In the interval tree problem, we have given a set of intervals and three types of queries
- addInterval(x,y): Add an interval (x,y) to the set
- removeInterval(x,y): Remove an interval (x,y) from the set
- checkInterval(x,y): Check if interval (x,y) overlaps with some existing interval
Design a data structure( Interval Tree ) to perform the above mentioned 3 operations.
Table of Contents
Example
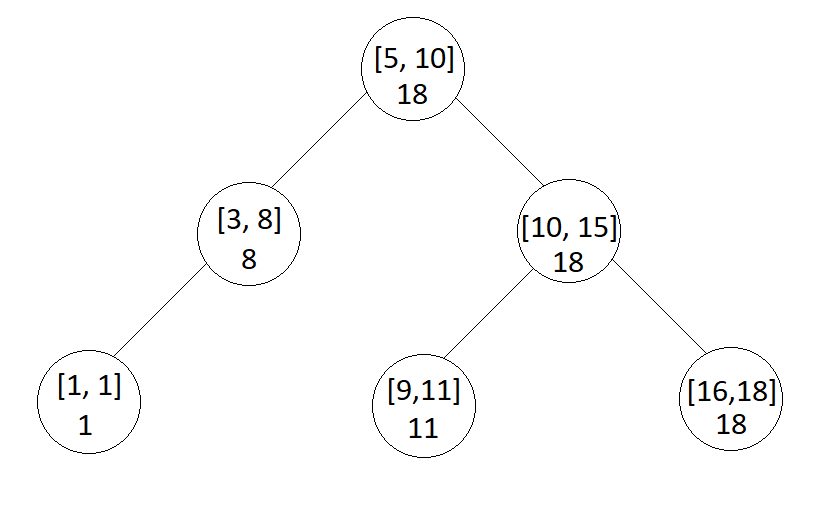
Input
Insert(5, 10)
Insert(3, 8)
Insert(10, 15)
Insert(16, 18)
Insert(9, 11)
Insert(1, 1)
CheckOverlap(1, 2)
CheckOverlap(7, 11)
CheckOverlap(20, 25)
Delete(1, 1)
Delete(10, 15)
CheckOverlap(12, 14)
CheckOverlap(8, 15)
CheckOverlap(1, 2)
Delete(5, 10)
Delete(1, 2)
Delete(8, 15)
Output
true
true
false
false
true
false
Algorithm for Interval Tree
The idea is to use an augmented self balancing Binary Tree. Every node stores the following information
- An interval [l, r], where l is the starting point of the interval, and r is the ending point of the interval.
- max, the maximum ending point in the left and right subtree rooted with this node.
Insertion and Deletion
The starting point (l) of the interval is used to maintain the order in self balancing Binary Search Tree.
Insert and Delete are operations are performed the same as general self-balancing Binary Search Tree.
Overlap Searching
Search if an interval I(x, y) overlaps with some interval in the self-balancing Binary Search Tree,
- Start from the root, if I(x, y) overlaps with root, return root.
- If the max value of the current node is greater than the starting point of I, search in the left subtree.
- Else search in the right subtree.
JAVA Code for Interval Tree
public class IntervalTree {
// class representing the node of interval tree
static class Node {
int l;
int r;
int max;
Node left, right;
public Node(int l, int r) {
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
this.max = r;
}
}
// Function to insert an interval in interval tree
public static Node insert(Node root, int l, int r) {
// Insert like normal BST, by considering root.l as the key element
if (root == null) {
return new Node(l, r);
}
if (l < root.l) {
root.left = insert(root.left, l, r);
} else if (l > root.l) {
root.right = insert(root.right, l, r);
} else {
if (r < root.r) {
root.left = insert(root.left, l, r);
} else {
root.right = insert(root.right, l, r);
}
}
// If current node's max is less than r, then update max
if (root.max < r) {
root.max = r;
}
return root;
}
private static boolean checkOverlap(Node root, int l, int r) {
// If current node is null, return false
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
// If overlaps return true
if (root.l <= r && l <= root.r) {
return true;
}
// If max value of current is greater than starting point of I(l)
// search in left subtree
if (root.left != null && root.left.max >= l) {
return checkOverlap(root.left, l, r);
}
// Else search in right subtree
return checkOverlap(root.right, l, r);
}
// Function to delete a binary tree, same as normal delete in a BST
private static Node delete(Node root, int l, int r) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (l < root.l) {
root.left = delete(root.left, l, r);
} else if (l > root.l) {
root.right = delete(root.right, l, r);
} else {
if (r < root.r) {
root.left = delete(root.left, l, r);
} else if (r > root.r) {
root.right = delete(root.right, l, r);
} else {
if (root.left == null)
return root.right;
else if (root.right == null)
return root.left;
// Find the minimum value in the right subtree of root
Node curr = root.right;
while (curr.left != null) {
curr = curr.left;
}
root.l = curr.l;
root.r = curr.r;
root.right = delete(root.right, root.l, root.r);
}
}
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 5, 10);
root = insert(root, 3, 8);
root = insert(root, 10, 15);
root = insert(root, 16, 18);
root = insert(root, 9, 11);
root = insert(root, 1, 1);
System.out.println(checkOverlap(root, 1, 2));
System.out.println(checkOverlap(root, 7, 11));
System.out.println(checkOverlap(root, 20, 25));
root = delete(root, 1, 1);
root = delete(root,10, 15);
System.out.println(checkOverlap(root, 12, 14));
System.out.println(checkOverlap(root, 1, 2));
System.out.println(checkOverlap(root, 8, 15));
}
}true true false false false true
C++ Code for Interval Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// class representing the node of interval tree
class Node {
public:
int l, r, max;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int lVal, int rVal) {
l = lVal;
r = rVal;
max = rVal;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to create a new Node
Node* newNode(int l, int r) {
Node* node = new Node(l, r);
return node;
}
// Function to insert an interval in interval tree
Node* insert(Node* root, int l, int r) {
if (root == NULL) {
return newNode(l, r);
}
if (l < root->l) {
root->left = insert(root->left, l , r);
} else if (l > root->l) {
root->right = insert(root->right, l, r);
} else {
if (r < root->r) {
root->left = insert(root->left, l, r);
} else {
root->right = insert(root->right, l, r);
}
}
// If current node's max is less than r, then update max
if (root->max < r) {
root->max = r;
}
return root;
}
bool checkOverlap(Node *root, int l, int r) {
// If current node is null, return false
if (root == NULL) {
return false;
}
// If overlaps return true
if (root->l <= r && l <= root->r) {
return true;
}
// If max value of current is greater than starting point of I(l)
// search in left subtree
if (root->left != NULL && root->left->max >= l) {
return checkOverlap(root->left, l, r);
}
// Else search in right subtree
return checkOverlap(root->right, l, r);
}
// Function to delete a binary tree, same as normal delete in a BST
Node* deleteInterval(Node* root, int l, int r) {
if (root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (l < root->l) {
root->left = deleteInterval(root->left, l, r);
} else if (l > root->l) {
root->right = deleteInterval(root->right, l, r);
} else {
if (r < root->r) {
root->left = deleteInterval(root->left, l, r);
} else if (r > root->r) {
root->right = deleteInterval(root->right, l, r);
} else {
// This is the interval to be deleted
if (root->left == NULL)
return root->right;
else if (root->right == NULL)
return root->left;
// Find the minimum value in the right subtree of root
Node* curr = root->right;
while (curr->left != NULL) {
curr = curr->left;
}
root->l = curr->l;
root->r = curr->r;
root->right = deleteInterval(root->right, root->l, root->r);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
Node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 5, 10);
root = insert(root, 3, 8);
root = insert(root, 10, 15);
root = insert(root, 16, 18);
root = insert(root, 9, 11);
root = insert(root, 1, 1);
if (checkOverlap(root, 1, 2))
cout<<"true"<<endl;
else
cout<<"false"<<endl;
if (checkOverlap(root, 7, 11))
cout<<"true"<<endl;
else
cout<<"false"<<endl;
if (checkOverlap(root, 20, 25))
cout<<"true"<<endl;
else
cout<<"false"<<endl;
root = deleteInterval(root, 1, 1);
root = deleteInterval(root,10, 15);
if (checkOverlap(root, 12, 14))
cout<<"true"<<endl;
else
cout<<"false"<<endl;
if (checkOverlap(root, 8, 15))
cout<<"true"<<endl;
else
cout<<"false"<<endl;
if (checkOverlap(root, 1, 2))
cout<<"true"<<endl;
else
cout<<"false"<<endl;
return 0;
}true true false false true false
Complexity Analysis for Interval Tree
For insertion and deletion:
Time Complexity= O(h), where h is the height of BST (Binary Search Tree) and for a balanced BST h is log(n).
For searching:
Time Complexity = O(h), where h is the height of BST(Binary Search Tree) and for a balanced BST h is log(n).