In combination sum problem we have given an array of positive integers arr[] and a sum s, find all unique combinations of elements in arr[] where the sum of those elements is equal to s. The same repeated number may be chosen from arr[] an unlimited number of times. Elements of each combination must be printed in nondescending order.
The combinations themselves must be sorted in ascending order, i.e., the combination with the smallest first element should be printed first. If there is no combination possible then print “No such combination found”.
Table of Contents
Examples
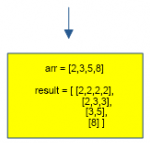
Input: arr[] = [2,3,5,8], sum = 8
Output: [2, 2, 2, 2]
[2, 3, 3]
[3, 5]
[8]
Input: arr[] = [2,4,6,8], sum = 11
Output: No such combination found
Input: arr[] = [3,5,6,11], sum = 19
Output: [3, 3, 3, 5, 5]
[3, 5, 5, 6]
[3, 5, 11]
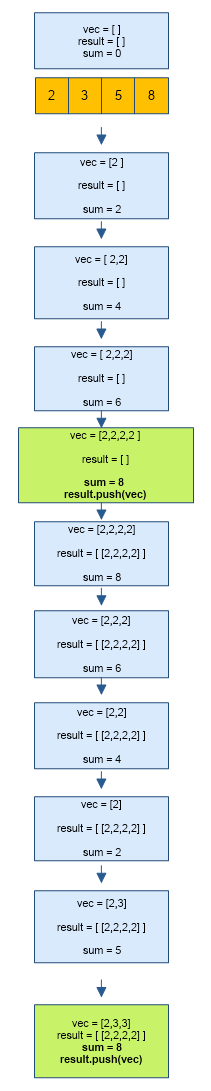
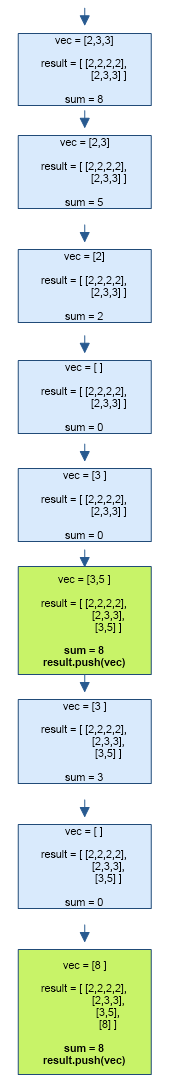
Algorithm for Combination Sum
- Sort the array in ascending order.
- Remove all duplicate elements from the array.
- Use backtracking and recursion in the following way :
- Recursively add arr[i] into a vector ‘vec’ until the sum of all elements in vec is less than the given sum.
- If the sum of all elements in vec becomes equal to the given sum, add vec to ‘result’ (vector of vectors).
- If the sum of all elements in vec exceeds the given sum, add nothing to result.
- when cases 2 and 3 occur, pop the last element from vec.
- advance i to next array index (i.e. i++).
- repeat steps 1-4 until all the combinations with a given sum are appended to result.
Implementation for Combination Sum
C++ Program
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to find all combinations of
// elements of an array that add upto a given sum
void findCombination(vector<int> &arr, int sum,
vector<vector<int>> &result,
vector<int> &vec, int i)
{
// sum of elements in vec becomes greater than original sum
if (sum < 0)
return;
// sum of elements in vec is exactly equal to original sum
if (sum == 0)
{
// add that particular combination to result
result.push_back(vec);
return;
}
// recur for all remaining elements that
// have value smaller than original sum.
while (i < arr.size() && sum-arr[i] >= 0)
{
// add every element of the array to the vec starting from i
// that adds/contributes to 'sum'
vec.push_back(arr[i]);
// recur to adding arr[i] to vec
// if it contributes to 'sum'
findCombination(arr, sum - arr[i], result, vec, i);
// move to next element in case
// sum of elements becomes greater than
// or equal to the required sum
i++;
// remove the last number from the combination list
// to add next element (basically backtracking)
vec.pop_back();
}
}
// Returns all combinations of arr[] that have given sum.
vector<vector<int> > combinationSum(vector<int>& arr, int sum)
{
// sort input array
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
// remove duplicates
// create an array to add all the unique elements to it
vector <int> uniq;
// create a set to check whether an element
// has been added to unique array or not
unordered_set <int> us;
for(auto i : arr)
{
if(us.find(i) == us.end())
{
us.insert(i);
uniq.push_back(i);
}
}
// copy the unique array back to original array
arr = uniq;
// to store a unique combination
vector<int> vec;
// stores all the unique combinations
vector<vector<int>> result;
findCombination(arr, sum, result, vec, 0);
return result;
}
// implementing above functions
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = {2,3,5,8};
int n = arr.size();
int sum = 8;
vector<vector<int>> result = combinationSum(arr, sum);
// If result vector is empty
// no combinations of array elements with given sum exist
if (result.empty())
{
cout << "No such combination found";
return 0;
}
// Print all combinations stored in result.
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++)
{
if (!result[i].empty())
{
cout << "[ ";
for (int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++)
cout << result[i][j] << " ";
cout << "]";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
[ 2 2 2 2 ] [ 2 3 3 ] [ 3 5 ] [ 8 ]
Java Program
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class tutorialcup
{
// function to find all combinations of
// elements of an array that add upto a given sum
static void findCombination(ArrayList<Integer> arr, int sum,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result,
ArrayList<Integer> vec, int i)
{
// sum of elements in vec becomes greater than original sum
if (sum < 0)
return;
// sum of elements in vec is exactly equal to original sum
if (sum == 0)
{
// add that particular combination to result
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(vec));
return;
}
// recur for all remaining elements that
// have value smaller than original sum.
while (i < arr.size() && sum-arr.get(i) >= 0)
{
// add every element of the array to the vec starting from i
// that adds/contributes to 'sum'
vec.add(arr.get(i));
// recur to adding arr[i] to vec
// if it contributes to 'sum'
findCombination(arr, sum - arr.get(i), result, vec, i);
// move to next element in case
// sum of elements becomes greater than
// or equal to the required sum
i++;
// remove the last number from the combination list
// to add next element(basically backtracking)
vec.remove(vec.size()-1);
}
}
// Returns all combinations of arr[] that have given sum.
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> combinationSum(ArrayList<Integer> arr, int sum)
{
// sort input array
Collections.sort(arr);
// remove duplicates
// create an array to add all the unique elements to it
ArrayList <Integer> uniq = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// create a set to check whether an element
// has been added to unique array or not
HashSet <Integer> hs = new HashSet <Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++)
{
if(hs.contains(arr.get(i)) == false)
{
hs.add(arr.get(i));
uniq.add(arr.get(i));
}
}
// copy the unique array back to original array
arr = uniq;
// to store a unique combination
ArrayList <Integer> vec = new ArrayList <Integer>();
// stores all the unique combinations
ArrayList <ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
findCombination(arr, sum, result, vec, 0);
return result;
}
// implementing above function
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList <Integer> arr = new ArrayList <Integer> (Arrays.asList(2,3,5,8));
int n = arr.size();
int sum = 8;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
result = combinationSum(arr, sum);
// If result vector is empty
// no combinations of array elements with given sum exist
if (result.isEmpty())
{
System.out.println("No such combination found");
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<result.size();i++)
System.out.println(result.get(i));
}
}[2, 2, 2, 2] [2, 3, 3] [3, 5] [8]
Complexity Analysis for Combination Sum
- Time Complexity : T(n) = O(n*2n), n = size of the array