Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix LeetCode Solution – Given an m x n integers matrix, return the length of the longest increasing path in matrix.
From each cell, you can either move in four directions: left, right, up, or down. You may not move diagonally or move outside the boundary (i.e., wrap-around is not allowed).
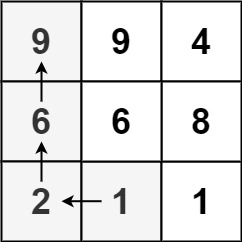
Input: matrix = [[9,9,4],[6,6,8],[2,1,1]] Output: 4 Explanation: The longest increasing path is [1, 2, 6, 9].
Explanation
(Solving the problem using Recursion):
- Now for each cell [i, j], we will find the longest path that can be taken if this current cell is considered.
- So the recursion goes this way: From the current cell, we will check whether we can go to any other neighboring cell.
- If YES we will go to that cell, and if NO we will return 1 (because we are considering the current cell).
But here we are doing the same thing again and again. So we will get TLE.
To get the max length of increasing sequences:
- Do DFS from every cell
- Compare every 4 directions and skip cells that are out of boundary or smaller
- Get matrix
maxfrom every cell’smax - Use
matrix[x][y] <= matrix[i][j]so we don’t need avisited[m][n]array - The key is to
cachethe distance because it’s highly possible to revisit a cell
Code
C++ Code for Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix
class Solution {
public:
int longestIncreasingPath(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int rows = matrix.size();
if (!rows) return 0;
int cols = matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(rows, vector<int>(cols, 0));
std::function<int(int, int)> dfs = [&] (int x, int y) {
if (dp[x][y]) return dp[x][y];
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
for (auto &dir : dirs) {
int xx = x + dir[0], yy = y + dir[1];
if (xx < 0 || xx >= rows || yy < 0 || yy >= cols) continue;
if (matrix[xx][yy] <= matrix[x][y]) continue;
dp[x][y] = std::max(dp[x][y], dfs(xx, yy));
}
return ++dp[x][y];
};
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
ret = std::max(ret, dfs(i, j));
}
}
return ret;
}
};Java Code for Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix
class Solution {
public static final int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
if(matrix.length == 0) return 0;
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[][] cache = new int[m][n];
int max = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int len = dfs(matrix, i, j, m, n, cache);
max = Math.max(max, len);
}
}
return max;
}
public int dfs(int[][] matrix, int i, int j, int m, int n, int[][] cache) {
if(cache[i][j] != 0) return cache[i][j];
int max = 1;
for(int[] dir: dirs) {
int x = i + dir[0], y = j + dir[1];
if(x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || matrix[x][y] <= matrix[i][j]) continue;
int len = 1 + dfs(matrix, x, y, m, n, cache);
max = Math.max(max, len);
}
cache[i][j] = max;
return max;
}
}Python Code for Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix
class Solution:
def longestIncreasingPath(self, matrix):
def dfs(i, j):
if not dp[i][j]:
val = matrix[i][j]
dp[i][j] = 1 + max(
dfs(i - 1, j) if i and val > matrix[i - 1][j] else 0,
dfs(i + 1, j) if i < M - 1 and val > matrix[i + 1][j] else 0,
dfs(i, j - 1) if j and val > matrix[i][j - 1] else 0,
dfs(i, j + 1) if j < N - 1 and val > matrix[i][j + 1] else 0)
return dp[i][j]
if not matrix or not matrix[0]: return 0
M, N = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
dp = [[0] * N for i in range(M)]
return max(dfs(x, y) for x in range(M) for y in range(N))Complexity Analysis for Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix LeetCode Solution
Time Complexity
O(V+E)
Space Complexity
O(V)