Before we proceed, we first know what BT really is? Binary Tree is a type of data structure that is hierarchical in nature. A BT is represented by nodes where every node has left, a right pointer, and data as the weight of node. Each node can contain a maximum of 2 children which refer to the left and right child of a parent node.

Table of Contents
Why we need Binary Trees? | Why we use binary Trees?
- Using BT we can do fast search, insertion, and deletion on data(given in some priority order… like BST).
- Using BT we can also find the closest item.
- Store the data in a hierarchical manner(Ex. File system in the computer).
- Implement BT using pointer which takes less time to perform any action.
- Implement dictionaries with prefix lookup.
- Fast search in the fixed text of the given dataset.
Properties of Binary Trees
- Maximum number of nodes at any level: 2^L where L is a number of levels (0<=L<=H).
- Minimum and maximum number of nodes in a BT of height H: Minimum- H+1 and Maximum- 2^(H+1) – 1 where level 0 as height 0.
- Minimum possible height of a given BT having N nodes: log2(N+1)-1 where level 0 as height 0.
- Total number of leaf nodes: Total number of nodes with 2 children + 1.
- Minimum number of levels of a BT having L leaf nodes: (log2 L) +1.
Types of Binary Trees
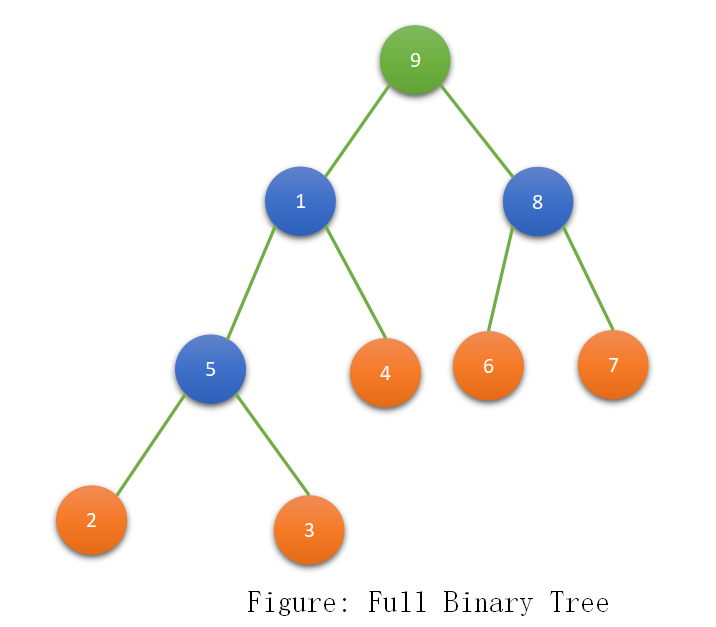
Full Binary Trees
A Binary Tree whose root and intermediate nodes have 2 child nodes. In other words, we can also say that except leaf nodes every node has 2 child nodes.
Note: Number of leaf nodes in a full binary tree: Number of internal nodes+1.
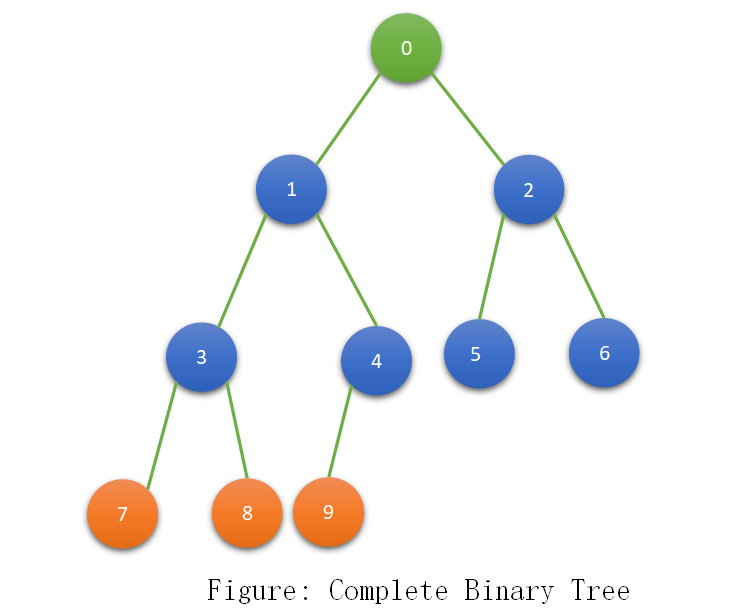
Complete Binary Tree
A Binary Tree whose all levels except the last level are totally filled and all nodes are filled from left to right
Note: Binary Heap is an example of a complete binary tree.
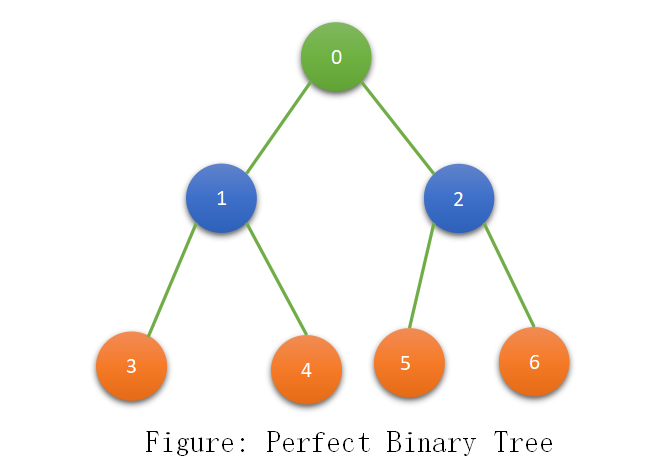
Perfect Binary Tree
A Binary Tree whose internal nodes and root node have 2 children and all leaf at the same level.
Note: Total number of nodes in Perfect Binary Tree: 2^H -1 where H is the height of BT.
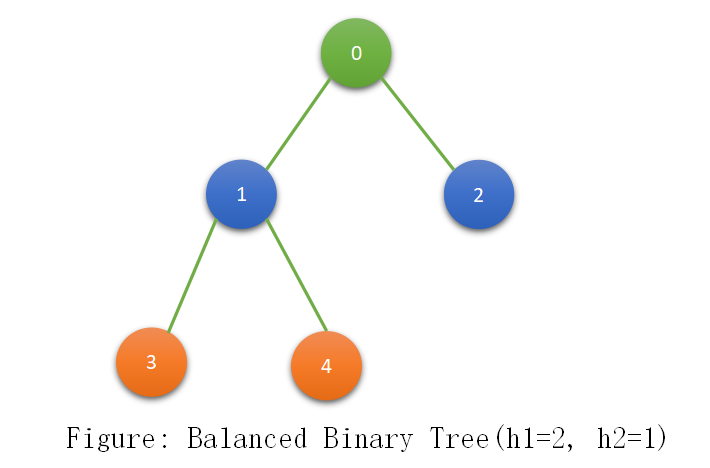
Balanced Binary Tree
A Binary Tree whose left subtree height h1 and right subtree height h2 then |h1-h2| <= 1.
Note: AVL and R-B tree maintain a balanced binary tree.
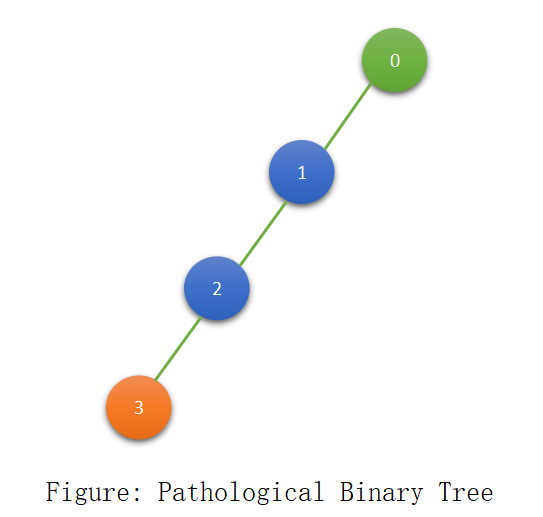
Pathological Binary Tree (Skewed BT/ Degenerate BT)
A Binary Tree whose all internal nodes have only one child may be left child or it may be a right child.
Note: Pathological BT Height: Number of nodes-1.