This tutorial will help you understand how to append a string in Java using different methods and string concatenation with examples.
String concatenation means appending two or more strings together to form a single string. The term append denotes to include an extra string to the existing string variable.
For example, a string contains the text “Welcome”. You have another string “Java”. When we want both strings together as a single string, we can append or concatenate both the strings to a single string.
Exanple: String1 = "Welcome" String2 = "Java" Output: "Welcome Java"
Table of Contents
Different ways to append a string
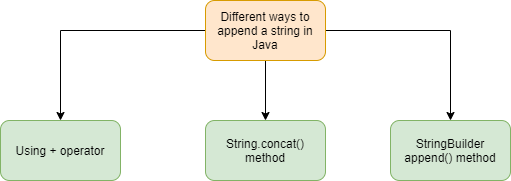
There are different ways to concatenate or append a string in Java:
- Using + operator
- concat() method
- append() method
Using + operator
This is the simplest way to append a string. We can use the ‘+’ operator to concatenate two or more strings. The below example shows you how to append a string in Java using the + operator.
public class StringConcat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Hello,";
String s2 = "how are you";
String s3 = s1 + s2;
System.out.println("String 1: " + s1);
System.out.println("String 2: " + s2);
System.out.println("Concatenated string: " + s3);
}
}
String 1: Hello, String 2: how are you Concatenated string: Hello,how are you
This method internally uses the append() method of the StringBuilder class. We will see this in detail towards the end.
String s = (new StringBuilder()).append("Hello,").append("how are you").toString();We can append even primitive values along with string values using the ‘+’ operator.
System.out.println("Welcome Java" + 2020);Welcome Java2020
String.concat() method
Another way is to use the concat() method of the String class to append a string in Java. The below example shows you how to append a string in Java using the concat() method.
public class StringConcat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Hello,";
String s2 = "how are you";
String s3 = s1.concat(s2);
System.out.println("String 1: " + s1);
System.out.println("String 2: " + s2);
System.out.println("Concatenated string: " + s3);
}
}
String 1: Hello, String 2: how are you Concatenated string: Hello,how are you
StringBuilder append() method
The StringBuilder class has an append() method that accepts different types of parameters as in the below table.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| append(boolean b) | Appends a boolean parameter. Either true or false |
| append(char c) | Appends a single character |
| append(char[] ch) | Appends an array of characters |
| append(CharSequence s) | Appends a character sequence |
| append(double d) | Appends a double value parameter |
| append(float f) | Appends a float value parameter |
| append(int i) | Appends an integer value parameter |
| append(long l) | Appends a long value parameter |
| append(Object o) | Appends an object representation as parameter |
| append(String s) | Appends a string value parameter |
| append(StringBuffer sb) | Appends the StringBuffer as parameter |
| append(char[] ch, int offset, int len) | Appends the subarray of the character array starting from the specified offset for the required length |
| append(CharSequence cs, int start, int end) | Appends the specified character sequence based on the specified start and end parameter |
append(boolean b)
The below code appends a boolean value to the current string in Java.
public class StringAppend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boolean b = true;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
sb.append(b);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Javatrue
append(char c)
The below code appends a character to the input string.
public class StringAppend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c = 'A';
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
sb.append(c);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
JavaA
append(char[] ch)
The below code appends an array of characters to the current string.
public class StringAppend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] ch = {'J','A','V','A'};
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
sb.append(ch);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
JavaJAVA
append(char[] ch, int offset, int len)
The below code appends a specific character array length to the current string.
public class StringAppend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] ch = {'L','A','N','G','U','A','G','E'};
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
sb.append(ch, 0, 4);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
JavaLANG
append(double d)
The below code appends a double value to the current string.
public class StringAppend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d = 54.56;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
sb.append(d);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Java54.56
append(float f)
The below code appends a float value to the current string.
public class StringAppend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float f = 224.65f;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
sb.append(f);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Java224.65
append(int i)
Below is a program to append an integer value to the current string.
public class StringAppend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 100;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
sb.append(i);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Java100
append(String s)
The below code shows how to append a string to the input string in Java.
public class StringAppend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "Programming";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
sb.append(s);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
JavaProgramming