In binary tree to binary search tree conversion problem, we have given a binary tree convert it to Binary Search Tree without changing the structure of the tree.
Table of Contents
Example
Input
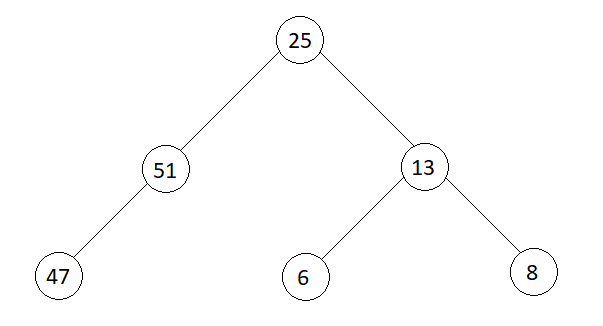
Output
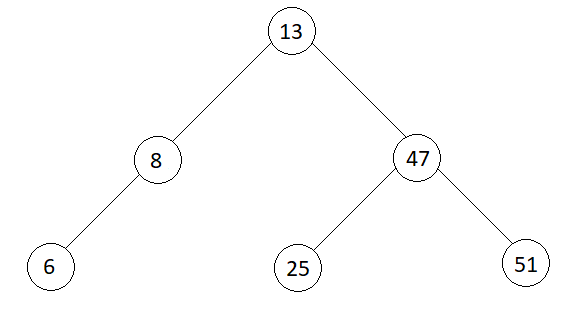
pre-order : 13 8 6 47 25 51
Algorithm
We do not have to change the structure of the binary tree and convert it to Binary Search Tree. Note the property of a Binary Search Tree that the inorder traversal of a Binary Search Tree leads to the sorted data. We will use this property to achieve the desired result.
The idea is to store the inorder traversal of Binary Tree into an array, sort the array and then traverse the array and Binary Tree(in inorder form) and replace every node in the Binary Tree with the corresponding element in the array. This will convert the Binary Tree to Binary Search Tree.
- Create an array, named inOrder.
- Traverse the given Binary Tree in in-order form and store the value of nodes in the array ‘inOrder’.
- Sort the array.
- Simultaneously traverse the array and Binary Tree in in-order form and replace the corresponding node’s value in Binary Tree with the value in inOrder array.
- The Binary Tree is converted to Binary Search Tree.
Time Complexity = O(n log(n))
Space Complexity = O(n), as we used an array to store the in-order traversal
where n is the number of node in given Binary Tree.
Explanation
Consider the binary tree shown in the example above.
Step 1 & 2
Store the in-order traversal of Binary Tree in an array.
inOrder[] = {47, 51, 25, 6, 13, 8}
Step 3
Sort the array.
inOrder = {6, 8, 13, 25, 47, 51}
Step 4
Simultaneously traverse the array and Binary Tree and replace the element of a binary tree with the corresponding element of the sorted inOrder array.
The Binary Tree now looks like,

The Binary Tree is converted to Binary Search Tree.
JAVA Code for Binary Tree to Binary Search Tree Conversion
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class BinaryTreeToBinarySearchTreeConversion {
// class representing Node of a Binary Tree
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// class to provide a wrapper around index
// so that we can pass it by reference
static class Index {
int index;
public Index(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
}
// function to print pre order traversal of a binary tree
private static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
// function to traverse in binary tree in in-order form and store the elements
// in a list
private static void inOrderAndFormList(Node root, ArrayList<Integer> inorder) {
if (root != null) {
inOrderAndFormList(root.left, inorder);
// store the current value in the list
inorder.add(root.data);
inOrderAndFormList(root.right, inorder);
}
}
// function to traverse in binary tree in in-order form and
// change the value of elements accordingly
private static void inOrderAndChange(Node root, ArrayList<Integer> inOrder, Index index) {
if (root != null) {
inOrderAndChange(root.left, inOrder, index);
// change the current element of Tree with current element of list
root.data = inOrder.get(index.index);
// increment index by 1
index.index++;
inOrderAndChange(root.right, inOrder, index);
}
}
private static void convertToBST(Node root) {
// create a list and store the inorder of the given Binary Tree
ArrayList<Integer> inOrder = new ArrayList<>();
inOrderAndFormList(root, inOrder);
// Sort the list
Collections.sort(inOrder);
// traverse in binary tree and list simultaneously and change the required values
inOrderAndChange(root, inOrder, new Index(0));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example Tree
Node root = new Node(25);
root.left = new Node(51);
root.right = new Node(13);
root.left.left = new Node(47);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(8);
convertToBST(root);
preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
}
}13 8 6 47 25 51
C++ Code for Binary Tree to Binary Search Tree Conversion
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// class representing Node of a Binary Tree
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
}
};
// global variable index
int index = 0;
void preOrder(Node *root) {
if (root != NULL) {
cout<<root->data<<" ";
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
// function to traverse in binary tree in in-order form and store the elements
// in a list
void inOrderAndFormList(Node *root, vector<int> &inOrder) {
if (root != NULL) {
inOrderAndFormList(root->left, inOrder);
// store the current value in the list
inOrder.push_back(root->data);
inOrderAndFormList(root->right, inOrder);
}
}
// function to traverse in binary tree in in-order form and
// change the value of elements accordingly
void inOrderAndChange(Node *root, vector<int>& inOrder) {
if (root != NULL) {
inOrderAndChange(root->left, inOrder);
// change the current element of Tree with current element of list
root->data = inOrder[index];
index++;
inOrderAndChange(root->right, inOrder);
}
}
void convertToBST(Node *root) {
// create a list and store the inorder of the given Binary Tree
vector<int> inOrder;
inOrderAndFormList(root, inOrder);
// Sort the list
sort(inOrder.begin(), inOrder.end());
// traverse in binary tree and list simultaneously and change the required values
index = 0;
inOrderAndChange(root, inOrder);
}
int main() {
// Example Tree
Node *root = new Node(25);
root->left = new Node(51);
root->right = new Node(13);
root->left->left = new Node(47);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(8);
convertToBST(root);
preOrder(root);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}13 8 6 47 25 51