Table of Contents
Problem Statement
The problem “Check if a queue can be sorted into another queue using a stack” states that you are given a queue containing n elements, the elements in the queue are a permutation of numbers 1 to n. Check if this queue can be arranged in increasing order in any other queue with the help of a stack.
Example
queue = 8 -> 7 -> 5 -> 6 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
false
queue = 4 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3
true
Algorithm to check Check if a queue can be sorted into another queue using a stack
Initially, the second queue and stack are empty and the elements are present in some random order in the first queue.
The goal is to sort and place the elements in the second queue with the use of a stack.
Note that we can insert an element in queue 2 from either queue 1 or the stack. That is either the front of queue 1 is enqueued to queue 2 or the top of the stack is enqueued.
Also, we have to insert 1 as the first element in the queue 2, 2 as the second element and so on.
1. Initialize a variable next as 1, this indicates that this variable should be inserted into queue 2. 2. If the front of the queue 1 or top of the stack is equals to next, remove the front or the top as required and move it to the queue 2, and increment next by 1. 3. Else if none of them is next, remove the front of queue 1 and push it to the stack and if the front of queue 1 is greater than top of stack, return false. 4. If all the elements are present in the queue 2, that is, both queue 1 and stack are empty, then it is possible to sort the queue, return true.
Explanation
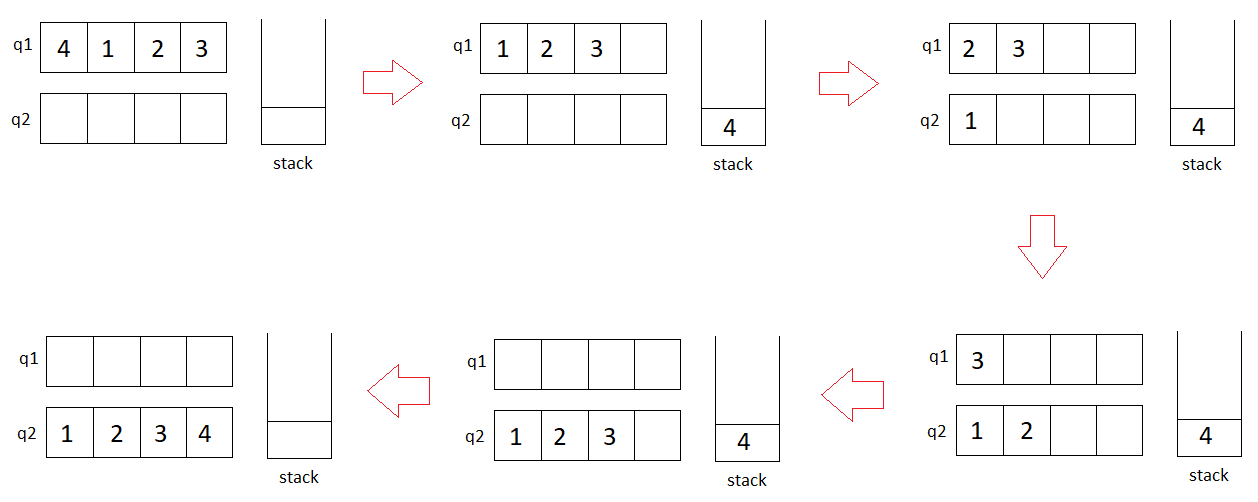
Consider the second example,
queue = 4 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3
Initially,
q1 = 4 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3
q2 = null
stack = null
Code
Java code to Check if a queue can be sorted into another queue using a stack
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
class CheckIfAQueueCanBeSortedIntoAnotherQueueUsingAStack {
private static boolean checkIfPossible(Queue<Integer> q) {
// Initialize next as 1
int next = 1;
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>();
while (!q.isEmpty() || !st.isEmpty()) {
// if front of queue is next, remove it and increment next
if (!q.isEmpty() && q.peek() == next) {
q.poll();
next++;
}
// if top of stack is next, remove it and increment next
else if (!st.isEmpty() && st.peek() == next) {
st.pop();
next++;
} else {
// if q is empty return false
if (q.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
// remove front of queue and push it to top of stack
else {
int front = q.poll();
if (st.isEmpty()) {
st.push(front);
} else {
// if front of queue is greater than top of stack, return false
if (front > st.peek()) {
return false;
} else {
st.push(front);
}
}
}
}
}
// all the elements can be sorted, return true
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q1.add(8);
q1.add(7);
q1.add(5);
q1.add(6);
q1.add(4);
q1.add(3);
q1.add(2);
q1.add(1);
System.out.println(checkIfPossible(q1));
// Example 2
Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<>();
q2.add(4);
q2.add(1);
q2.add(2);
q2.add(3);
System.out.println(checkIfPossible(q2));
}
}false true
C++ code to Check if a queue can be sorted into another queue using a stack
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool checkIfPossible(queue<int> &q) {
stack<int> st;
// Initialize a variable next as 1
int next = 1;
while (!q.empty() || !st.empty()) {
// if front of queue is next, remove it and increment next
if (!q.empty() && q.front() == next) {
q.pop();
next++;
}
// if top of stack is next, remove it and increment next
else if (!st.empty() && st.top() == next) {
st.pop();
next++;
} else {
// if q is empty return false
if (q.empty()) {
return false;
}
// remove front of queue and push it to top of stack
else {
int front = q.front();
q.pop();
if (st.empty()) {
st.push(front);
} else {
// if front of queue is greater than top of stack, return false
if (front > st.top()) {
return false;
} else {
st.push(front);
}
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
// Example 1
queue<int> q1;
q1.push(8);
q1.push(7);
q1.push(5);
q1.push(6);
q1.push(4);
q1.push(3);
q1.push(2);
q1.push(1);
if (checkIfPossible(q1)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
// Example 2
queue<int> q2;
q2.push(4);
q2.push(1);
q2.push(2);
q2.push(3);
if (checkIfPossible(q2)) {
cout<<"true"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}false true
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
O(N), as we traversed through whole of the input. The algorithm takes linear time complexity.
Space Complexity
O(N), as we have stored the elements into queue or stack. The algorithm takes linear space.