Coin Change Problem – Given some coins of different values c1, c2, … , cs (For instance: 1,4,7….). We need an amount n. Use these given coins to form the amount n. You can use a coin as many times as required. Find the total number of ways in which amount n can be obtained using these coins.
For instance – let amount n=3 and coins c={1,2} then the possible solutions are {1,1,1} i.e. three coins of value 1 will result in amount 3 and {1,2} i.e. one coin each of value 1 and 2. Therefore, the output is 2.
Table of Contents
Example
Input : n=5 and c={1, 2, 3}
Output : 5
Input : n=34 and c={1, 2, 10}
Output : 42
Recursive Method for Coin Change Problem
Algorithm
- Initialize a variable n and an array c of available coins.
- First base case – if n is zero return 1 as the only solution is to use 0 coins.
- Second – if n is less than zero return zero as there is no possible solution.
- Third – if n is greater than zero but no coins are available that is size=0 return 0.
- Recursive case – return count (sum of solutions including last coin value) + count (sum of solutions excluding last coin value)
Time Complexity: O(2n)
Space Complexity: O(size)
C++ Program for Coin Change Problem
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int coin_count(int arr[], int size, int n){
// If n is 0 then
// do not include any coin
if(n==0)
return 1;
// If n is less than 0
// no solution exists
if(n<0)
return 0;
// If coins do not exist and n
// is greater than 0,
// no solution exist
if((size<=0)&&(n>=1))
return 0;
return coin_count(arr,size-1,n)+coin_count(arr,size,n-arr[size-1]);
}
int main(){
int c[] = {1, 2, 3};
int n=5;
int size = sizeof(c)/sizeof(c[0]);
cout<<coin_count(c, size, n);
return 0;
}Output : 5
Java Program for Coin Change Problem
import java.io.*;
class Coins{
static int coin_count(int arr[], int size, int n){
// If n is 0 then
// do not include any coin
if(n==0)
return 1;
// If n is less than 0
// no solution exists
if(n<0)
return 0;
// If coins do not exist and n
// is greater than 0,
// no solution exist
if((size<=0)&&(n>=1))
return 0;
return coin_count(arr,size-1,n)+coin_count(arr,size,n-arr[size-1]);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int c[]={1, 2, 3};
int n=5;
int size=c.length;
System.out.println(coin_count(c, size, n));
}
}Output : 5
Recursion tree of above code
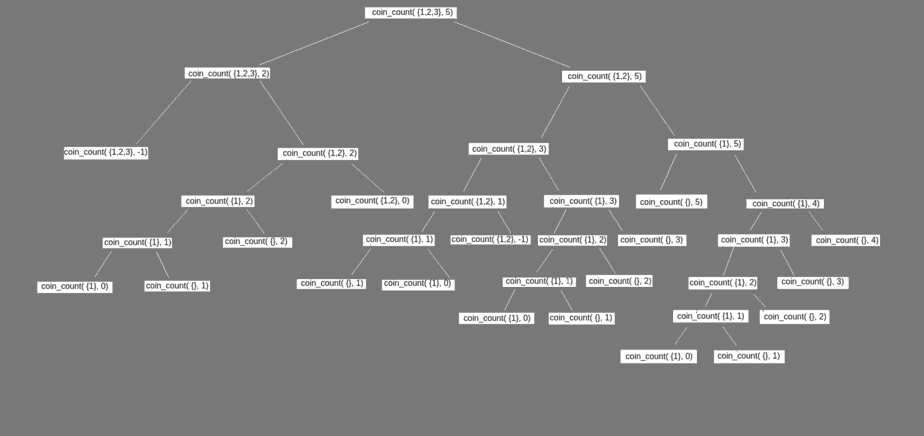
We can see from the above tree that some functions are being called more than once. This is called Overlapping Sub-problems property.
Dynamic Programming Method
To avoid the re-computations of the same problems as discussed above an array will be constructed in a bottom-up manner.
Algorithm
- Initialize a variable n and an array c of available coins.
- If n is zero stores 1 in array count as the only solution is to use 0 coins.
- Traverse all the coin values one by one and update the count array values after the index greater than or equal to the value of the picked coin.
- Return count [n].
Time Complexity: O(mn)
Space Complexity: O(n)
C++ Program for Coin Change Problem
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int coin_count(int arr[], int m, int n){
int count[n+1];
// Initialise all count values as 0
memset(count, 0, sizeof(count));
//if n=0
count[0] = 1;
// update the count[]
// values after the index >=
// the value of the picked coin
for (int i=0; i<m; i++)
for (int j=arr[i]; j<=n; j++)
count[j] += count[j-arr[i]];
return count[n];
}
int main(){
int c[] = {1, 2, 3};
int n=5;
int size = sizeof(c)/sizeof(c[0]);
cout<<coin_count(c, size, n);
return 0;
}Output : 5
Java Program for Coin Change Problem
import java.util.Arrays;
class Coins{
static long coin_count(int arr[], int m, int n){
long[] count = new long[n+1];
//Initialise all values of count as 0
Arrays.fill(count, 0);
//if n=0
count[0] = 1;
// update the count[]
// values after the index >=
// the value of the picked coin
for (int i=0; i<m; i++)
for (int j=arr[i]; j<=n; j++)
count[j] += count[j-arr[i]];
return count[n];
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int c[] = {1, 2, 3};
int size = c.length;
int n = 5;
System.out.println(coin_count(c, size, n));
}
}Output : 5