Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Maximum Product of Splitted Binary Tree LeetCode Solution – Given the root of a binary tree, split the binary tree into two subtrees by removing one edge such that the product of the sums of the subtrees is maximized.
Return the maximum product of the sums of the two subtrees. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Note that you need to maximize the answer before taking the mod and not after taking it.
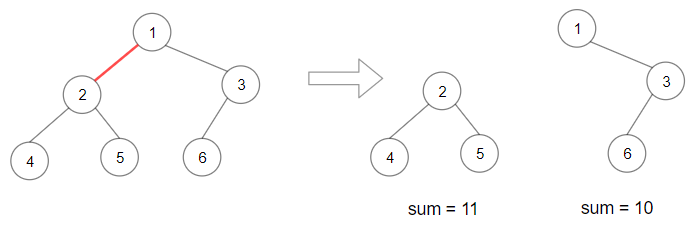
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: 110 Explanation: Remove the red edge and get 2 binary trees with sum 11 and 10. Their product is 110 (11*10)
Explanation
When I read the problem, this problem seems to be super hard. The approaches that come to my mind are:-
- Let’s convert the tree into an array and then divide the array into two subsets with the maximum product of the sum. This approach seems to work but doesn’t guarantee that we will get the splitted tree.
- Now thinking randomly of different solutions, Maybe DP, Maybe BFS, Maybe DFS… I don’t know this sucks!!!!. I am done, moving on to the next question.
- But wait there is a hint below, let’s read this, If we know the sum of a subtree, the answer is max( (total_sum – subtree_sum) * subtree_sum) in each node.
- I read the hint 4 times then I just converted the given tree into a sum tree. In the sum tree, every node contains the sum of its left subtree and right subtree. You can do this in quadratic time as well as in linear, (In code I implemented the linear time solution).
- Now what’s next, what can I achieve with this sum tree? Again read the hint, then finally come up with the idea. When you have the sum tree then what are you waiting for just split from every possible edge and get the maximum result.
- Why didn’t I see this before!. One truth prevails! (Case Closed fans get the Sarcasm).
Code
C++ Code for Maximum Product of Splitted Binary Tree
class Solution {
int tot = 0;
int mod = 1e9+7;
public:
// function to convert the tree into sum tree - this works in linear time
int convert_To_SumTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
if(root->left == NULL and root->right == NULL)
return root->val;
int leftSum = convert_To_SumTree(root->left);
int rightSum = convert_To_SumTree(root->right);
root->val += leftSum+rightSum;
return root->val;
}
void splitTree(TreeNode* root, long long& res) {
if(root == NULL)
return;
// maximise sum from left
if(root->left) {
long long sum1 = root->left->val;
long long sum2 = tot - sum1;
long long curr = sum1*sum2;
if(curr > res)
res = curr;
}
// maximise sum from right
if(root->right) {
long long sum1 = root->right->val;
long long sum2 = tot - sum1;
long long curr = sum1*sum2;
if(curr > res)
res = curr;
}
// call for left and right
splitTree(root->left, res);
splitTree(root->right, res);
}
int maxProduct(TreeNode* root) {
// convert the tree into sum tree
// so that each node stores the sum of its
// left and right subtrees
tot = convert_To_SumTree(root);
if(tot == 0) return 0;
// now try to split at every location
// and get the maximum ans
long long res = 0;
splitTree(root, res);
return res%mod;
}
};Java Code for Maximum Product of Splitted Binary Tree
class Solution {
int MOD = (int) (1e9) + 7;
public int maxProduct(TreeNode root) {
Set<Long> sums = new HashSet<>();
int total = dfs(root, sums);
long max = 0;
for (long sum : sums) {
max = Math.max(max, sum * (total - sum));
}
return (int) (max % MOD);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, Set<Long> sums) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
root.val += dfs(root.left, sums);
root.val += dfs(root.right, sums);
sums.add((long) (root.val));
return root.val;
}
}Python Code for Maximum Product of Splitted Binary Tree
class Solution:
def maxProduct(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if root == None: return 0
currSum = dfs(root.left) + dfs(root.right) + root.val
self.ans = max(self.ans, currSum * (self.totalSum - currSum))
return currSum
self.ans, self.totalSum = 0, 0
self.totalSum = dfs(root) # Firstly, get total sum of all nodes in the Binary Tree
dfs(root) # Then dfs in post order to calculate sum of each subtree and its complement
return self.ans % (10 ** 9 + 7)Complexity Analysis for Maximum Product of Splitted Binary Tree LeetCode Solution
Time Complexity
- Time:
O(N), whereN <= 5*10^4is the number of nodes in the Binary Tree.
Space Complexity
- Space:
O(H), whereHis the height of the Binary Tree, it’s the stack depth of the recursion.- In the best case, the binary tree is balanced, the height is
O(logN) - In the worst case, the binary tree is a skewed binary tree, the height is
O(N)
- In the best case, the binary tree is balanced, the height is