Quick Sort is a sorting algorithm. Given an unsorted array sort it using quick sort algorithm.
Example
Input: {8, 9, 5, 2, 3, 1, 4}
Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9}
Table of Contents
Theory
- It’s a Divide and Conquer sorting Algorithm.
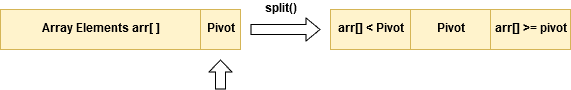
- It picks a pivot element in the array, splits the array into two parts. One part consists of array elements having a value less than the pivot, another part contains array elements greater than the pivot. It then places the pivot in between these parts and recursively sorts left and right subarrays.

- Pivot element can be selected in the following ways :
- first array element
- last array element (implemented here)
- median array element
- Any Array element.
- After selecting pivot we apply the split() function to split the rest of the array around the pivot.
- split() places array elements less than pivot towards left of the pivot
- split() places array elements greater than pivot towards the right of the pivot
- the left and right subarrays (of the pivot) may or may not be sorted
- we recursively sort left and right subarrays to obtain completely sorted array.
Quick Sort Algorithm
we mainly apply two functions
- split() – select pivot and split the array around the pivot, we select the last element as pivot.
- quickSortServe() – recursively sort left and right subarrays.

C++ Code for Quick Sort
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// funtion to split array around pivot
int split(int arr[],int lo,int hi)
{
int i = lo-1;
// select last element as pivot
int pivot = hi;
// All elements less than arr[pivot] are brought to left side
// This splits array into two parts
// array -> [left subarr] [pivot] [right subarr]
for(int j=lo;j<pivot;j++)
{
if(arr[j] < arr[pivot])
{
i++;
swap(arr[i],arr[j]);
}
}
// Bring pivot element to it's correct postion in sorted array
// by swapping smallest element of right subarray with pivot
swap(arr[i+1],arr[pivot]);
return i+1;
}
// Service function to recursively perfrom split()
// for left and right subarrays
void quickSortServe(int arr[],int lo,int hi)
{
if(lo < hi)
{
int pivot = split(arr,lo,hi);
// recursively perfrom split() for right and left subarrays
quickSortServe(arr,lo,pivot-1);
quickSortServe(arr,pivot+1,hi);
}
}
// Function to implement quick sort algorithm
void quickSort(int arr[],int size)
{
quickSortServe(arr,0,size-1);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {8,9,5,2,3,1,4};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
quickSort(arr,n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}Output
1 2 3 4 5 8 9
Java Code for Quick Sort
import java.io.*;
class QSort
{
int split(int arr[],int lo,int hi)
{
int i = lo-1;
// select last element as pivot
int pivot = hi;
// All elements less than arr[pivot] are brought to left side
// This splits array into two parts
// array -> [left subarr] [pivot] [right subarr]
for(int j=lo;j<pivot;j++)
{
if(arr[j] < arr[pivot])
{
i++;
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[pivot];
arr[pivot] = temp;
}
}
// Bring pivot element to it's correct postion in sorted array
// by swapping smallest element of right subarray with pivot
int temp = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = arr[pivot];
arr[pivot] = temp;
return i+1;
}
// Service function to recursively perfrom split()
// for left and right subarrays
void quickSortServe(int arr[],int lo,int hi)
{
if(lo < hi)
{
int pivot = split(arr,lo,hi);
// recursively perfrom split() for right and left subarrays
quickSortServe(arr,lo,pivot-1);
quickSortServe(arr,pivot+1,hi);
}
}
// Function to implement quick sort algorithm
void quickSort(int arr[],int size)
{
quickSortServe(arr,0,size-1);
}
// main function
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = {8,9,5,2,3,1,4};
int n = arr.length;
QSort obj = new QSort();
obj.quickSort(arr,n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
}Output
1 2 3 4 5 8 9
Complexity Analysis of Quick Sort
Time Complexity
- Best case: O(nlogn)
- Worst case: O(n2)
- Average case: O(nlogn)
Supplementary Information
- Quicksort is not a stable sorting algorithm.
- Quicksort is an in-place sorting algorithm – doesn’t require auxiliary space.
- In Practice, quicksort is faster than Merge and Heap sort in cases where data is small and/or stored in external storage space.
- Quicksort performs better than Merge sort in case of arrays and requires no extra space for sorting purposes.
- It is also a cache-friendly sorting algorithm as it has a good locality of reference when used for arrays.
- It is also tail recursive, therefore tail-call optimizations are done.
- Merge Sort is preferred over Quick sort for sorting linked lists.