Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List LeetCode Solution says that – Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a “linked list”:
- The “linked list” should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The “linked list” should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
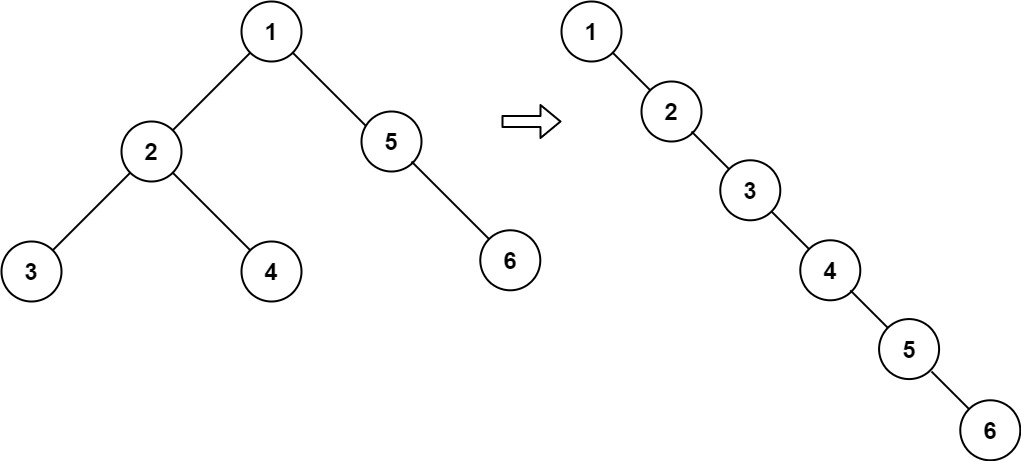 Input:
Input:
root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
Output:
[1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input:
root = []
Output:
[]
Example 3:
Input:
root = [0]
Output:
[0]
ALGORITHM –
IDEA –
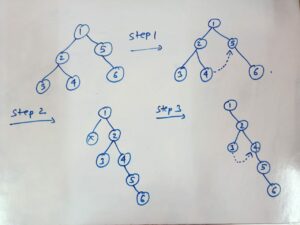
- In order to flatten a binary tree, we will first find the rightmost element of the left subtree and after we got the rightmost element we will link the right-pointer of that node with a right subtree of a given tree.
- In step 2 we will link the right pointer of the root node with the left-subtree and set the left-subtree as null.
- In step 3 now our root node is a right-subtree node same process will happen with this node and the process will still continue until all the left parts become null.
Approach for Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List Leetcode Solution –
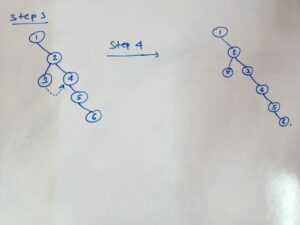
– At first, i will run a loop i.e. while(root != null) then will take two variables and store the left-subtree.
– then will check check for the rightmost node of left-subtree by using while(k.left != null) and will link that node with right subtree using (k.right = root.right).
– then link right pointer of root node with left subtree(root.right = left) and set left pointer of root node as null(root.left=null) and will update by ( root = root.right ) so now root is right subtree node.
– this process will continue until all left-subtree parts become right subtree. Hence, the binary tree will get flattened.
Python Solution:
class Solution:
def flatten(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None:
while(root):
if root.left:
k = root.left
temp = root.left
while(k.right):
k = k.right
k.right = root.right
root.right = temp
root.left = None
root = root.rightJava Solution:
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
while (root != null) {
if (root.left != null) {
TreeNode k = root.left;
TreeNode temp = root.left;
while (k.right != null) k = k.right;
k.right = root.right;
root.right = temp;
root.left = null;
}
root = root.right;
}
}
}Time complexity: O(N)
Space Complexity: O(1)
As we have traversed only once, time complexity will be o(n).
and as we haven’t taken any extra space, space complexity will be o(1) constant extra space.
Similar Question – https://tutorialcup.com/interview/linked-list/flattening-linked-list.htm