In sorted linked list to balanced BST problem, we have given a singly Linked list in sorted order, construct a Balanced Binary Tree from the singly Linked List.
Table of Contents
Examples
Input
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
Output
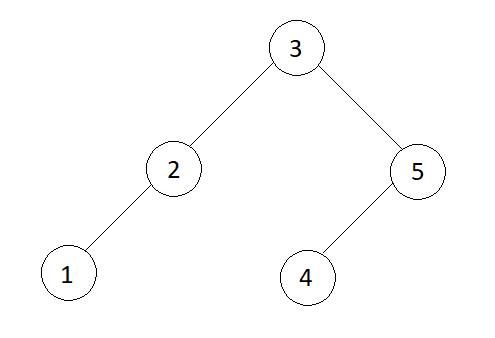
Pre-order : 3 2 1 5 4
Input
7 -> 11 -> 13 -> 20 -> 22 -> 41
Output
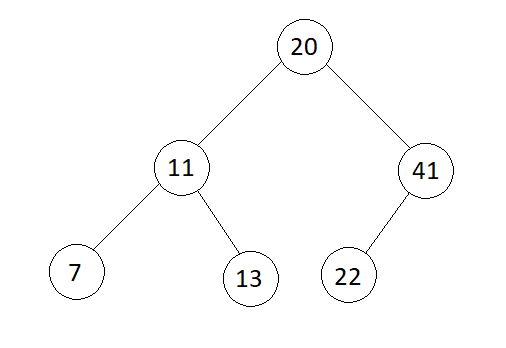
Pre-order : 20 11 7 13 41 22
Naive Approach
If we look closely, we can see that the middle node of the linked list is always the root of BST, and the elements present before the middle node forms the left sub-tree and elements present after middle node forms the right sub-tree.
So by repeating the above approach recursively on the left and right sub-tree also, we can form the Balanced Binary Search Tree.
- Traverse the linked list and find the middle element. Allocate memory for it and make it the root.
- Recursively do this for the left half, find the middle make it root, and repeat. Assign the root of the left half to the root’s left.
- Recursively do this for the right half also, find the middle make it root and repeat. Assign the root of the right half to the root’s right.
Time Complexity = O(n log(n))
Space Complexity = O(n), due to recursion
where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
JAVA Code to convert Sorted Linked List to Balanced BST
public class SortedLinkedListToBalancedBST {
// class representing node of a linked list
static class ListNode {
int data;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// class representing node of a tree
static class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode left, right;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// function to print the pre order traversal of a tree
private static void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
private static TreeNode convertToBalancedBST(ListNode node) {
// if the node is null, return null
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
// Count the number of nodes in the linked list
ListNode temp = node;
int n = 0;
while (temp != null) {
temp = temp.next;
n++;
}
if (n == 1) {
return new TreeNode(node.data);
}
// First n/2 nodes contributes to the left subtree
ListNode leftHalf = new ListNode(node.data);
ListNode leftTemp = leftHalf;
for (int i = 0; i < n/2 - 1; i++) {
node = node.next;
leftTemp.next = new ListNode(node.data);
leftTemp = leftTemp.next;
}
node = node.next;
// node is pointing to the middle element of the list
// make this element as the root of the BST
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(node.data);
// move node ahead
node = node.next;
// Remaining nodes form the right subtree of the BST
ListNode rightHalf = null;
if (node != null) {
rightHalf = new ListNode(node.data);
ListNode rightTemp = rightHalf;
node = node.next;
while (node != null) {
rightTemp.next = new ListNode(node.data);
rightTemp = rightTemp.next;
node = node.next;
}
}
// Recursively call the method for left and right halfs
root.left = convertToBalancedBST(leftHalf);
root.right = convertToBalancedBST(rightHalf);
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1);
node1.next = new ListNode(2);
node1.next.next = new ListNode(3);
node1.next.next.next = new ListNode(4);
node1.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(5);
TreeNode root1 = convertToBalancedBST(node1);
preOrder(root1);
System.out.println();
// Example 2
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(7);
node2.next = new ListNode(11);
node2.next.next = new ListNode(13);
node2.next.next.next = new ListNode(20);
node2.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(22);
node2.next.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(41);
TreeNode root2 = convertToBalancedBST(node2);
preOrder(root2);
System.out.println();
}
}3 2 1 5 4 20 11 7 13 41 22
C++ Code to convert Sorted Linked List to Balanced BST
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// class representing node of a linked list
class ListNode {
public:
int data;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int d) {
data = d;
}
};
// class representing node of a tree
class TreeNode {
public:
int data;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int d) {
data = d;
}
};
// function to print the pre order traversal of a tree
void preOrder(TreeNode *root) {
if (root != NULL) {
cout<<root->data<<" ";
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
TreeNode* convertToBalancedBST(ListNode *node) {
// if the node is null, return null
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// Count the number of nodes in the linked list
ListNode *temp = node;
int n = 0;
while (temp != NULL) {
n++;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (n == 1) {
return new TreeNode(node->data);
}
// First n/2 nodes contributes to the left subtree
ListNode *leftHalf = new ListNode(node->data);
ListNode *leftTemp = leftHalf;
for (int i = 0; i < n/2 - 1; i++) {
node = node->next;
leftTemp->next = new ListNode(node->data);
leftTemp = leftTemp->next;
}
node = node->next;
// node is pointing to the middle element of the list
// make this element as the root of the BST
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(node->data);
// move node ahead
node = node->next;
// Remaining nodes form the right subtree of the BST
ListNode *rightHalf = NULL;
if (node != NULL) {
rightHalf = new ListNode(node->data);
ListNode *rightTemp = rightHalf;
node = node->next;
while (node != NULL) {
rightTemp->next = new ListNode(node->data);
rightTemp = rightTemp->next;
node = node->next;
}
}
// Recursively call the method for left and right halfs
root->left = convertToBalancedBST(leftHalf);
root->right = convertToBalancedBST(rightHalf);
return root;
}
int main() {
// Example 1
ListNode *node1 = new ListNode(1);
node1->next = new ListNode(2);
node1->next->next = new ListNode(3);
node1->next->next->next = new ListNode(4);
node1->next->next->next->next = new ListNode(5);
TreeNode *root1 = convertToBalancedBST(node1);
preOrder(root1);
cout<<endl;
// Example 2
ListNode *node2 = new ListNode(7);
node2->next = new ListNode(11);
node2->next->next = new ListNode(13);
node2->next->next->next = new ListNode(20);
node2->next->next->next->next = new ListNode(22);
node2->next->next->next->next->next = new ListNode(41);
TreeNode *root2 = convertToBalancedBST(node2);
preOrder(root2);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}3 2 1 5 4 20 11 7 13 41 22
Optimal Approach
The above approach can be optimized if we build the tree starting from the leaf nodes to the root of the tree.
The idea is to build the left sub-tree, then root and then right sub-tree and attach those left and right sub-tree to the root.
- Count the number of nodes in the given linked list. Let it be n.
- Then repeat steps 3 to 5.
- The first n/2 nodes form the left sub-tree, recursively call the steps 3 to 5 to form the left sub-tree from the first n/2 nodes.
- The next node after n/2 nodes forms the root of the BST.
- The remaining nodes from the right sub-tree, recursively call steps 3 to 5 to form the right sub-tree from remaining nodes.
- Attach the left and right sub-tree with the root.
Time Complexity = O(n)
Space Complexity = O(n), due to recursion
where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
JAVA Code to convert Sorted Linked List to Balanced BST
public class SortedLinkedListToBalancedBST {
// class representing node of a linked list
static class ListNode {
int data;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// class representing node of a tree
static class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode left, right;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private static ListNode globalNode = null;
// function to print the pre order traversal of a tree
private static void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
private static TreeNode convertToBalancedBST(ListNode node) {
// Count the number of nodes in the list
int n = 0;
ListNode temp = node;
while (temp != null) {
n++;
temp = temp.next;
}
// this to use the node by reference
globalNode = node;
return convertToBalancedBSTRecursive(n);
}
private static TreeNode convertToBalancedBSTRecursive(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return null;
}
// recursively construct the left subtree
// left subtree contains n/2 nodes
TreeNode leftSubTree = convertToBalancedBSTRecursive(n/2);
// construct the root node
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(globalNode.data);
// move one step ahead
globalNode = globalNode.next;
// link the left subtree with root
root.left = leftSubTree;
// construct right subtree and link it with root
// right subtree contains (n - n/2 - 1) nodes
root.right = convertToBalancedBSTRecursive(n - n/2 - 1);
// return the root
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1);
node1.next = new ListNode(2);
node1.next.next = new ListNode(3);
node1.next.next.next = new ListNode(4);
node1.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(5);
TreeNode root1 = convertToBalancedBST(node1);
preOrder(root1);
System.out.println();
// Example 2
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(7);
node2.next = new ListNode(11);
node2.next.next = new ListNode(13);
node2.next.next.next = new ListNode(20);
node2.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(22);
node2.next.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(41);
TreeNode root2 = convertToBalancedBST(node2);
preOrder(root2);
System.out.println();
}
}3 2 1 5 4 20 11 7 13 41 22
C++ Code to convert Sorted Linked List to Balanced BST
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// class representing node of a linked list
class ListNode {
public:
int data;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int d) {
data = d;
}
};
// class representing node of a tree
class TreeNode {
public:
int data;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int d) {
data = d;
}
};
ListNode *globalNode = NULL;
// function to print the pre order traversal of a tree
void preOrder(TreeNode *root) {
if (root != NULL) {
cout<<root->data<<" ";
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
TreeNode* convertToBalancedBSTRecursive(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return NULL;
}
// recursively construct the left subtree
// left subtree contains n/2 nodes
TreeNode *leftSubTree = convertToBalancedBSTRecursive(n/2);
// construct the root node
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(globalNode->data);
// move one step ahead
globalNode = globalNode->next;
// link the left subtree with root
root->left = leftSubTree;
// construct right subtree and link it with root
// right subtree contains (n - n/2 - 1) nodes
root->right = convertToBalancedBSTRecursive(n - n/2 - 1);
// return the root
return root;
}
TreeNode* convertToBalancedBST(ListNode *node) {
// Count the number of nodes in the list
int n = 0;
ListNode *temp = node;
while (temp != NULL) {
n++;
temp = temp->next;
}
globalNode = node;
return convertToBalancedBSTRecursive(n);
}
int main() {
// Example 1
ListNode *node1 = new ListNode(1);
node1->next = new ListNode(2);
node1->next->next = new ListNode(3);
node1->next->next->next = new ListNode(4);
node1->next->next->next->next = new ListNode(5);
TreeNode *root1 = convertToBalancedBST(node1);
preOrder(root1);
cout<<endl;
// Example 2
ListNode *node2 = new ListNode(7);
node2->next = new ListNode(11);
node2->next->next = new ListNode(13);
node2->next->next->next = new ListNode(20);
node2->next->next->next->next = new ListNode(22);
node2->next->next->next->next->next = new ListNode(41);
TreeNode *root2 = convertToBalancedBST(node2);
preOrder(root2);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}3 2 1 5 4 20 11 7 13 41 22