The House Robber Problem states that, in a neighborhood in a city, there is a single row of n houses. A thief is planning to carry a heist in this neighborhood. He knows how much gold is concealed in each of the houses.
However, in order to avoid triggering an alarm and raise suspicion, he plans to carry heist in such a way that no two consecutive houses are looted. i.e. if the house at index = i is looted, the houses at i-1 and i+1 are not looted.
Find out what is the maximum number of gold the thief can steal following the given constraints.
Table of Contents
Example
Input 1: arr[] = [2,3,4,2,3]
Maximum gold = [2, X, 4, X, 3] = 9
Output: 6
Input 2: arr[] = [3,8,10,4,2,3]
Maximum gold = [3, X, 10, X, X, 3] = 16
Output: 15
Input 2: arr[] = [3,8,10,4,2,3,11]
Maximum gold = [3, X, 10, X, 2, X, 11] = 26
Output: 26Explanation: in example 2, the thief has to get to 1st, 3rd, and 6th house to collect the maximum number of gold given the constraints.
Types of Solution
- Recursive
- Dynamic Programming :
- Memoized Solution
- Tabulated Solution
- Space Optimized DP solution
Recursive solution for House Robber
Given an array, the solution is to find the maximum sum subsequence where no two selected elements are adjacent. we implement this in the following way:
- Start traversing arr[] from right to left.
- If an element arr[i] is selected then the next element (arr[i-1]) cannot be selected.
- If an element(arr[i]) is not selected then the next element arr[i-1] can be selected.
- Perform steps 2 and 3 recursively and return the maximum of values obtained in steps 2 and 3.
C++ Program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int maxGold (int gold[],int n)
{
if(n <= 0)
return 0;
// select the current element
int select = gold[n-1] + maxGold(gold,n-2);
// not selecting the current element
int notselect = maxGold(gold,n-1);
// return maximum of both of above
return max(select,notselect);
}
int main()
{
int gold[] = {3,8,10,4,2,3};
int n = sizeof(gold)/sizeof(int);
cout<<"Maximum gold looted = "<<maxGold(gold,n);
return 0;
}Maximum gold looted = 16
Java Program
import java.io.*;
class tutorialcup
{
static int maxGold (int gold[],int n)
{
if(n <= 0)
return 0;
// select the current element
int select = gold[n-1] + maxGold(gold,n-2);
// not selecting the current element
int notselect = maxGold(gold,n-1);
// return maximum of both of above
return Math.max(select,notselect);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int gold[] = {3,8,10,4,2,3};
int n = gold.length;
System.out.print("Maximum gold looted = "+maxGold(gold,n));
}
}Maximum gold looted = 16
Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity T(n) = O(2n), recursive calls.
- Space complexity A(n) = O(1)
Dynamic Programming
The major drawback of the recursive solution is its exponential time complexity. This Happens as the recursive solution tries to solve certain subproblems repeatedly. This increases the time taken by the algorithm. The exponential time complexity of the recursive solution can be reduced to linear time complexity using dynamic programming. This method utilizes extra space to store solutions of the subproblems, later in the program if that subproblem is called again, it’s stored value can be directly used instead of recalculating it. This reduces the complexity from exponential to linear order.
We will implement Dynamic Programming Solution in the following ways :
Memoized Solution for House Robber
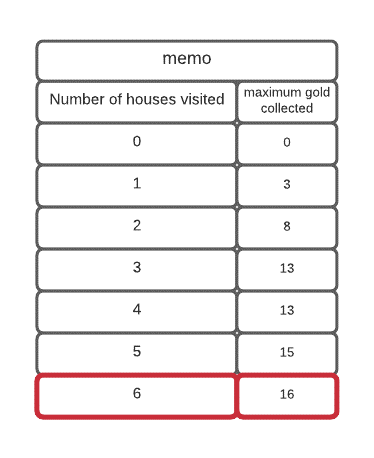
here we create a map memo and store subproblems as it’s keys and solutions to the subproblems as values of the map. The implementation code is similar to the recursive approach, except for slight changes and usage of Map.
The memo map is given below:
C++ Program
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxGold (int gold[],int n, unordered_map <int,int> &memo)
{
int key = n;
// if solution for subproblem maxGold(gold,n,memo)
// has not been calculated
// calulate it
if(memo.find(key) == memo.end())
{
if(n <= 0)
{
memo[key] = 0;
return memo[key];
}
// select the current element
int select = gold[n-1] + maxGold(gold,n-2,memo);
// not selecting the current element
int notselect = maxGold(gold,n-1,memo);
// return maximum of both of above
memo[key] = max(select,notselect);
}
// return value of subproblem after being calculated
// or if already present
return memo[key];
}
// main function to implement above function
int main()
{
int gold[] = {3,8,10,4,2,3};
int n = sizeof(gold)/sizeof(int);
// map to store mapping between particular subproblem and it's value
unordered_map <int,int> memo;
cout<<"Maximum gold looted = "<<maxGold(gold,n,memo);
return 0;
}Maximum gold looted = 16
Java Program
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class tutorialcup
{
static int maxGold (int gold[],int n, HashMap <Integer,Integer> memo)
{
int key = n;
// if solution for subproblem maxGold(gold,n,memo)
// has not been calculated
// calulate it
if(!memo.containsKey(key))
{
if(n <= 0)
{
memo.put(key,0);
return memo.get(key);
}
// select the current element
int select = gold[n-1] + maxGold(gold,n-2,memo);
// not selecting the current element
int notselect = maxGold(gold,n-1,memo);
// return maximum of both of above
memo.put(key, Math.max(select,notselect));
}
// return value of subproblem after being calculated
// or if already present
return memo.get(key);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int gold[] = {3,8,10,4,2,3};
int n = gold.length;
HashMap <Integer,Integer> memo = new HashMap <Integer,Integer>();
System.out.print("Maximum gold looted = "+maxGold(gold,n,memo));
}
}Maximum gold looted = 16
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity : T(n) = O(n), single array traversal.
- Space Complexity : A(n) = O(n), extra space for map.
Tabulated Solution for House Robber
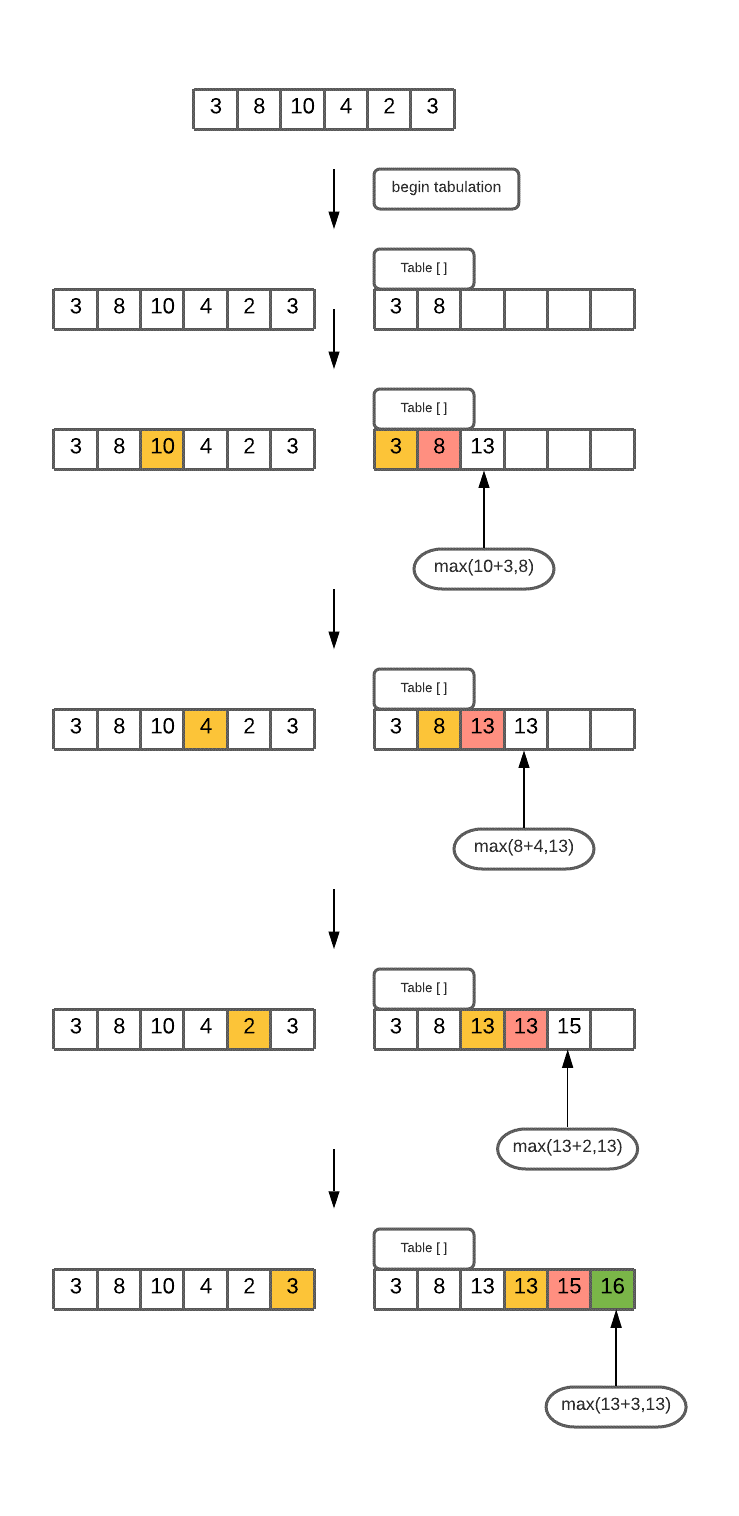
we create a table (linear array) where the subproblems are the array index and solutions to the subproblems are the value at that particular index.
Algorithm
- Create an array table[] to store the sub-problems
- Define some base cases (for n = 0,1,2).
- return 0 for n = 0.
- Update table[0] = gold[0] and table[1] = max(gold[0], gold[1]).
- Traverse the array from i = 2 to the end of the array.
- For every index, update table[i] = max(table[i-2] + gold[i] , table[i-1]), this step defines the two cases, if an element is selected then the previous element cannot be selected and if an element is not selected then the previous element can be selected.
- return the value table[n-1].
We display the above process below:
C++ Program
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxGold (int gold[],int n1)
{
// base cases
if (n1 == 0)
return 0;
if (n1 == 1)
return gold[0];
if (n1 == 2)
return max(gold[0], gold[1]);
// table[i] represent the maximum value stolen
// so far after reaching house i.
int table[n1];
// Initialize the table[0] and table[1]
table[0] = gold[0];
table[1] = max(gold[0], gold[1]);
// Fill remaining positions
for (int i = 2; i<n1; i++)
table[i] = max(gold[i]+table[i-2], table[i-1]);
return table[n1-1];
}
// main function to implement above function
int main()
{
int gold[] = {3,8,10,4,2,3};
int n = sizeof(gold)/sizeof(int);
cout<<"Maximum gold looted = "<<maxGold(gold,n);
return 0;
}Maximum gold looted = 16
Java Program
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class tutorialcup
{
static int maxGold (int gold[],int n)
{
// base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return gold[0];
if (n == 2)
return Math.max(gold[0], gold[1]);
// table[i] represent the maximum value stolen
// so far after reaching house i.
int table[] = new int[n];
// Initialize the table[0] and table[1]
table[0] = gold[0];
table[1] = Math.max(gold[0], gold[1]);
// Fill remaining positions
for (int i = 2; i<n; i++)
table[i] = Math.max(gold[i]+table[i-2], table[i-1]);
return table[n-1];
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int gold[] = {3,8,10,4,2,3};
int n = gold.length;
System.out.print("Maximum gold looted = "+maxGold(gold,n));
}
}Maximum gold looted = 16
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity : T(n) = O(n), single traversal.
- Space Complexity : A(n) = O(n), for table[].
Space Optimized DP solution for House Robber
By carefully observing the tabulated DP solution, we deduce that only the last two indices (i-1 and i-2) are required to calculate the solution of the i-th subproblem. i.e. we need only table[i-2] and table[i-1] to calculate the value of table[i]. So, we eliminate the table[] array and replace it with two auxiliary variables.
Algorithm
- Define some base cases (for n = 0,1,2).
- return 0 for n = 0.
- Create two variables val1 and val2.
- assign val1 = gold[0] , value2 = max(gold[0], gold[1]).
- define a variable maxLoot to store the answer.
- Traverse the array from the second element to the end of the array.
- For every index = i, update maxLoot = max(val1 + gold[i],val2), this step defines the two cases, if an element is selected then the previous element cannot be selected and if an element is not selected then the previous element can be selected.
- Also, For every index, Update val1= val2 and val2 = maxLoot.
- return the final value of maxLoot, after the array traversal.
C++ Program
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxGold (int gold[],int n)
{
// base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return gold[0];
if (n == 2)
return max(gold[0], gold[1]);
// define and initialize val1 and val2
int val1 = gold[0];
int val2 = max(gold[0], gold[1]);
// define maxLoot to obtain maximum value of gold stolen
int maxLoot;
// traverse to find the final value of maxLoot
for (int i = 2; i<n; i++)
{
maxLoot = max(gold[i]+val1, val2);
val1 = val2;
val2 = maxLoot;
}
return maxLoot;
}
// main function to implement above function
int main()
{
int gold[] = {3,8,10,4,2,3};
int n = sizeof(gold)/sizeof(int);
cout<<"Maximum gold looted = "<<maxGold(gold,n);
return 0;
}Maximum gold looted = 16
Java Program
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class tutorialcup
{
static int maxGold (int gold[],int n)
{
// base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return gold[0];
if (n == 2)
return Math.max(gold[0], gold[1]);
// define and initialize val1 and val2
int val1 = gold[0];
int val2 = Math.max(gold[0], gold[1]);
int maxLoot = 0;
// traverse to find the final value of maxLoot
for (int i = 2; i<n; i++)
{
maxLoot = Math.max(gold[i]+val1, val2);
val1 = val2;
val2 = maxLoot;
}
return maxLoot;
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int gold[] = {3,8,10,4,2,3};
int n = gold.length;
System.out.print("Maximum gold looted = "+maxGold(gold,n));
}
}Maximum gold looted = 16
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity : T(n) = O(n), single traversal.
- Space Complexity : A(n) = O(1), used only two extra variables .