Range Sum of BST LeetCode Solution says that –
Given the root the node of a binary search tree and two integers low and high, return the sum of values of all nodes with a value in the inclusive range [low, high].
Example 1:
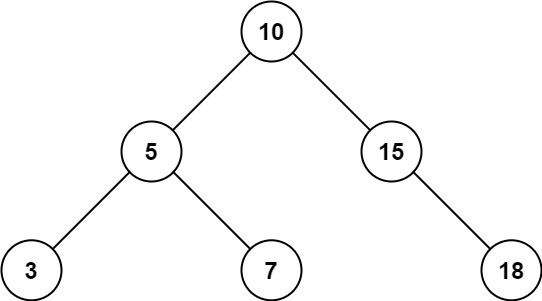 Input:
Input:
root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15
Output:
32
Explanation:
Nodes 7, 10, and 15 are in the range [7, 15]. 7 + 10 + 15 = 32.
Example 2:
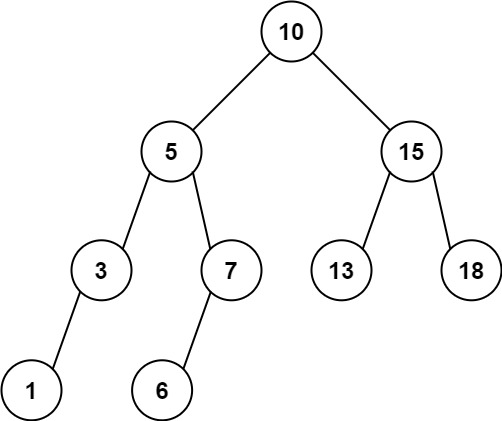 Input:
Input:
root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10
Output:
23
Explanation:
Nodes 6, 7, and 10 are in the range [6, 10]. 6 + 7 + 10 = 23.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 2 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 1051 <= low <= high <= 10- All
Node.valare unique.
Table of Contents
Algorithm:
Idea:
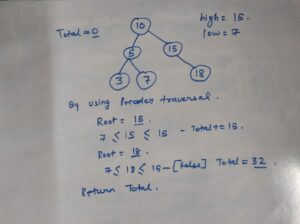
- In order to find the Range Sum of BST. First, we will focus on the node whose value lies in the range of low and high. So What we will do in this question is we will use pre-order traversal and make one variable total within the root condition we will check if node.val lies within the range then we add that value into the total and at last, we will return the total.
Approach:
- At first, we will make one variable and the value of that variable will be 0.
- After that, we will use pre-order traversal and within the root condition, we will if the root value lies within the range then simply add that value to the total and return the Total.
- Hence, the Range Sum of BST will be calculated.
IMAGE OF Range Sum of BST LeetCode Solution –

class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> int:
total = [0]
self.helper(root,low,high,total)
return total[0]
def helper(self,root,low,high,total):
if not root:
return
if low <= root.val <= high:
total[0] += root.val
self.helper(root.left,low,high,total)
self.helper(root.right,low,high,total)
class Solution {
int total = 0;
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
helper(root, low, high);
return total;
}
void helper(TreeNode root, int low, int high){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(low <= root.val && root.val <= high){
total += root.val;
}
helper(root.left, low, high);
helper(root.right, low, high);
}
}TIME COMPLEXITY: O(N), As we have used pre-order traversal.
SPACE COMPLEXITY: O(H), Due to recursion stack.
SIMILAR QUESTION –https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/count-bst-nodes-that-are-in-a-given-range/