Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Find K Closest Elements LeetCode Solution – Given a sorted integer array arr, two integers k and x, return the k closest integers to x in the array. The result should also be sorted in ascending order.
An integer a is closer to x than an integer b if:
|a - x| < |b - x|, or|a - x| == |b - x|anda < b
Example 1:
Input:
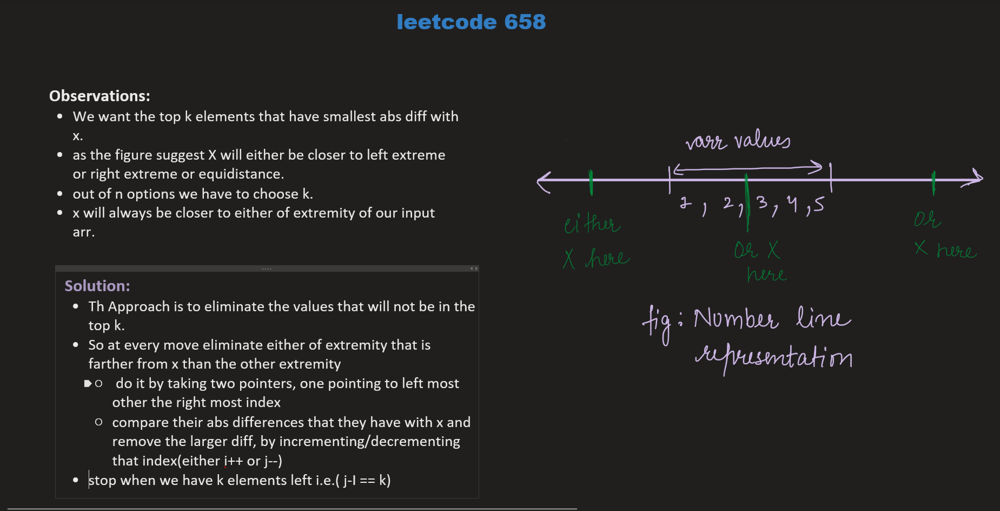
arr = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 4, x = 3
Output:
[1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
Input:
arr = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 4, x = -1
Output:
[1,2,3,4]
Constraints:
1 <= k <= arr.length1 <= arr.length <= 104arris sorted in ascending order.-104<= arr[i], x <= 104
Approach
Idea:
- in this problem, we have to find the k nearest elements to an element x.
- first, we sort the array.
- then we find the lower bound of ele x in the array.
- lower bound returns an iterator pointing to the first element in the range [first, last) which has a value not less than val.
- we can say that arr[idx]>=x and also arr[idx-1]<x where idx is index of lower bound.
- now we apply 2 pointer approach to fit k elements inside our window
- we take two pointers where i=idx-1 and j=idx (here idx is an index of lower bound)
- now if i is close to x then we take ith ele and do i–
- otherwise, we take jth element and do j++
Code:
Find K Closest Elements C++ Solution:
vector<int> findClosestElements(vector<int>& arr, int k, int x) {
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end());
vector<int> ans;
auto lowerBound=lower_bound(arr.begin(),arr.end(),x);
int idx=lowerBound-arr.begin();
int i=idx-1,j=idx;
while(i>=0 && j<arr.size())
{
int diff1=x-arr[i],diff2=arr[j]-x;
if(diff1<=diff2)
{
ans.push_back(arr[i]);
i--;
}
else
{
ans.push_back(arr[j]);
j++;
}
if(ans.size()==k){
break;}
}
if(i>=0)
{
while(ans.size()!=k)
{
ans.push_back(arr[i]);
i--;
}
}
if(j<arr.size())
{
while(ans.size()!=k)
{
ans.push_back(arr[j]);
j++;
}
}
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());
return ans;
}Find K Closest Elements Java Solution:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findClosestElements(int[] arr, int k, int x) {
int n = arr.length;
int l = 0, r = n - 1, lowerBoundIdx = n;
while(l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
if(arr[m] <x) {
l = m + 1;
}
else {
lowerBoundIdx = m;
r = m - 1;
}
}
int i=lowerBoundIdx-1,j=lowerBoundIdx;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while(i>=0 && j<n)
{
int diff1=x-arr[i],diff2=arr[j]-x;
if(diff1<=diff2)
{
ans.add(arr[i]);
i--;
}
else
{
ans.add(arr[j]);
j++;
}
if(ans.size()==k){
break;}
}
if(i>=0)
{
while(ans.size()!=k)
{
ans.add(arr[i]);
i--;
}
}
if(j<n)
{
while(ans.size()!=k)
{
ans.add(arr[j]);
j++;
}
}
Collections.sort(ans);
return ans;
}
}Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity:
The Time Complexity of the above solution is O(logn).
Space Complexity:
The Space Complexity of the above solution is O(1) since we are using constant extra space.