In the next permutation problem we have given a word, find the lexicographically greater_permutation of it.
Table of Contents
Example
input : str = "tutorialcup" output : tutorialpcu input : str = "nmhdgfecba" output : nmheabcdfg input : str = "algorithms" output : algorithsm input : str = "spoonfeed" output : Next Permutation Doesnt exist
Lexicographical Order
All the permutations of a word when arranged in a dictionary, the order of words so obtained is called lexicographical order.
Ex :
word = 'cat' lexicographical order of permutations of 'cat' : act atc cat cta tac tca
we can see, ‘cat’ is lexicographically greater than ‘act’.
Algorithm for Next Permutation
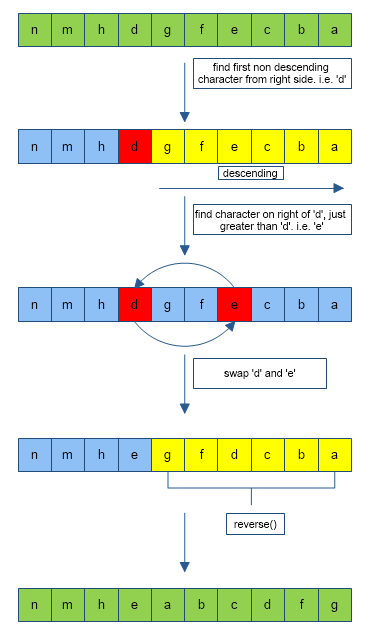
For a word that is completely sorted in descending order, ex: ”nmhgfedcba” doesn’t have the next permutation. We can find the next permutation for a word that is not completely sorted in descending order. ex : “nmhdgfecba”.Below is the algorithm:
Given : str = “nmhdgfecba”
- Traverse from the right of the string and look for the first character that does not follow the descending order. ‘d’ in str doesn’t follow descending order. index of ‘d’ = 3.
- To the right of ‘d’, search for the character that is just (or closest) greater than ‘d’ in ASCII value. ‘e’ in [nmhd]gfecba is just greater than ‘d’.This is done using binarySearch() function.
- swap ‘e’ and ‘d’.The resulting string is “nmhegfdcba”.
- Now reverse (done using the reverse() function) the part of resulting string occurring after the index found in step 1. reverse “gfdcba” and append it back to the main string.
- output = “nmheabcdfg”,it is the lexicographically next permutation of “nmhgfedcba”.

Implementation for Next Permutation
C++ Program
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to reverse the string between index l and r
void reverse(string &str,int l,int r)
{
while(l < r)
swap(str[l++],str[r--]);
}
// function to search a character lying between index l and r
// which is closest greater (just greater) than val
// and return it's index
int binarySearch(string& str,int l,int r,char val)
{
int index = -1;
while (l <= r)
{
int mid = (l+r)/2;
if (str[mid] <= val)
{
r = mid - 1;
}
else
{
l = mid + 1;
if (index == -1 || str[index] >= str[mid])
index = mid;
}
}
return index;
}
// this function generates next permutation (if there exists any such permutation) from the given string
// and returns True
// Else returns false
bool nextPermutation(string& str)
{
int len = str.length();
int i = len-2;
while (i >= 0 && str[i] >= str[i+1])
i--;
if (i < 0)
return false;
else
{
int index = binarySearch(str,i+1,len-1,str[i]);
swap(str[i],str[index]);
reverse(str,i+1,len-1);
return true;
}
}
// main function to find next permutation
int main()
{
string str = "nmhdgfecba";
bool is = nextPermutation(str);
if(is == false)
cout<< "Next Permutation Doesnt exist" <<endl;
else
cout<<str<<endl;
return 0;
}
nmheabcdfg
Java Program
class permutation
{
// swap two characters of string
static void swap(StringBuilder sb,int l,int r)
{
char temp = sb.charAt(l);
sb.setCharAt(l,sb.charAt(r));
sb.setCharAt(r,temp);
}
// function to reverse the string between index l and r
static void reverse(StringBuilder sb,int l,int r)
{
while(l < r)
{
swap(sb,l,r);
l++;
r--;
}
}
// function to search a character lying between index l and r
// which is closest greater (just greater) than val
// and return it's index
static int binarySearch(StringBuilder sb,int l,int r,char val)
{
int index = -1;
while (l <= r)
{
int mid = (l+r)/2;
if (sb.charAt(mid) <= val)
{
r = mid - 1;
}
else
{
l = mid + 1;
if (index == -1 || sb.charAt(index) >= sb.charAt(mid))
index = mid;
}
}
return index;
}
// this function generates next permutation (if there exists any such permutation) from the given string
// and returns True
// Else returns false
static boolean nextPermutation(StringBuilder sb)
{
int len = sb.length();
int i = len-2;
while (i >= 0 && sb.charAt(i) >= sb.charAt(i+1))
i--;
if (i < 0)
return false;
else
{
int index = binarySearch(sb,i+1,len-1,sb.charAt(i));
swap(sb,i,index);
reverse(sb,i+1,len-1);
return true;
}
}
// main function to find next permutation
public static void main(String args[])
{
String str = "nmhdgfecba";
// strings in java are immutable,so we convert strings into StringBuilder
// StringBuilder are mutable strings
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(str);
boolean is = nextPermutation(sb);
if(is == false)
System.out.println("Next Permutation Doesnt exist");
else
System.out.println(sb);
}
}nmheabcdfg
Next Permutation using STL library
STL library of C++ contains function next_permutation() that generates the next permutation of given string
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h> // STL library of C++
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str = "nmhdgfecba";
// next_permutation() is present in STL library
// next_permutation() generates Next Permutation of a string if it exists
// and returns true
// else returns false
if(next_permutation(str.begin(),str.end()))
cout<<str<<endl;
else
cout<<"Next Permutation Doesnt exist";
return 0;
}nmheabcdfg
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity: Overall Time complexity T(n) = O(n)
- In the worst case, the first step of nextPermutation() takes O(n) time.
- binarySearch() takes O(logn) time.
- reverse() takes O(n) time.
- Space Complexity: A(n) = O(1) because here we don’t use any auxiliary space during computation of the task. That’ s means the space complexity of next permutation problem, in this case, is constant.