Table of Contents
Problem Statement
The problem Same Tree says Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
Example:
Test Case 1:
Input:
p = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
q = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
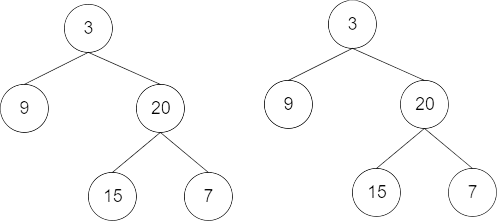
Output:
true
Test Case 2:
Input:
p = [10, 20]
q = [10, null, 20]

Output:
false
Explanation:
i) For the first test case, both the trees have the same structure and values. So the output is true.
ii) In the second test case, although both the trees have the same values but structure of both the trees is different. So the output is false.
Approach
Idea:
We can divide both the trees into smaller, smaller sub-trees recursively and check if they are the same. While dividing the trees, we can check if the left subtree of one parent tree is the same as the left subtree of the other parent tree. We can do the same for the right subtrees also. If all the subtrees are equal, the output will be true otherwise the output will be false.
Note: We might feel, if the traversal of both the trees is the same, the trees will be the same but for some trees (for ex: test case 2) the traversal value will be the same but the trees are not the same.
Code
Java Program for Same Tree LeetCode Solution
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null&&q==null)
return true;
if(p==null||q==null||p.val!=q.val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
}C++ Program for Same Tree LeetCode Solution
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL||q==NULL||p->val!=q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
};Complexity Analysis for Same Tree LeetCode Solution
Time Complexity
Here we visit each node exactly once. So time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the tree.
Space Complexity
In the case of a balanced tree, the space complexity will be O(logn). In the case of an unbalanced tree, the space complexity will be O(n).
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_tree