Table of Contents
Problem Statement
N-Queens LeetCode Solution – The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on a n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle. You may return the answer in any order.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens’ placement, where 'Q' and '.' both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
Example
Test Case 1:
Input:
n = 4
Output:
[[“.Q..”,”…Q”,”Q…”,”..Q.”],[“..Q.”,”Q…”,”…Q”,”.Q..”]]
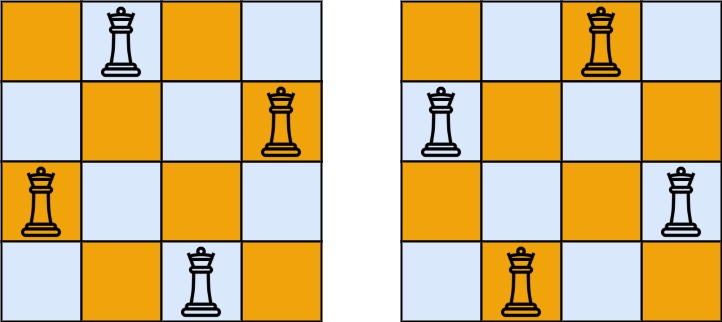
Explanation:
There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above.
Approach:
1. Each row contains 1 queen
2. For each row, keep track of the valid columns for queen placement. # (NOTE in a clever way)
3. DFS, start from the first row, try each valid column and backtrack if necessary.
NOTE that we can encode left/right diagonals as indexes in the following way
For any (r, c),
its top-left to the bottom-right diagonal index is r – c, ∈ (-n, n)
its bottom-left to the top-right diagonal index is r + c, ∈ [0, 2n)
Each (r, c) takes the r-th row, c-th column, and the two diagonal indexes encoded above.
Thus we can use 4 sets to indicate whether those row/col/diagonal have been taken, if yes, a queen cannot be placed at (r, c).
Moreover, if we search via dfs, proceeding row by row, we can avoid keeping # the row set, getting away with 3 sets only (column, and 2 diagonals).
Each set indicates whether the column/diagonal with the specified index has been taken.
Code for N-Queens
Java Program
class Solution {
private Set<Integer> col = new HashSet<Integer>();
private Set<Integer> diag1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
private Set<Integer> diag2 = new HashSet<Integer>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
dfs(res,new ArrayList<String>(), 0, n);
return res;
}
private void dfs(List<List<String>> res, List<String> list, int row, int n){
if (row == n){
res.add(new ArrayList<String>(list));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (col.contains(i) || diag1.contains(row + i) || diag2.contains(row - i)) continue;
char[] charArray = new char[n];
Arrays.fill(charArray, '.');
charArray[i] = 'Q';
String rowString = new String(charArray);
list.add(rowString);
col.add(i);
diag1.add(row + i);
diag2.add(row - i);
dfs(res, list, row + 1, n);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
col.remove(i);
diag1.remove(row + i);
diag2.remove(row - i);
}
}
}C++ Program
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<std::vector<std::string> > solveNQueens(int n) {
std::vector<std::vector<std::string> > res;
std::vector<std::string> nQueens(n, std::string(n, '.'));
solveNQueens(res, nQueens, 0, n);
return res;
}
private:
void solveNQueens(std::vector<std::vector<std::string> > &res, std::vector<std::string> &nQueens, int row, int &n) {
if (row == n) {
res.push_back(nQueens);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col != n; ++col)
if (isValid(nQueens, row, col, n)) {
nQueens[row][col] = 'Q';
solveNQueens(res, nQueens, row + 1, n);
nQueens[row][col] = '.';
}
}
bool isValid(std::vector<std::string> &nQueens, int row, int col, int &n) {
//check if the column had a queen before.
for (int i = 0; i != row; ++i)
if (nQueens[i][col] == 'Q')
return false;
//check if the 45° diagonal had a queen before.
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; --i, --j)
if (nQueens[i][j] == 'Q')
return false;
//check if the 135° diagonal had a queen before.
for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; --i, ++j)
if (nQueens[i][j] == 'Q')
return false;
return true;
}
};Complexity Analysis for N-Queens LeetCode Solution
Time Complexity: O(N**N).
Space Complexity: O(N**2)