Table of Contents
Java LinkedBlockingDeque
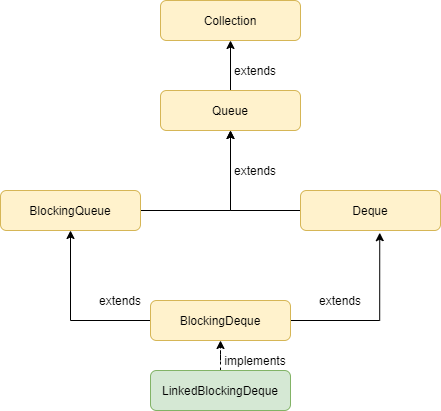
LinkedBlockingDeque is a class in Java that implements the BlockingDeque interface. It is part of the Collections framework and is present in java.util.concurrent package. It internally stores elements in the form of linked nodes or LinkedList data structure. A LinkedBlockingDeque blocks the thread during insertion operation if the queue reaches its maximum capacity. Similarly, it blocks during deletion operation if the queue is empty. We can specify the capacity in the constructor else it denotes capacity with value as Integer.MAXVALUE.
Constructor in Java LinkedBlockingDeque
Below are the constructors present in the LinkedBlockingDeque class
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| LinkedBlockingDeque() | Creates an empty LinkedBlockingDeque with capacity as Integer.MAX_VALUE |
| LinkedBlockingDeque(int capacity) | Creates an empty LinkedBlockingDeque with the specified capacity |
| LinkedBlockingDeque(Collection c) | Creates a LinkedBlockingDeque with the specified elements in the Collection |
Methods in LinkedBlockingDeque
LinkedBlockingDeque imports the methods from BlockingDeque, Deque, Collections, and Abstract Collection interfaces.
| Method | Description | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Boolean add(Element e) | Adds the specified element to the end of the deque. | e - the element to be added. Return value - True |
| Boolean addAll(Collection c) | Adds a collection of specified elements to the deque. | c - collection of elements to be added Return value - true |
| void addFirst(Element e) | Inserts an element at the beginning of the deque | e - the element to be inserted |
| void addLast(Element e) | Inserts an element at the end of the deque | e - the element to be inserted |
| Boolean contains(Object o) | Checks if the deque contains the specified element | Return value - true if the deque contains the element |
| int drainTo(Collection c) | Removes the elements from the deque and adds it to the specified collection | |
| Object element() | Returns the first element(head) in the deque | |
| Object getFirst() | Returns the first element(head) in the deque | |
| Object getLast() | Returns the last element(tail) in the deque | |
| Iterator iterator() | Retrieves the iterator of deque in sequence | Return value - Iterator |
| Boolean offer(Object e) | Inserts the element as the tail | e - element to be added |
| Boolean offerFirst(Object e) | Inserts the element at the front of the deque | e - element to be added |
| Boolean offerLast(Object e) | Inserts the element at the end of the deque | e - element to be added |
| Object peek() | Retrieves the first element of the deque(head) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object peekFirst() | Retrieves the first element of the deque(head) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object peekLast() | Retrieves the last element of the deque(tail) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object poll() | Retrieves and removes the first element of the deque(head) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object pollFirst() | Retrieves and removes the first element of the deque(head) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object pollLast() | Retrieves and removes the last element of the deque(tail) | Returns null if the deque is empty |
| Object pop() | Retrieves or removes the first element from the stack of the deque | |
| void push(Object e) | Inserts the element to the front of the deque | e - the element to be added |
| void put(Object e) | Inserts the specified element into the deque | e - element to be inserted |
| void putFirst(Object e) | Inserts the specified element at the beginning of the deque | e - element to be inserted |
| void putLast(Object e) | Inserts the specified element at the end of the deque | e - element to be inserted |
| Object remove() | Removes the first element from the deque | |
| Boolean remove(Object o) | Removes the first occurrence of the specified object from the deque if present | o - The element that needs to be removed Return value - true if deque contains the element |
| Object removeFirst() | Removes the first element of the deque | |
| Boolean removeFirstOccurence(Object e) | Removes the first occurrence of the element specified in the deque | e - the element to be removed |
| Object removeLast() | Removes the last element from the deque | |
| Boolean removeLastOccurence(Object e) | Removes the last occurrence of the specified element from the deque | e - the element to be removed |
| int size() | Fetches the size of the deque | Return value - size of the deque |
| Element take() | Retrieves and removes the head element from the deque | Return value - the head element that is removed from the deque |
| Element takeFirst() | Retrieves and removes the first element from the deque | Return value - the first element that is removed from the deque |
| Element takeLast() | Removes the last element from the deque | Return value - the last element present in the deque |
Java LinkedBlockingDeque Examples
In this section, we will see various Java examples using the methods of the LinkedBlockingDeque class.
Example: Add elements
This example shows how to add elements using the various methods present in LinkedBlockingDeque. The add(), addFirst(), push(), offerFirst(), putFirst() methods insert the element at the beginning of the Deque. The addLast(), offerLast(), putLast(), offer() and put() inserts the element at the end.
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class LinkedBlockingDequeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer> lbq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer>(12);
lbq.add(10);
lbq.add(20);
lbq.addFirst(30);
lbq.addLast(40);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using add operations: " + lbq);
lbq.offer(50);
lbq.offerFirst(60);
lbq.offerLast(70);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using offer operations: " + lbq);
lbq.push(80);
lbq.put(90);
lbq.putFirst(100);
lbq.putLast(110);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using put operations: " + lbq);
System.out.println("Size of LinkedBlockingDeque: " + lbq.size());
System.out.println("Remaining capacity: " + lbq.remainingCapacity());
}
}
Elements inserted using add operations: [30, 10, 20, 40] Elements inserted using offer operations: [60, 30, 10, 20, 40, 50, 70] Elements inserted using put operations: [100, 80, 60, 30, 10, 20, 40, 50, 70, 90, 110] Size of LinkedBlockingDeque: 11 Remaining capacity: 1
Example: Remove elements
The below example demonstrates how to remove elements from the LinkedBlockingDeque using various methods. The remove(), removeFirst(), poll(), pollFirst(), take(), takeFirst() operations remove the head element from the queue. The removeLast(), pollLast() and takeLast() methods retrieve and remove the last element from the queue.
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class LinkedBlockingDequeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer> lbq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer>(12);
lbq.add(10);
lbq.add(20);
lbq.addFirst(30);
lbq.addLast(40);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using add operations: " + lbq);
lbq.offer(50);
lbq.offerFirst(60);
lbq.offerLast(70);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using offer operations: " + lbq);
lbq.push(80);
lbq.put(90);
lbq.putFirst(100);
lbq.putLast(110);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using put operations: " + lbq);
System.out.println("Size of LinkedBlockingDeque: " + lbq.size());
System.out.println("Remaining capacity: " + lbq.remainingCapacity());
System.out.println("Removing elements....");
lbq.remove();
lbq.remove(40);
lbq.removeFirst();
lbq.removeLast();
System.out.println("Elements in queue after remove operations: " + lbq);
lbq.poll();
lbq.pollFirst();
lbq.pollLast();
System.out.println("Elements in queue after poll operations: " + lbq);
System.out.println("Pop element: " + lbq.pop());
System.out.println("take element: " + lbq.take());
System.out.println("takeFirst element: " + lbq.takeFirst());
System.out.println("takeLast element: " + lbq.takeLast());
System.out.println("Elements in queue after take operations: " + lbq);
}
}
Elements inserted using add operations: [30, 10, 20, 40] Elements inserted using offer operations: [60, 30, 10, 20, 40, 50, 70] Elements inserted using put operations: [100, 80, 60, 30, 10, 20, 40, 50, 70, 90, 110] Size of LinkedBlockingDeque: 11 Remaining capacity: 1 Removing elements.... Elements in queue after remove operations: [60, 30, 10, 20, 50, 70, 90] Elements in queue after poll operations: [10, 20, 50, 70] Pop element: 10 take element: 20 takeFirst element: 50 takeLast element: 70 Elements in queue after take operations: []
Example: Access elements
There are various methods to access the head and tail element from the queue. This example shows how to retrieve the elements. The element(), getFirst(), peek(), peekFirst() methods retrieve the head element. The getLast(), peekLast() methods retrieve the tail element.
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class LinkedBlockingDequeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer> lbq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer>(12);
lbq.add(10);
lbq.add(20);
lbq.addFirst(30);
lbq.addLast(40);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using add operations: " + lbq);
lbq.offer(50);
lbq.offerFirst(60);
lbq.offerLast(70);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using offer operations: " + lbq);
lbq.push(80);
lbq.put(90);
lbq.putFirst(100);
lbq.putLast(110);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using put operations: " + lbq);
System.out.println("element output: " + lbq.element());
System.out.println("getFirst element: " + lbq.getFirst());
System.out.println("getLast element: " + lbq.getLast());
System.out.println("peek element: " + lbq.peek());
System.out.println("peekFirst element: " + lbq.peekFirst());
System.out.println("peekLast element: " + lbq.peekLast());
}
}
Elements inserted using add operations: [30, 10, 20, 40] Elements inserted using offer operations: [60, 30, 10, 20, 40, 50, 70] Elements inserted using put operations: [100, 80, 60, 30, 10, 20, 40, 50, 70, 90, 110] element output: 100 getFirst element: 100 getLast element: 110 peek element: 100 peekFirst element: 100 peekLast element: 110
Example: Iterate elements
This example shows how to iterate through elements in Java LinkedBlockingDeque using the iterate() method.
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class LinkedBlockingDequeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer> lbq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer>(12);
lbq.add(10);
lbq.add(20);
lbq.addFirst(30);
lbq.addLast(40);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using add operations: " + lbq);
lbq.offer(50);
lbq.offerFirst(60);
lbq.offerLast(70);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using offer operations: " + lbq);
lbq.push(80);
lbq.put(90);
lbq.putFirst(100);
lbq.putLast(110);
System.out.println("Elements inserted using put operations: " + lbq);
System.out.println("Iterating elements...");
Iterator<Integer> it = lbq.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
}
Elements inserted using add operations: [30, 10, 20, 40] Elements inserted using offer operations: [60, 30, 10, 20, 40, 50, 70] Elements inserted using put operations: [100, 80, 60, 30, 10, 20, 40, 50, 70, 90, 110] Iterating elements... 100 80 60 30 10 20 40 50 70 90 110