, 0, nums.length);
}
static TreeNode construct(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (l == r)
return null;
int max_i = max(nums, l, r);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[max_i]);
root.left = construct(nums, l, max_i);
root.right = construct(nums, max_i + 1, r);
return root;
}
static int max(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
int max_i = l;
for (int i = l; i < r; i++) {
if (nums[max_i] < nums[i])
max_i = i;
}
return max_i;
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
int[] a = {3, 2, 1, 6, 0, 5};
TreeNode root = constructMaximumBinaryTree(a);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}
}6
Complexity Analysis for Maximum Binary Tree
Time Complexity
O(n2) (construct function is called n times. We traverse all the n nodes to find the maximum element at each level. In the worst case, depth of tree can be up to n which results in complexity to be n2)
Space Complexity
O(n) because in the worst case the size of the string can grow up to n where n is the size of the given input string.