What can be so special about a number?
Let us find out.
We have with us an array of N numbers. A number can be special if it is divisible by one or more numbers except for the number itself.
Firstly let us clear this with a few examples before we jump into anything else
Array of 1,2,3
Special numbers 2 and 3
Why?
2 is divisible by 1 as well 3
The array of 1,2,5,9
Special numbers will be 2,5 and 9
Why?
As these numbers are divisible by 1
An array of 2,3,4,6,8,9
Special numbers will be 4.6.8.9
Secondly, let us look at how to approach this problem
Table of Contents
Approach 1 for Special Number
Brute Force
- We traverse through the array
- We check the elements that divide each element
Java Code For Special Numbers
// "static void main" must be defined in a public class.
public class Main
{
public static void diCheck(List<Integer> arr, int n)
{
Set<Integer> store = new HashSet<Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<arr.size();j++)
{
if(arr.get(j)%arr.get(i)==0)
store.add(arr.get(j));
}
}
for(Integer a:store)
{
System.out.print(a+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<Integer> arr = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 8, 6, 9, 5);
int n = arr.size();
diCheck(arr, n);
}
}C++ Code For Special Numbers
void diCheck(int arr[], int n)
{
unordered_set<int> store;
int maxs = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(arr[j]%arr[i]==0)
store.insert(arr[j]);
}
}
for (auto x : store)
cout << x << " ";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 6, 9, 10 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
diCheck(arr, n);
return 0;
}Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity=O(n^2)
How?
- The above approach uses two loops
- Firstly, an outer one to go over the divisor
- Secondly. inner one to go over the dividend
- This brings the time complexity to O(n^2)
Space Complexity=O(1)
How?
We use only a variable thus we do not need much space
Approach 2 for Special Number
Using a hash table
Firstly, let us break down the approach into small bite-sized palatable pieces.
- Firstly sort all the elements
- Find the max element using a variable
- Need of the max element?
- To use it to find the available divisors up to that number
- We start from num*2
- We add the number to itself to get the multiples
- Every time we get a multiple we store it into a set
- We store the numbers into sets to ensure that none of the numbers we obtain is duplicate
- If there is a divisor then the number is special
- The special number is thus added
Secondly, let me get a small image to run through the entire process. This would ensure that everyone who could not get a grip on the problem understands it fully.
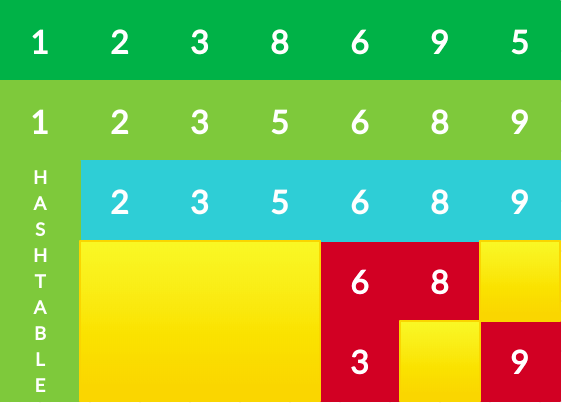
The red places here suggest that the numbers have already been added to the map.
Java Code
// "static void main" must be defined in a public class.
public class Main
{
public static void diCheck(List<Integer> arr, int n)
{
List<Integer> store = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
store.add(arr.get(i));
max = Math.max(max,arr.get(i));
}
LinkedHashSet<Integer>ans=new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(arr.get(i)!=0)
{
for(int j=arr.get(i)*2;j<max;j++)
{
if(store.contains(j))
ans.add(j);
}
}
}
List<Integer>ret=new ArrayList<Integer>(ans);
for(int i=0;i<ret.size();i++)
System.out.print(ret.get(i)+" ");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<Integer> arr = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 8, 6, 9, 5);
int n = arr.size();
diCheck(arr, n);
}
}C++ Code
void diCheck(int arr[], int n)
{
unordered_set<int> store;
int maxs = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
store.insert(arr[i]);
//Finding the max element
maxs= max(maxs, arr[i]);
}
// Traversing the array elements and storing the multiples
unordered_set<int> res;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] != 0)
{
for (int j = arr[i] * 2; j <= maxs; j++)
{
if (store.find(j) != store.end())
res.insert(j);
}
}
}
unordered_map<int, int> map;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
map[arr[i]]=map[arr[i]]+1;
unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it;
vector<int> ans;
for (it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); it++)
{
if (it->second >= 2)
{
if (res.find(it->first) == res.end())
{
int val = it->second;
while (val--)
ans.push_back(it->first);
}
}
// If frequency is greater than 1 and is divisible by any other number
if (res.find(it->first) != res.end())
{
int val = it->second;
while (val--)
ans.push_back(it->first);
}
}
//Printing special numbers
for (auto x : ans)
cout << x << " ";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 6, 9, 10 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
diCheck(arr, n);
return 0;
}1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 6, 9, 10
2,3,5,8,9,10
Note: The above approach works well only for small numbers
Complexity Analysis For Special Number
Time Complexity=O(n^2)
- The time complexity for the approach sums up to O(n^2)
- The sorting takes O(n log n) time
- We go over the outer loop and select a number from the hash
- In the inner loop, we look for the divisors and add them to the set if they are present
- Eventually summing up the time complexity to O(nlogn)+O(n^2)
- As n^2>n logn
- The time complexity becomes O(n^2)
Space Complexity=O(n)
- We use a hash and a set to keep track of the elements.
- We have an array/ArrayList/vector of size n provided.
- Thus space taken in storing all the elements sums up to O(n).