Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Contiguous Array LeetCode Solution – Given a binary array nums, return the maximum length of a contiguous subarray with an equal number of 0 and 1.
Input: nums = [0,1] Output: 2 Explanation: [0, 1] is the longest contiguous subarray with an equal number of 0 and 1.
Explanation
Now what we will do is, convert all the “0” to “-1” in the example, so we get something like:- [1, -1, -1, 1, -1, 1, 1]. If you see this, the problem is somewhat like returning the longest subarray length whose sum is “ZERO”
Because equal no. of 1’s & 0’s, so we had replaced 0 with -1. So, that means the same as well there will be equal no. of 1 & -1.
That’s the thing if in any subarray there is an equal no. of 1 & -1 their sum will be 0. We have to return that subarray length, whose sum is 0. And we have to find the longest subarray.
Let’s just see how we will solve this problem using HashMap.
We will use the help of cumulative sum, which means what is the sum from the 0th index to the 6th index.
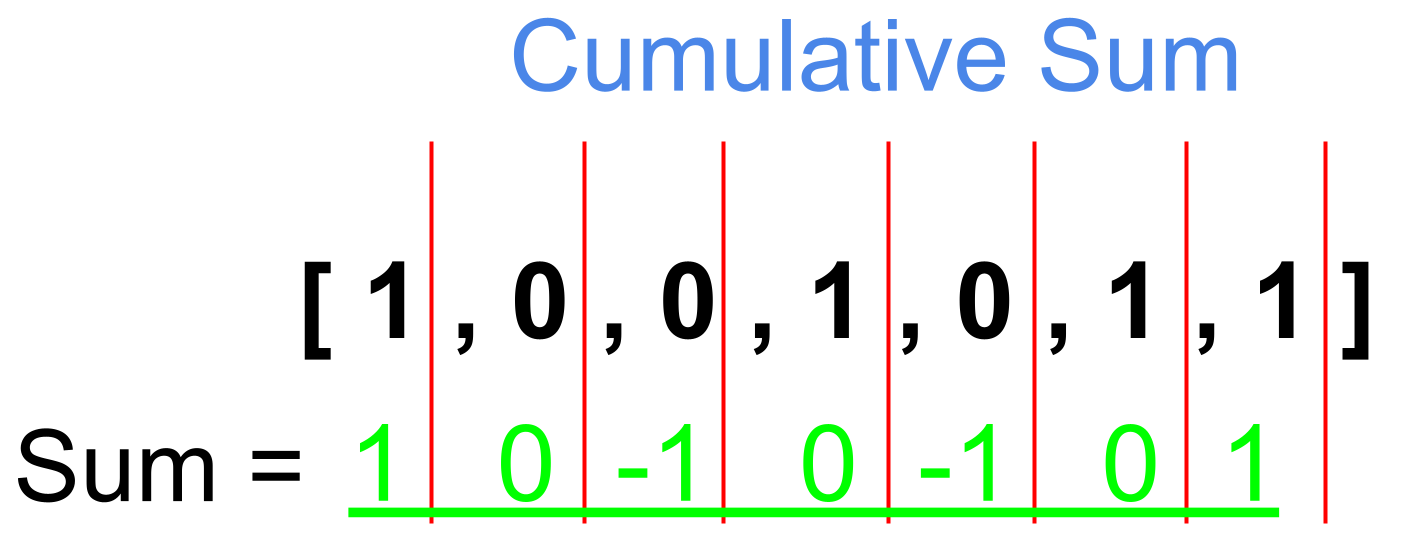
Using this cumulative sum, we will solve this problem in O(N).
In our hashMap, we will have key & value.
- Initially let’s assume our gain is 0 & we are standing at an index of -1
- We move forward and get a gain of 1. And in our hashmap for reference, we put key 0 -> -1 value. Why this, because initially we are at no-where & our gain is 0 & our final answer is 0 at index -1.
Just hold on you will understand - At index 0 we get 1. And if we look in our HashMap, do we have key-value pair for 1? No, then we will create key 1 -> 0 value pair in hashmap.
Our cumulative sum is 0 + 1 = 1 - Now moving to index 1 we get a gain of -1 & loss of 1. Now our gain becomes 0 because
Our cumulative sum is 1 + (-1) = 0so what does it represent is in the Journey from -1th index to 1st index, we found a subarray i.e. [1, 0]. The subarray has equal no. of 0s & 1s. Now to calculate its length we started the journey from index -1 to index 1.Thus, 1 - (-1) = 2. - So, to trace this 2 we put our initial key 0 & value -1. Now hope you got an idea a bit, anyways. We will update it’s
current & final-ans with 2 - Now moving further & at index 2 we got a gain of -1 as
Our cumulative sum is 0 + (-1) = -1And if we look at hashmap -1 is not present we will make key-value pair of -1 -> 2. - Now moving further & at index 3 we get 1 & our gain becomes 0 as
Our cumulative sum is 1 + (-1) = 0. And if we look at the hashmap 0 is present with a value of -1. Now to calculate its length we started the journey from index 2 to index 3.Thus, 3 - (-1) = 4, then update ourcurrent & final-ans with 4And Till now we have found a subarray of size 4 - Now moving further & at index 4 we got a gain of -1 as
Our cumulative sum is 0 + (-1) = -1. And if we look at the hashmap -1 is present at the key-value pair of -1 -> 2. We got one more subarray in the Journey from the 3rd index to the 4th index. But, if we calculate its length, it will be4 - (+2) = 2& update our current with 2 and compare with final-ans i.e. 4 which is less, we will not consider it. - Now moving further & at index 5 we get 1 & our gain becomes 0 as
Our cumulative sum is 1 + (-1) = 0. We got one more subarray in the Journey from the 4th index to the 5th index. calculate its length, it will be5 - (-1) = 6, then update ourcurrent & final-ans with 6. - Finally moving at index 6th, we get 1 & our gain becomes 1 as
Our cumulative sum is 0 + 1 = 1. And if we look at the hashmap 1 is present at the key-value pair of 1 -> 0. We got one more subarray in the Journey from the 5th index to the 6th index. As we calculate its length, it will be6 - (0) = 6& compare with current & final-ans i.e. 6 which is equal to it. - In the end, we get 2 big subarrays having equal no. of 1s & 0s
- [1,0,0,1,0,1]
- [0,0,1,0,1,1]
Code
Java Code for Contiguous Subarray
class Solution {
public int findMaxLength(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) { // Base Case
return 0;
}
// Converting all 0 to -1
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] == 0) nums[i] = -1;
}
int sum = 0; // current
int max = 0; // final-ans
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(0, -1); // put reference in the starting of 0 & -1, as i have tell you in the starting
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
sum += nums[i]; // cumulative sum
if(map.containsKey(sum)){ // if cumulative sum key :- 0, -1, 1 already present
int last = map.get(sum); // we get it's value
max = Math.max(max, i - last); // and update max
}
else{ // if it's not present then create it's key-value pair
map.put(sum, i);
}
}
return max; // finally return it
}
}C++ Code for Contiguous Subarray
class Solution {
public:
int findMaxLength(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int,int> mp; //map of <gain,index> form
mp[0]=-1; //add starting index with default gain of 0 at -1
//change all zeros to -1
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
nums[i]==0?nums[i]=-1:nums[i]=1;
}
int sum=0,res=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
//cumulative sum
sum+=nums[i];
//check if value already exists in the map
if(mp.find(sum)!=mp.end()){
//finding the length of possible subarray and comparing with the max result
res=max(res,i-mp[sum]);
}
else{
//adding value to our map
mp[sum]=i;
}
}
return res;
}
};Python Code for Contiguous Subarray
class Solution(object):
def findMaxLength(self, nums):
count = 0
max_length=0
table = {0: 0}
for index, num in enumerate(nums, 1):
if num == 0:
count -= 1
else:
count += 1
if count in table:
max_length = max(max_length, index - table[count])
else:
table[count] = index
return max_lengthComplexity Analysis for Contiguous Array LeetCode Solution
Time Complexity
O(N)
Space Complexity
O(N)