Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Minimum Moves to Equal Array Elements LeetCode Solution – Given an integer array nums of size n, return the minimum number of moves required to make all array elements equal.
In one move, you can increment n - 1 elements of the array by 1.
Example 1:
Input 1:
nums = [1, 2, 3]
Output:
3
Explanation:
Only 3 moves are needed. In each move, we can increment (n-1) ~ (3-1) = 2 elements.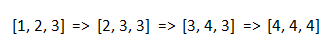
Approach:
- To make elements equal, we need to make the difference between the min element and the max element in the array equal to 0.
- In each move, we can increase all
n-1elements by one. We should never choose to increase our max element, so we choose to increase other elements except for our current max element, which means we decrease the difference between the max element and the min element by one. - So in each move, we need to decrease the current max element by one to util every element become a min element.
- The problem becomes counting the difference between other elements with our min element in the array.
- For example:
nums = [1, 2, 3]- Step 1, increase other elements except for a maximum element
3,nums = [2, 3, 3] - Step 2, increase other elements except for a maximum element,
nums = [3, 4, 3]. - Step 3, increase other elements except for a maximum element,
nums = [4, 4, 4].
- Step 1, increase other elements except for a maximum element
Code for Minimum Moves to Equal Array Elements
Java Code
class Solution {
public int minMoves(int[] nums) {
int min = nums[0];
for (int x : nums) min = Math.min(min, x);
int ans = 0;
for (int x : nums)
ans += x - min;
return ans;
}
}Python Code
class Solution:
def minMoves(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
mi = min(nums)
ans = 0
for x in nums:
ans += x - mi
return ans
Complexity Analysis for Minimum Moves to Equal Array Elements LeetCode Solution
Time Complexity
O(N), where N <= 10^5 is the length of the input array.
Space Complexity
O(1), as we are using constant space.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Array_data_structure