Table of Contents
What is Kruskal Algorithm?
Kruskal’s algorithm is used to find the minimum spanning tree(MST) of a connected and undirected graph.
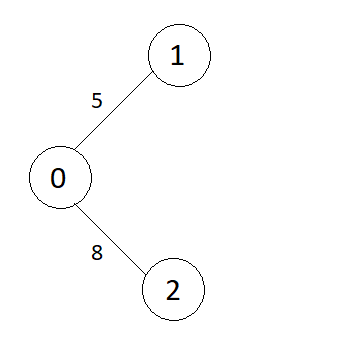
Example
Graph
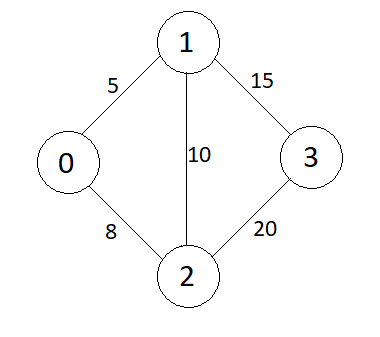
Minimum Spanning Tree(MST)
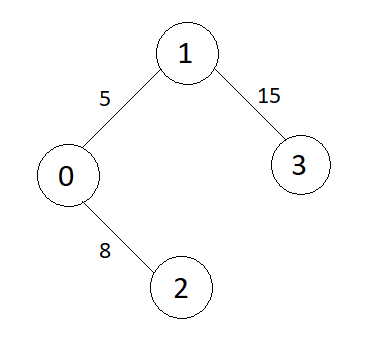
Algorithm
Kruskal’s algorithm is a greedy algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree.
- Sort the edges in ascending order according to their weights.
- At every step, choose the smallest edge(with minimum weight). If this edge forms a cycle with the MST formed so far, discard the edge, else, add it to the MST.
- Repeat step 2, until all the vertices are not present in MST.
Explanation
Consider the graph shown in above example,
The edges in the above graph are,
Edges = {{0 to 1, wt = 5}, {0 to 2, wt = 8}, {1 to 2, wt = 10}, {1 to 3, wt = 15}, {2 to 3, wt = 20}}
After sorting, edges are,
Edges = {{0 to 1 wt = 5}, {0 to 2, wt = 8}, {1 to 2, wt = 10}, {1 to 3, wt = 15}, {2 to 3, wt = 20}}
- {0 to 1, wt = 5}, include in MST

- {0 to 2, wt = 8}, include in MST

- {1 to 2, wt = 10}, forms a cycle, do not include in MST
- {1 to 3, wt = 15}, include in MST

All the vertices are included in MST, so we stop here.
JAVA Program For Kruskal Algorithm
public class KruskalAlgorithm {
// Function to find the set of element i
private static int find(Subset subsets[], int i) {
// Path Compression
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent = find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
// Function to perform union of two sets of x and y
private static void Union(Subset subsets[], int x, int y) {
int xRoot = find(subsets, x);
int yRoot = find(subsets, y);
// (Union by Rank)
if (subsets[xRoot].rank < subsets[yRoot].rank) {
subsets[xRoot].parent = yRoot;
} else if (subsets[xRoot].rank > subsets[yRoot].rank) {
subsets[yRoot].parent = xRoot;
} else {
// If rank are same, then make one as root and increment
// its rank by one
subsets[yRoot].parent = xRoot;
subsets[xRoot].rank++;
}
}
private static void findPrintMST(ArrayList<Edge> graph[], Edge edges[]) {
// Sort the edges in ascending order of their weights
Arrays.sort(edges, Edge.comp);
// Stores the mst
Edge mst[] = new Edge[graph.length - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length - 1; i++) {
mst[i] = new Edge(-1, -1, -1);
}
int e = 0; // Number of edges included in mst
// Create v subsets, v is the number of vertices
Subset subsets[] = new Subset[graph.length];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
subsets[i] = new Subset();
}
// Initialise parent of all as itself and rank as 0
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
subsets[i].parent = i;
subsets[i].rank = 0;
}
// One by one traverse all the edges
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
// Find the set of vertices present on this edge
int x = find(subsets, edges[i].from);
int y = find(subsets, edges[i].to);
// If the set is not same(that is, no cycle is formed)
// Add this edge to mst
if (x != y) {
mst[e].from = edges[i].from;
mst[e].to = edges[i].to;
mst[e].weight = edges[i].weight;
Union(subsets, x, y);
e++;
} else {
// Discard the edge
}
// If all the vertices are included in MST, stop here
if (e == graph.length - 1) {
break;
}
}
// Print the MST
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length - 1; i++) {
System.out.println("From " + mst[i].from + " to " + mst[i].to + " weight " + mst[i].weight);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Graph
ArrayList<Edge> graph[] = new ArrayList[4];
// Stores all the edges of the graph
Edge edges[] = new Edge[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
// Make the graph in given example
graph[0].add(new Edge(0, 1, 5));
graph[0].add(new Edge(0, 2, 8));
graph[1].add(new Edge(1, 0, 5));
graph[1].add(new Edge(1, 2, 10));
graph[1].add(new Edge(1, 3, 15));
graph[2].add(new Edge(2, 0, 8));
graph[2].add(new Edge(2, 1, 10));
graph[2].add(new Edge(2, 3, 20));
graph[3].add(new Edge(3, 1, 15));
graph[3].add(new Edge(3, 2, 20));
// Store all the edges of the graph
edges[0] = new Edge(0, 1, 5);
edges[1] = new Edge(0, 2, 8);
edges[2] = new Edge(1, 2, 10);
edges[3] = new Edge(1, 3, 15);
edges[4] = new Edge(2, 3, 20);
// Find MST using Kruskal's Algorithm and print it
findPrintMST(graph, edges);
}
static class Edge {
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
public static final Comparator<Edge> comp = new Comparator<Edge>() {
@Override
public int compare(Edge o1, Edge o2) {
// Sort according to edge weights
return Integer.compare(o1.weight, o2.weight);
}
};
}
// Subset class is used to detect cycle while adding an edge
static class Subset {
int parent;
int rank;
}
}C++ Program For Kruskal Algorithm
#include <iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// class representing an Edge of a graph
class Edge {
public:
int from;
int to;
int weight;
Edge(int f, int t, int w) {
from = f;
to = t;
weight = w;
}
};
// Subset class is used to detect cycle while adding an edge
class Subset {
public:
int parent;
int rank;
};
// Function to find the set of element i
int find(Subset subsets[], int i) {
// Path compression
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent = find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
// Function to perform union of two sets of x and y
void Union(Subset subsets[], int x, int y) {
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
// Union by Rank
if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank) {
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
} else if (subsets[xroot].rank > subsets[yroot].rank) {
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
} else {
// If ranks are same, then make one as root and
// increment its rank by one
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
void findPrintMST(vector<Edge> graph[], vector<Edge> &edges, int v) {
// Sort the edges in ascending order of their weights
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end(),
[](const Edge& lhs, const Edge& rhs) {
return lhs.weight < rhs.weight;
});
// Stores the mst
vector<Edge> mst;
int e = 0; // Number of edges included in mst
// Create v subsets, v is the number of vertices
Subset *subsets = new Subset[(v * sizeof(Subset))];
// Initialise parent of all as itself and rank as 0
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
subsets[i].parent = i;
subsets[i].rank = 0;
}
// One by one traverse all the edges
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
// Find the set of vertices present on this edge
int x = find(subsets, edges[i].from);
int y = find(subsets, edges[i].to);
// If the set is not same(that is, no cycle is formed)
// Add this edge to mst
if (x != y) {
Edge curr(edges[i].from, edges[i].to, edges[i].weight);
mst.push_back(curr);
Union(subsets, x, y);
e++;
} else {
// Discard the edge
}
// If all the vertices are included in MST, stop here
if (e == v - 1) {
break;
}
}
// Print the mst
for (int i = 0; i < mst.size(); i++) {
cout<<"From "<<mst[i].from<<" to "<<mst[i].to<<" weight "<<mst[i].weight<<endl;
}
}
int main() {
vector<Edge> graph[4];
vector<Edge> edges;
// Make the graph in given example
Edge e1(0, 1, 5);
Edge e2(0, 2, 8);
Edge e3(1, 0, 5);
Edge e4(1, 2, 10);
Edge e5(1, 3, 15);
Edge e6(2, 0, 8);
Edge e7(2, 1, 10);
Edge e8(2, 3, 20);
Edge e9(3, 1, 15);
Edge e10(3, 2, 20);
graph[0].push_back(e1);
graph[0].push_back(e2);
graph[1].push_back(e3);
graph[1].push_back(e4);
graph[1].push_back(e5);
graph[2].push_back(e6);
graph[2].push_back(e7);
graph[2].push_back(e8);
graph[3].push_back(e9);
graph[3].push_back(e10);
// Edges in the graph
edges.push_back(e1);
edges.push_back(e2);
edges.push_back(e4);
edges.push_back(e5);
edges.push_back(e8);
// Find MST using Kruskal's Algorithm and print it
findPrintMST(graph, edges, 4);
return 0;
}Output
From 0 to 1 weight 5 From 0 to 2 weight 8 From 1 to 3 weight 15
Time Complexity
O(E * log(E) + E * log (V)) where E denotes the Number of edges in the graph and V denotes the Number of vertices in the graph.