Table of Contents
Problem statement
In the problem ” Lexicographical Numbers” we are given a number n. Our task is to print numbers between 1 and n in lexicographical order.
Example
n=13
[1 10 11 12 13 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
Explanation: As we have to print numbers between 1-13 in lexicographical order, the numbers are [1 10 11 12 13 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9].
Brute Force Approach for Lexicographical Numbers Leetcode Solution
The brute force approach to solve the problem is as follows:
- Convert all the positive integer numbers between 1 to n into strings.
- Now, sort the strings. This will arrange the numbers in lexicographical order.
- Now convert the sorted strings into integers again and this will give the result.
Implementation
C++ code for Lexicographical Numbers
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> lexicalOrder(int n) {
string a[n];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
a[i-1]=to_string(i);
sort(a,a+n);
vector<int>ans;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
ans.push_back(stoi(a[i-1]));
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n=13;
vector<int> ans=lexicalOrder(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}[1 10 11 12 13 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
Java code for Lexicographical Numbers
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Set ;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.*;
public class Tutorialcup {
public static List<Integer> lexicalOrder(int n) {
String[] a = new String[n];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
a[i-1]=Integer.toString(i);
Arrays.sort(a);
List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
ans.add( Integer.parseInt(a[i-1]));
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=13;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(n);
ans=lexicalOrder(n);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ans.toArray()));
}
}[1 10 11 12 13 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
Complexity Analysis of Lexicographical Numbers Leetcode Solution
Time complexity
The time complexity of the above code is O(nlogn) because we are sorting the strings with n string. Here n is the given number.
Space complexity
The space complexity of the above code is O(1) because we are using only a variable to store answer.
DFS Approach for Lexicographical Numbers Leetcode Solution
The idea is pretty simple. Every time we start with a single digit from 1-9 and then keep on adding digits from 0-9 on those numbers as long as it is smaller than n. So this is exactly the same as the Depth-First-Search algorithm.
So we will start with 1 and will perform DFS for it as long as it is smaller or equal to n.
We will repeat these for all digits till 9 then store and print the DFS result.
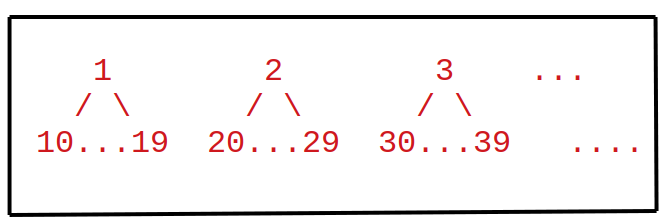
Implementation
C++ code for Lexicographical Numbers
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void dfs(int cur, int n, std::vector<int>& ret)
{
if (cur <= n)
{
ret.push_back(cur);
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; ++i)
{
dfs(cur*10+i, n, ret);
}
}
}
vector<int> lexicalOrder(int n) {
vector<int> ret;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i)
{
dfs(i, n, ret);
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int n=13;
vector<int> ans=lexicalOrder(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}[1 10 11 12 13 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
Java code for Lexicographical Numbers
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Set ;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.*;
public class Tutorialcup {
public static List<Integer> lexicalOrder(int n) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1;i<10;++i){
dfs(i, n, res);
}
return res;
}
public static void dfs(int cur, int n, List<Integer> res){
if(cur>n)
return;
else{
res.add(cur);
for(int i=0;i<10;++i){
if(10*cur+i>n)
return;
dfs(10*cur+i, n, res);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=13;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(n);
ans=lexicalOrder(n);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ans.toArray()));
}
}[1 10 11 12 13 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
Complexity Analysis of Lexicographical Numbers Leetcode Solution
Time complexity
The time complexity of the above code is O(n) because we are traversing the elements only once. Here n is the given value.
Space complexity
The space complexity of the above code is O(log(h)) because we are using DFS. Here h is the height of the DFS tree.