In Find Median from the data Stream problem, we have given that integers are being read from a data stream. Find the median of all the elements read so far starting from the first integer till the last integer.
Table of Contents
Example
Input 1: stream[ ] = {3,10,5,20,7,6}
Output : 3 6.5 5 7.5 7 6.5
Input 2: stream[ ] = {20,1,11,19,21,17,6}
Output : 20 10.5 11 15 19 18 17Median: it can be defined as the element in the data set which separates the higher half of the data sample from the lower half. When the size of input data is odd, the median of input data is the middle element of sorted input data. When the size of the input data is even, the median is the average middle two elements in sorted input data.
Types of Solution
- insertion sort
- using a heap data structure
- using ordered multiset data structure(Tree set with multiple same values)
Insertion Sort
The idea is to keep elements already received from the stream in sorted order. Once we receive a new element from the stream, we find it’s correct place in the sorted order and place the new element at the correct place to find the median of the newly obtained sorted order. This is what we do in the insertion sort algorithm.
C++ Program for Find Median from data Stream
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// placing the last element recieved at it's correct position in a sorted vector
void insertionSort(vector <int>& sorted)
{
int last_inserted = sorted.size()-1;
while(last_inserted > 0 && sorted[last_inserted] < sorted[last_inserted-1])
{
swap(sorted[last_inserted-1],sorted[last_inserted]);
last_inserted--;
}
}
// prints median out of a given stream of integer values
void printMedian(vector <int> stream)
{
// vector to store values in sorted order
// for printing of the median value
vector <int> sorted;
for(int i=0;i<stream.size();i++)
{
sorted.push_back(stream[i]);
if(sorted.size() == 1)
cout<<sorted[0]<<"\t";
else
{
// sort the sorted vector
insertionSort(sorted);
// if number of elements recieved is odd
// middle element is the median
if(sorted.size()%2 == 1)
{
int mid = sorted.size()/2;
cout<<sorted[mid]<<"\t";
}
// if size is even
// average of middle two elements is the median
else
{
int mid1 = (sorted.size()-1)/2;
int mid2 = sorted.size()/2;
cout<<(float)(sorted[mid1]+sorted[mid2])/2<<"\t";
}
}
}
}
// main function to implement median of stream of integers
int main()
{
vector <int> stream = {3,10,5,20,7,6};
printMedian(stream);
return 0;
}3 6.5 5 7.5 7 6.5
Java Program for Find Median from data Stream
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class tutorialcup
{
// placing the last element recieved at it's correct position in a sorted vector
static void insertionSort(ArrayList <Integer> sorted)
{
int last_inserted = sorted.size()-1;
while(last_inserted > 0 && sorted.get(last_inserted) < sorted.get(last_inserted-1))
{
int temp = sorted.get(last_inserted-1);
sorted.set(last_inserted-1,sorted.get(last_inserted));
sorted.set(last_inserted,temp);
last_inserted--;
}
}
// prints median out of a given stream of integer values
static void printMedian(ArrayList <Integer> stream)
{
// vector to store values in sorted order
// for printing of the median value
ArrayList <Integer> sorted = new ArrayList <Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<stream.size();i++)
{
sorted.add(stream.get(i));
if(sorted.size() == 1)
System.out.print(sorted.get(0)+"\t");
else
{
// sort the sorted vector
insertionSort(sorted);
// if number of elements recieved is odd
// middle element is the median
if(sorted.size() %2 == 1)
{
int mid = sorted.size()/2;
System.out.print(sorted.get(mid)+"\t");
}
// if size is even
// average of middle two elements is the median
else
{
int mid1 = (sorted.size()-1)/2;
int mid2 = sorted.size()/2;
float median = (float)(sorted.get(mid1)+sorted.get(mid2))/2;
System.out.print(median + "\t");
}
}
}
}
// main function to implement median of stream of integers
public static void main (String[] args)
{
ArrayList <Integer> stream = new ArrayList <Integer> (Arrays.asList(3,10,5,20,7,6));
printMedian(stream);
}
}3 6.5 5 7.5 7 6.5
Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity: T(n) = O(n2), linear sorting(insertion sort) is nested with array traversal.
- Space Complexity: A(n) = O(1), no space is taken other than storing the stream.
Using Heap Data structure
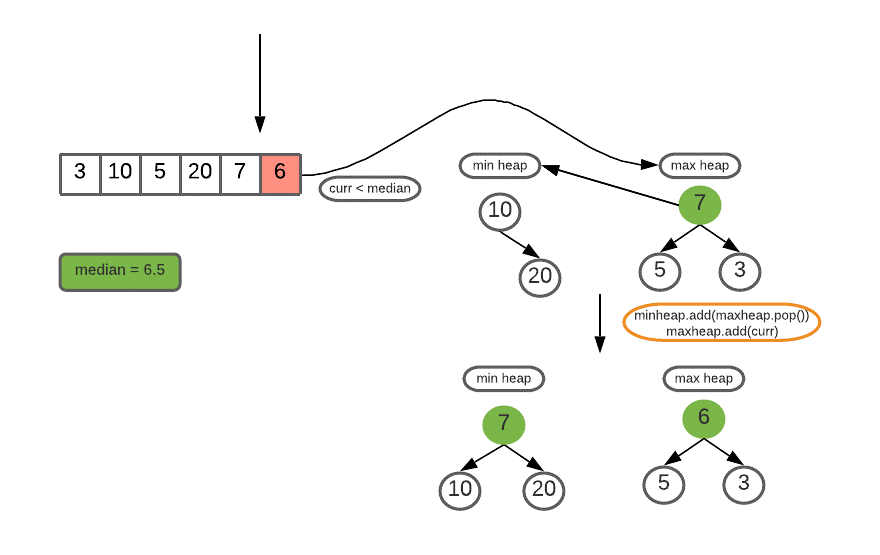
The idea is to use max heap and min-heap data structure to store the elements of the lower half and higher half respectively. Using the root values of both the heaps, we are able to calculate the median of the running stream of integers. The algorithm is implemented in the following ways :
Algorithm
- Create two heaps. One max heap (maxheap) to maintain elements of the lower half and one min heap(minheap) to maintain elements of the higher half at any point in time.
- Initially, the value of median is 0.
- For the current element received from the stream insert it into either of the heaps and calculate the median described in the following statements.
- If the size of both the heaps is the same.
- if the current element is greater than the median value, insert it into min heap.return the root of minheap as the new median.
- else if the current element is less than the median value, insert it into max heap.return the root of maxheap as the new median.
- else If the size of maxheap is greater than minheap :
- if the current element is greater than the median, insert the current element in minheap.
- else if the current element is less than the median, pop the root of maxheap and insert it into minheap. Now insert the current element to maxheap.
- calculate the median as an average of the root of minheap and maxheap.
- else If the size of maxheap is less than minheap :
- if the current element is less than the median, insert the current element into maxheap.
- else if the current element is greater than the median, pop the top of minheap and insert it into maxheap. Now insert the current element to minheap.
- calculate the median as an average of the root of minheap and maxheap.

C++ Program for Find Median from data Stream
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// prints median out of a given stream of integer values
void printMedian(vector <int> stream)
{
// initial value of median is 0
float median = 0;
// to store the lower half of sorted stream
priority_queue <int> maxheap;
// to store the upper half of sorted stream
priority_queue <int,vector <int>,greater <int> > minheap;
// process the stream of values
for(int i=0;i<stream.size();i++)
{
int curr = stream[i];
// if size of both the heap is same
if(maxheap.size() == minheap.size())
{
if(curr >= median)
{
minheap.push(curr);
median = minheap.top();
}
else
{
maxheap.push(curr);
median = maxheap.top();
}
}
// if size of heaps are different
// after inserting the element from the stream
// size of both heap becomes equal
// median is average of roots of both the heaps
else
{
if(maxheap.size() > minheap.size())
{
if(curr > median)
minheap.push(curr);
else
{
minheap.push(maxheap.top());
maxheap.pop();
maxheap.push(curr);
}
}
else
{
if(curr < median)
maxheap.push(curr);
else
{
maxheap.push(minheap.top());
minheap.pop();
minheap.push(curr);
}
}
median = (float)(minheap.top()+maxheap.top())/2;
}
cout<<median<<"\t";
}
}
// main function to implement median of stream of integers
int main()
{
vector <int> stream = {3,10,5,20,7,6};
printMedian(stream);
return 0;
}3 6.5 5 7.5 7 6.5
Java Program for Find Median from data Stream
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class tutorialcup
{
// prints median out of a given stream of integer values
static void printMedian(ArrayList <Integer> stream)
{
// initial value of median is 0
float median = 0;
// to store the lower half of sorted stream
PriorityQueue <Integer> minheap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
// to store the upper half of sorted stream
PriorityQueue <Integer> maxheap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(Collections.reverseOrder());
// process the stream of values
for(int i=0;i<stream.size();i++)
{
int curr = stream.get(i);
// if size of both the heap is same
if(maxheap.size() == minheap.size())
{
if(curr >= median)
{
minheap.add(curr);
median = minheap.peek();
}
else
{
maxheap.add(curr);
median = maxheap.peek();
}
}
// if size of heaps are different
// after inserting the element from the stream
// size of both heap becomes equal
// median is average of roots of both the heaps
else
{
if(maxheap.size() > minheap.size())
{
if(curr > median)
minheap.add(curr);
else
{
minheap.add(maxheap.remove());
maxheap.add(curr);
}
}
else
{
if(curr < median)
maxheap.add(curr);
else
{
maxheap.add(minheap.remove());
minheap.add(curr);
}
}
median = (float)(minheap.peek()+maxheap.peek())/2;
}
System.out.print(median+"\t");
}
}
// main function to implement median of stream of integers
public static void main (String[] args)
{
ArrayList <Integer> stream = new ArrayList <Integer> (Arrays.asList(3,10,5,20,7,6));
printMedian(stream);
}
}3 6.5 5 7.5 7 6.5
Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity : T(n) = O(nlogn), for formation of heap of n elements.
- Space Complexity : A(n) = O(n), stream values are stored in a heap.
Using Ordered Multiset Data Structure
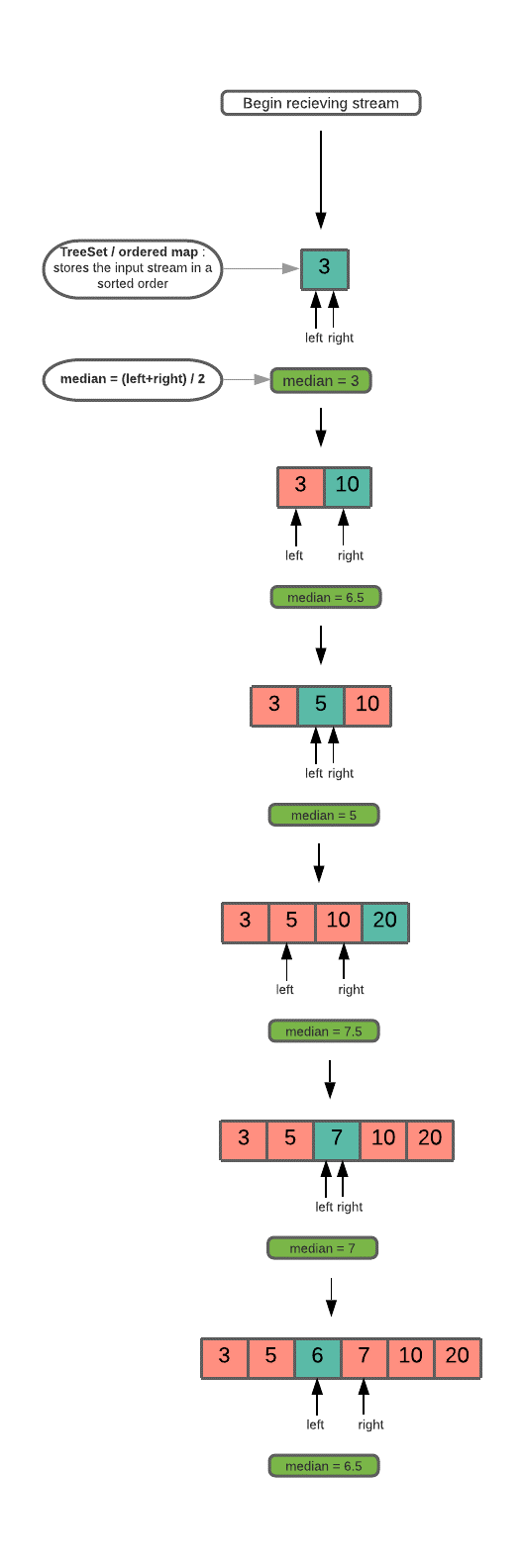
We use a multiset data structures with two iterator type pointers left and right, as and when we insert an element into the multiset, we modify these pointers to point at the middle element of the sorted stream. This is performed as below :
Algorithm
- creates a multiset variable sorted.
- create two iterators for sorted multiset left and right.
- Process each element (our current element) of the stream and insert the element into the sorted.
- if the size of sorted is 1 (the first element is inserted), point left and right to the first element of sorted.
- Else
- if sizeof(sorted) is even, ie left and right point to the same element in the middle.
- if the current element is greater than the element pointed by right, advance right to next element.
- else if the current element is less than element pointed by right, move back left to the previous element.
- if sizeof(sorted) is odd, ie left and right point to consecutive elements in the middle of the array.
- if the current element is greater than the element pointed by right, advance left to next element.
- else if the current element is less than element pointed by left, move right to the previous element.
- else if the current element is greater than left and less than right, move left forward and right to backward.
- if sizeof(sorted) is even, ie left and right point to the same element in the middle.
- calculate median at every step by using following : median = (left+right)/2.
C++ Program for Find Median from data Stream
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// prints median out of a given stream of integer values
void printMedian(vector <int> stream)
{
// declare multiset to store sorted order
multiset <int> sorted;
// declare iterators of multiset type
multiset<int>::iterator left,right;
// initialize median
float median = 0;
// process the stream
for(int i=0;i<stream.size();i++)
{
// insert each element into multiset
sorted.insert(stream[i]);
// for first element inserted
// initiate left and right pointers
if(sorted.size() == 1)
{
left = sorted.begin();
right = sorted.begin();
median = *left;
}
// for subsequent elements inserted
else
{
// if size of multiset is even
if(sorted.size()%2 == 0)
{
if(stream[i] >= *right)
right++;
else
left--;
}
// if size of multiset is odd
else
{
if(stream[i] >= *right)
left++;
else if(stream[i] <= *left)
right--;
else
{
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
// median is average of elements pointed by left and right
median = (float)(*left+*right)/2;
cout<<median<<"\t";
}
}
// main function to implement median of stream of integers
int main()
{
vector <int> stream = {3,10,5,20,7,6};
printMedian(stream);
return 0;
}3 6.5 5 7.5 7 6.5
Java Program for Find Median from data Stream
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// library to access ordered multiset in java
import com.google.common.collect.TreeMultiset;
class tutorialcup
{
// prints median out of a given stream of integer values
static void printMedian(ArrayList <Integer> stream)
{
// declare multiset to store sorted order
TreeMultiset <Integer> sorted = TreeMultiset.create();
// declare iterators of multiset type
Iterator <Integer> left = sorted.iterator();
Iterator <Integer> right = sorted.iterator();
// initialize median
float median = 0;
// process the stream
for(int i=0;i<stream.size();i++)
{
// insert each element into multiset
sorted.add(stream.get(i));
// for first element inserted
// initiate left and right pointers
if(sorted.size() == 1)
{
//left = sorted.begin();
//right = sorted.begin();
median = left.next();
}
// for subsequent elements inserted
else
{
// if size of multiset is even
if(sorted.size()%2 == 0)
{
if(stream.get(i) >= right.next())
right.hasNext();
else
left.hasPrevious();
}
// if size of multiset is odd
else
{
if(stream.get(i) >= right.next())
left.hasNext();
else if(stream.get(i) <= left.next())
right.hasPrevious();
else
{
left.hasNext();
right.hasPrevious();
}
}
}
// median is average of elements pointed by left and right
median = (float)(left.next()+right.next())/2;
System.out.print(median+"\t");
}
}
// main function to implement median of stream of integers
public static void main (String[] args)
{
ArrayList <Integer> stream = new ArrayList <Integer> (Arrays.asList(3,10,5,20,7,6));
printMedian(stream);
}
}3 6.5 5 7.5 7 6.5
Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity : T(n) = O(nlogn), for formation of multiset of n elements.
- Space Complexity : A(n) = O(n), stream values are stored in a set.